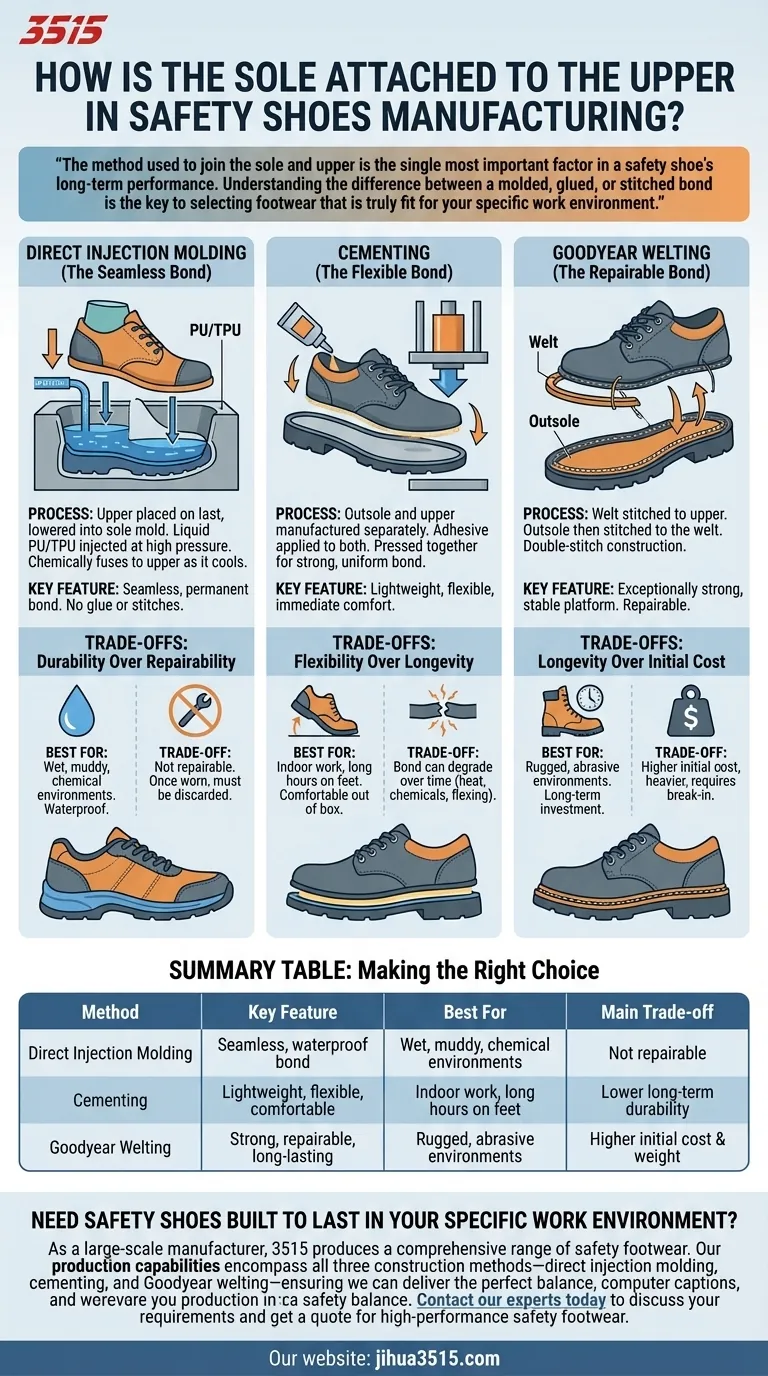
In safety shoe manufacturing, the sole is attached to the upper using one of three primary construction methods: direct injection molding, cementing, or Goodyear welting. Each technique creates a bond with fundamentally different properties, directly impacting the footwear's durability, water resistance, flexibility, and cost.
The method used to join the sole and upper is the single most important factor in a safety shoe's long-term performance. Understanding the difference between a molded, glued, or stitched bond is the key to selecting footwear that is truly fit for your specific work environment.

The Three Core Attachment Methods
The choice of construction is a deliberate engineering decision that balances performance goals with manufacturing complexity and cost. Each method serves a distinct purpose.
Direct Injection Molding (The Seamless Bond)
This high-tech process involves placing the finished shoe upper onto a specialized last which is then lowered into a sole mold.
Liquid material, typically Polyurethane (PU) or Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU), is injected into the mold under high pressure.
This liquid flows and fills the cavity, chemically fusing directly to the upper as it cools and solidifies. The result is a seamless, permanent bond between the sole and the upper without the need for glue or stitches.
Cementing (The Flexible Bond)
Cement construction is the most common method for modern, athletic-style safety footwear.
The outsole is manufactured as a separate unit. A powerful, flexible industrial adhesive (or "cement") is applied to both the bottom of the shoe's upper and the top of the outsole.
The two pieces are then precisely aligned and pressed together in a hydraulic press to ensure a strong, uniform bond. This method allows for the use of lighter-weight materials and more complex sole designs.
Goodyear Welting (The Repairable Bond)
Considered a hallmark of premium, heavy-duty footwear, Goodyear welting is the most labor-intensive method.
A durable strip of leather, rubber, or plastic—the "welt"—is first stitched to the perimeter of the shoe upper. In a separate step, the outsole is then stitched directly to this welt.
This double-stitch construction creates an exceptionally strong and stable platform. Crucially, it means the outsole can be removed and replaced by a cobbler without damaging the upper.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single construction method is universally superior. The optimal choice always depends on the intended application and involves a trade-off between durability, comfort, and cost.
Injection Molding: Durability Over Repairability
The primary advantage of injection molding is its incredibly strong, waterproof bond. Because there are no stitches or glued seams to fail, these shoes excel in wet and muddy conditions.
The major trade-off is repairability. Since the sole is chemically fused to the upper, it cannot be replaced. Once the tread wears down, the entire shoe must be discarded.
Cementing: Flexibility Over Longevity
Cemented shoes are known for being lightweight, flexible, and comfortable right out of the box with little to no break-in period required.
However, the adhesive bond can degrade over time, especially when exposed to high heat, certain chemicals, or constant flexing. This makes it less suitable for the most extreme industrial environments.
Goodyear Welting: Longevity Over Initial Cost
The key benefit of a Goodyear welt is its unparalleled durability and repairability. These shoes can be resoled multiple times, extending their service life for years and making them a long-term investment.
The downsides are cost, weight, and initial stiffness. The complex construction makes them the most expensive and heaviest type of safety shoe, and they often require a significant break-in period to become comfortable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Needs
Your ideal safety shoe construction depends entirely on your work environment and performance priorities.
- If your primary focus is maximum water resistance in wet, muddy, or chemical-heavy jobs: Choose shoes with direct injection molded soles for their seamless, impenetrable bond.
- If your primary focus is lightweight comfort and flexibility for indoor work or long hours on your feet: Cemented construction offers the best value and immediate comfort.
- If your primary focus is long-term value and durability in rugged, abrasive environments: Goodyear welted shoes are the superior investment due to their strength and repairability.
By understanding how a sole is attached, you move beyond surface-level features and gain the power to select footwear that truly performs for its intended purpose.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Feature | Best For | Main Trade-off |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Injection Molding | Seamless, waterproof bond | Wet, muddy, chemical environments | Not repairable |
| Cementing | Lightweight, flexible, comfortable | Indoor work, long hours on feet | Lower long-term durability |
| Goodyear Welting | Strong, repairable, long-lasting | Rugged, abrasive environments | Higher initial cost & weight |
Need safety shoes built to last in your specific work environment?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all three construction methods—direct injection molding, cementing, and Goodyear welting—ensuring we can deliver the perfect balance of durability, comfort, and value for your needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and get a quote for high-performance safety footwear.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Wholesale Mesh Steel Toe Safety Shoes with Dial Closure Factory Production
- Wholesale Slip-On Safety Boots Manufacturer - Custom Puncture-Proof & Steel Toe
- Wholesale Safety Footwear Manufacturer for Bulk & Custom OEM Orders
- Premium KPU Injection Athletic Style Safety Shoes
People Also Ask
- Is it normal to wear shoes in the house? A Guide to Hygiene, Comfort & Culture
- What are the differences between steel toe, composite toe, and alloy toe Wellington boots? Choose the Right Safety Toe for Your Job
- How do safety shoes contribute to cost savings for companies? A Strategic Investment in Risk and Cost Management
- What are the cultural perspectives on wearing shoes in the house? A Guide to Home Etiquette & Hygiene
- What are the primary protective functions of professional Safety Boots within the automotive maintenance process?



















