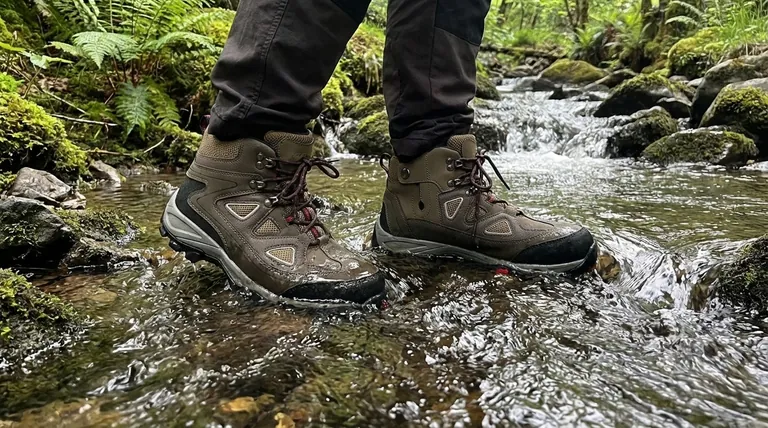
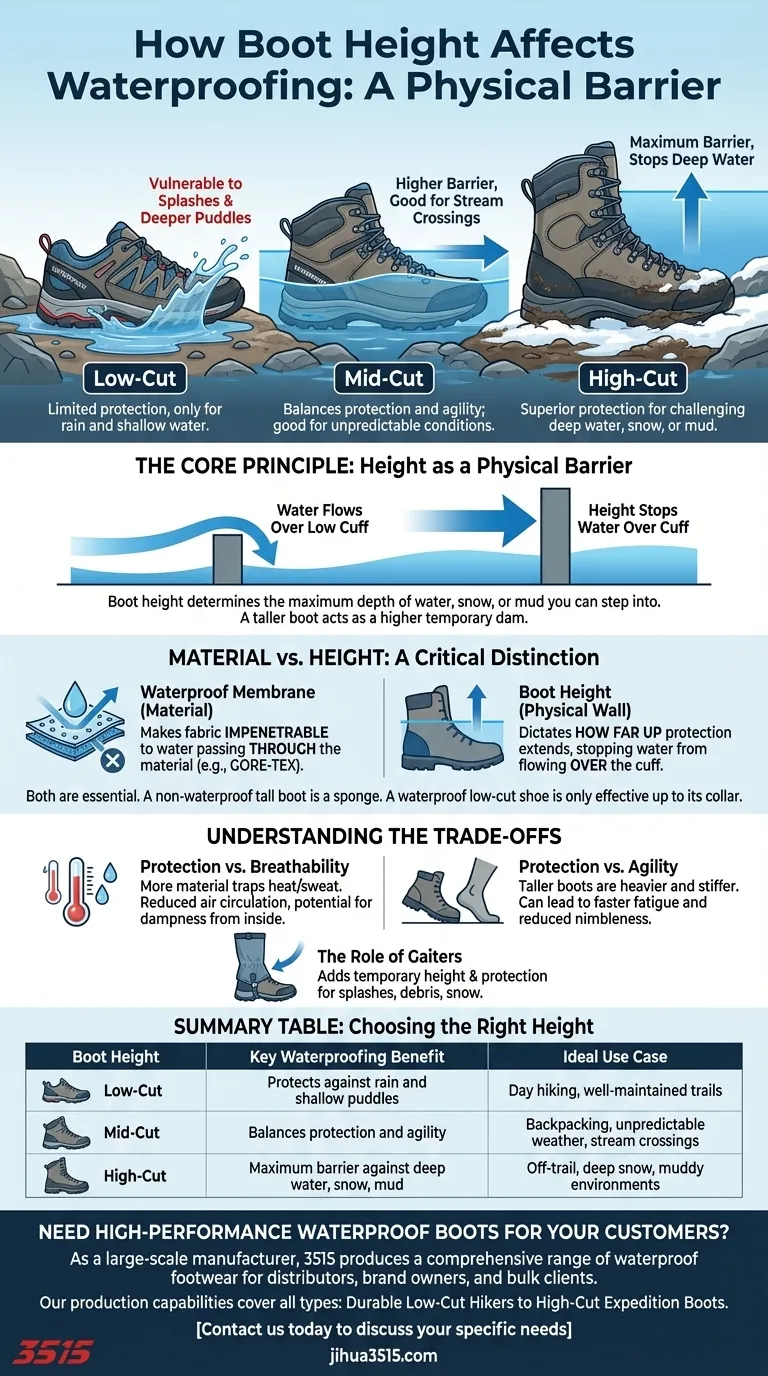
In short, a taller boot acts as a higher barrier. While the boot's materials provide its inherent waterproof quality, the height of the boot shaft determines the maximum depth of water, snow, or mud you can step into before moisture comes over the top. Low-cut boots are vulnerable to splashes and deeper puddles, whereas taller boots offer superior protection in more challenging conditions.
The core principle is simple: a boot's waterproof membrane keeps water from passing through the material, but its height is the physical wall that stops water from flowing over the cuff.

The Core Principle: Height as a Physical Barrier
Understanding how boot height functions is less about material science and more about basic physics. A taller boot simply creates a more significant obstacle against external moisture.
How Taller Boots Protect You
Think of a taller boot as a temporary dam for your foot. When you step into a stream, deep puddle, or snowdrift, the high cuff prevents water from immediately spilling inside.
This makes high-cut boots essential for environments where you expect to encounter standing or deep water.
The Vulnerability of Low-Cut Boots
Low-cut shoes, even if fully waterproof, have a low entry point for water. A splash from a misplaced step or wading into a puddle that's deeper than the shoe's collar will lead to wet feet instantly.
Their protection is limited to rain and very shallow water on the ground.
Material vs. Height
It is critical to distinguish between these two factors. A waterproof membrane (like GORE-TEX) makes the boot's fabric impenetrable to water. Boot height dictates how far up your leg that protection extends.
A non-waterproof, high-cut boot will absorb water like a sponge. Conversely, a waterproof low-cut shoe is effective, but only up to its ankle collar.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a taller boot for its superior waterproofing comes with compromises. You must weigh the need for protection against other critical performance factors.
Protection vs. Breathability
The more material you have covering your leg, the less air can circulate. Taller boots trap more heat and sweat, which can be a significant disadvantage in warm or dry climates.
Your own perspiration can make your socks damp from the inside, even if no external water gets in.
Protection vs. Agility
Taller, more protective boots are almost always heavier and stiffer. This added weight and reduced flexibility can lead to fatigue more quickly and make you feel less nimble on the trail.
Low-cut shoes offer maximum agility and minimum weight, making them ideal for fast-paced activity on predictable terrain.
The Role of Gaiters
A gaiter is a separate fabric tube that covers the top of your boot and extends up your calf. They are an excellent tool for adding temporary height and protection to a lower-cut boot.
Gaiters can effectively seal the gap between your pants and boots, keeping out debris, snow, and splashes without the full-time commitment to a heavy, high-cut boot.
Making the Right Choice for Your Activity
Selecting the correct boot height is about honestly assessing the conditions you are most likely to face.
- If your primary focus is day hiking on well-maintained trails: A low or mid-cut waterproof shoe provides an excellent balance of protection and agility.
- If your primary focus is backpacking with unpredictable weather and stream crossings: A mid to high-cut boot is essential for reliable water protection and ankle support.
- If your primary focus is navigating deep snow, mud, or off-trail conditions: A high-cut boot, often paired with gaiters, is the only dependable choice.
Ultimately, choosing the right boot height is about matching your tool to the specific demands of the terrain.
Summary Table:
| Boot Height | Key Waterproofing Benefit | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Low-Cut | Protects against rain and shallow puddles | Day hiking on well-maintained trails |
| Mid-Cut | Balances protection and agility; good for stream crossings | Backpacking in unpredictable weather |
| High-Cut | Maximum barrier against deep water, snow, and mud | Off-trail conditions, deep snow, or muddy environments |
Need High-Performance Waterproof Boots for Your Customers?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of waterproof footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Whether you need durable low-cut hikers or high-cut expedition boots, our production capabilities cover all types of shoes and boots to meet your market's demands.
Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and discover how we can help you supply the perfect waterproof footwear for any activity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
- Premium High-Cut Waterproof Safety Boots Manufacturing & Wholesale Solutions
- High Performance Fire-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots
- Premium KPU Injection Athletic Style Safety Shoes
People Also Ask
- What cultural and environmental considerations are tied to wearing shoes indoors? Balance Hygiene, Tradition, and Foot Health
- What are the differences between steel toe, composite toe, and alloy toe Wellington boots? Choose the Right Safety Toe for Your Job
- How do industrial safety shoes provide protection for personnel? Safeguard Your Team from Heavy Crane Hazards
- Why can metal protective toecaps become a risk factor for dorsal foot ulcers? Learn to Prevent Pressure Point Injuries
- What are the cultural perspectives on wearing shoes in the house? A Guide to Home Etiquette & Hygiene



















