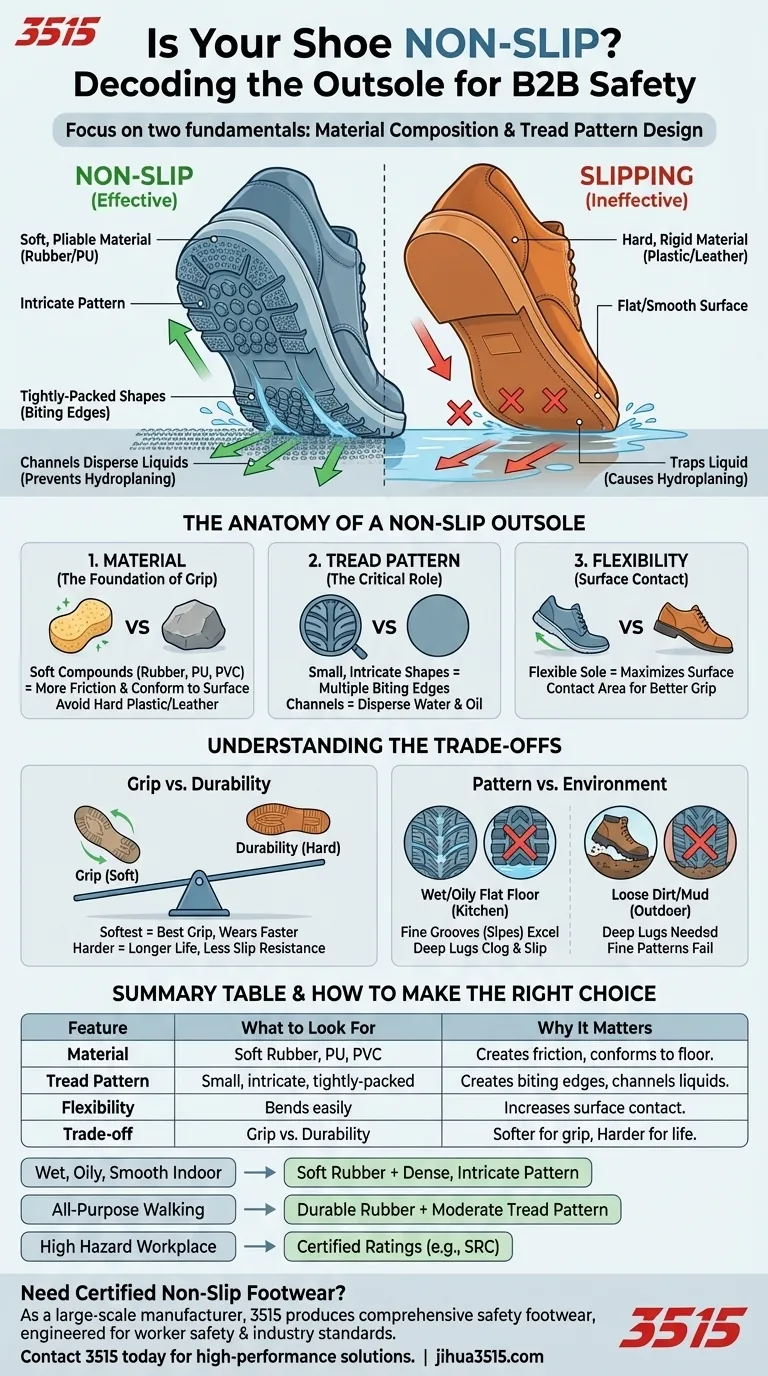
To determine if a shoe is non-slip by examining its outsole, you must focus on two fundamental characteristics: the material composition and the tread pattern design. A truly non-slip shoe will typically feature a soft, pliable material like rubber or polyurethane, combined with an intricate pattern of small, tightly-packed shapes that maximize surface contact and channel liquids away.
The real secret to identifying a non-slip shoe goes beyond a rugged appearance. It lies in the deliberate combination of a soft, flexible sole material and a tread pattern engineered to actively grip a surface, especially when it's wet or oily.

The Anatomy of a Non-Slip Outsole
A shoe's ability to resist slipping is not an accident; it's a result of intentional design choices in its foundation. Understanding these elements empowers you to look past marketing claims and assess the shoe's true performance potential.
Material is the Foundation of Grip
The material of the outsole is your first and most important clue. Softer compounds create more friction against a surface.
Look for materials like soft rubber, polyurethane, or PVC. These materials are more pliable and can conform better to microscopic imperfections in the floor, increasing the contact area and therefore the grip.
Conversely, be wary of hard, smooth plastic or dense leather soles. While durable, they offer very little friction, especially on wet or polished surfaces.
The Critical Role of the Tread Pattern
The design cut into the bottom of the sole is just as important as the material it's made from. A flat, smooth surface is a recipe for slipping.
An effective non-slip pattern consists of many small, intricate shapes. These shapes create numerous "biting edges" that grab the walking surface from multiple angles.
The channels between these shapes are essential. Their job is to disperse water, oil, and other liquids from underneath the shoe. This prevents a film from forming between the sole and the floor—a phenomenon known as hydroplaning—which is a primary cause of slips.
Flexibility and Surface Contact
A rigid sole can only make contact with the high points of a surface. A more flexible outsole can bend and adapt, allowing more of the tread pattern to connect with the ground.
This maximizes the shoe's effective surface area, ensuring that the material and tread pattern can do their jobs effectively across the entire foot.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single shoe design is perfect for every situation. Recognizing the inherent compromises in outsole design is key to choosing the right shoe for your specific needs.
Grip vs. Durability
There is often a direct trade-off between a shoe's grip and its lifespan.
The softest rubber compounds that provide the best traction also tend to wear down the fastest. Harder, more durable materials will last longer but typically offer less slip resistance.
Pattern Design vs. Environment
The ideal tread pattern is highly dependent on the environment.
A pattern with tiny, siped grooves is excellent for flat, wet surfaces like a commercial kitchen floor because it efficiently channels away thin layers of liquid. However, that same pattern would quickly become clogged and useless in thick mud.
Conversely, the deep lugs of a hiking boot, designed for loose dirt and rocks, can actually reduce surface contact and perform poorly on a smooth, oily floor.
How to Make the Right Choice
When you evaluate a shoe, you are acting as an inspector. Use your understanding of these principles to make an informed decision based on your most common environment.
- If your primary focus is safety on wet, oily, or smooth indoor surfaces: Prioritize shoes with soft rubber outsoles and dense, intricate patterns with many small channels.
- If your primary focus is all-purpose walking with occasional wet pavement: Look for a durable rubber sole with a moderate tread pattern that balances grip with longevity.
- If your primary focus is avoiding falls at all costs in a hazardous workplace: Go beyond visual inspection and look for official slip-resistance ratings (e.g., "SRC" certified) to guarantee performance.
By learning to read the distinct features of an outsole, you can move beyond guesswork and confidently select footwear that provides the safety and stability you need.
Summary Table:
| Feature | What to Look For | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Soft rubber, polyurethane, or PVC | Soft compounds create more friction and conform to floor surfaces. |
| Tread Pattern | Small, intricate, tightly-packed shapes | Creates multiple gripping edges and channels liquids away to prevent hydroplaning. |
| Flexibility | A sole that bends easily | Increases surface contact area, allowing the tread pattern to work effectively. |
| Trade-off | Grip vs. Durability | Softer soles offer better grip but may wear faster; harder soles last longer but offer less slip resistance. |
Need a reliable source for certified non-slip footwear?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of non-slip shoes and boots, engineered with the precise material compounds and tread patterns discussed in this article to ensure worker safety and meet industry standards.
Contact 3515 today to discuss your specific needs and secure a dependable supply of high-performance, non-slip footwear.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Premium KPU Athletic Safety Shoes for Wholesale
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Wholesale Breathable Training Shoes Custom Athletic Footwear Manufacturer
- Lightweight Breathable Training Shoes for Wholesale & Custom OEM Manufacturing
- Durable Rubber-Soled Utility Shoes for Wholesale & Custom Brand Manufacturing
People Also Ask
- How do industrial safety shoes contribute to safety in sugar production? Ensure High-Altitude Inspection Security
- What is the primary objective of utilizing dedicated safety shoes in nanomaterial work zones? Prevent Track-Out Now
- How do athletic-style safety shoes balance flexibility and safety? Perfect Agility for Active Professionals
- Why are metal surfaces often selected as the walking medium in studies concerning ramp safety? Achieve Lab-Grade Precision
- Why are industrial-grade safety shoes mandatory in metallurgical workshops? Essential Protection for Extreme Environments



















