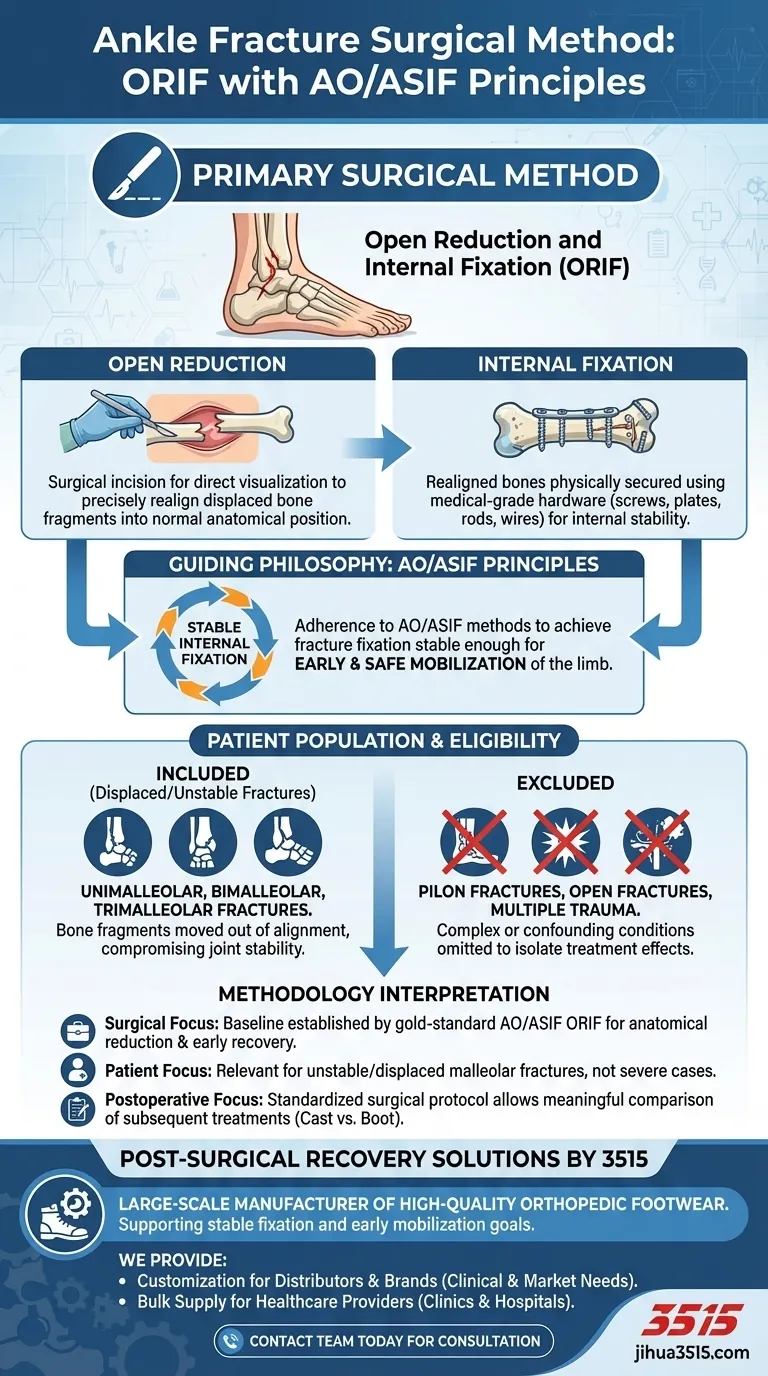
The primary surgical method used for all patients in this study was Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF). This procedure was performed in accordance with the established principles and techniques of the AO/ASIF (Association for the Study of Internal Fixation), ensuring a standardized approach to fracture care.
This study utilizes a single, well-defined surgical protocol—ORIF guided by AO/ASIF methods—to treat a specific subset of ankle fractures. This standardization is critical because it removes the surgical procedure as a variable, allowing for a focused analysis of the postoperative treatments.

Deconstructing the Surgical Protocol
To fully understand the study's methodology, it's essential to break down the components of the surgical intervention. The choice of ORIF based on AO principles is deliberate and has specific implications for treatment goals.
What is Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF)?
ORIF is a two-part surgical procedure designed to repair a severe bone fracture.
Open Reduction refers to the surgical incision made over the fracture site. This allows the surgeon to directly visualize and precisely realign the displaced bone fragments into their normal anatomical position.
Internal Fixation is the subsequent step where the realigned bones are physically secured. This is accomplished using medical-grade hardware such as screws, plates, rods, or wires, which hold the pieces together internally during the healing process.
The Guiding Philosophy: AO/ASIF Principles
The reference to AO/ASIF methods signifies a commitment to a specific surgical philosophy. The core goal of this approach is to achieve a fracture fixation that is stable enough to allow for early and safe mobilization of the limb.
This principle of stable internal fixation aims to restore function as quickly as possible, which directly relates to the study's subsequent comparison of a plaster cast versus a walking boot.
Defining the Patient Population
The surgical method was applied to a carefully selected group of patients to ensure the study's results were consistent and comparable.
Inclusion Criteria: Who Was Treated?
The study focused exclusively on patients with displaced or unstable ankle fractures. These are injuries where the bone fragments have moved out of their correct alignment, compromising the stability of the ankle joint.
This included specific injury patterns such as unimalleolar, bimalleolar, and trimalleolar fractures.
Exclusion Criteria: Why Certain Patients Were Omitted
The researchers explicitly excluded patients with more complex or confounding conditions. These included pilon fractures (which involve the weight-bearing surface of the tibia), open fractures (where the bone breaks the skin), and patients with multiple traumas.
Excluding these cases was necessary to isolate the effects of the treatment on a homogenous group of common ankle fractures, thereby increasing the validity of the study's conclusions.
How to Interpret This Methodology
Understanding the specifics of the surgical protocol is key to correctly applying the study's findings. The choice of ORIF was not arbitrary; it established the baseline for the entire experiment.
- If your primary focus is surgical technique: The study relies on the gold-standard AO/ASIF principles for ORIF, aiming for anatomical reduction and stable fixation to enable early functional recovery.
- If your primary focus is patient applicability: The findings of this study are most relevant to patients with unstable or displaced malleolar fractures and should not be generalized to more severe injuries like open or pilon fractures.
- If your primary focus is postoperative care: The standardized surgical protocol is the critical element that allows for a meaningful comparison between the plaster cast and walking boot interventions.
By controlling for the surgical variable, the researchers created a reliable foundation to assess the true impact of the postoperative management.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Surgical Method | Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF) |
| Guiding Protocol | AO/ASIF Principles |
| Goal of Surgery | Anatomical reduction & stable fixation for early functional recovery |
| Patient Population | Displaced/unstable unimalleolar, bimalleolar, or trimalleolar fractures |
| Excluded Conditions | Pilon fractures, open fractures, multiple trauma patients |
Need High-Quality Orthopedic Footwear for Post-Surgical Recovery?
As a leading large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of medical and functional footwear, including post-operative boots ideal for patients recovering from procedures like the ORIF detailed in this study. Our products are designed to support the goals of stable fixation and early mobilization.
We provide:
- Customization for Distributors & Brands: Tailor designs to meet specific clinical or market needs.
- Bulk Supply for Healthcare Providers: Reliable, high-volume production for clinics and hospitals.
Let's discuss how our footwear solutions can support your patients' recovery journey. Contact our team today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Wholesale Durable 6-Inch Work Boots | Custom & Private Label Manufacturer
- Durable Leather Work Boots Wholesale Manufacturer & Custom Factory
- Durable Steel Toe Safety Boots Wholesale & Custom Manufacturing
- Custom Wholesale Leather Safety Boots Direct Factory Manufacturing
- Wholesale Slip-On Safety Boots Manufacturer - Custom Puncture-Proof & Steel Toe
People Also Ask
- What are steel toe work boots and who should wear them? Essential PPE for Hazardous Jobs
- Is it normal to wear shoes in the house? A Guide to Hygiene, Comfort & Culture
- How do work boots differ from cowboy boots? Choosing the Right Footwear for Your Job
- Why is the last important in work boot design? It's the Anatomical Blueprint for Comfort & Safety
- What are the cultural perspectives on wearing shoes in the house? A Guide to Home Etiquette & Hygiene














