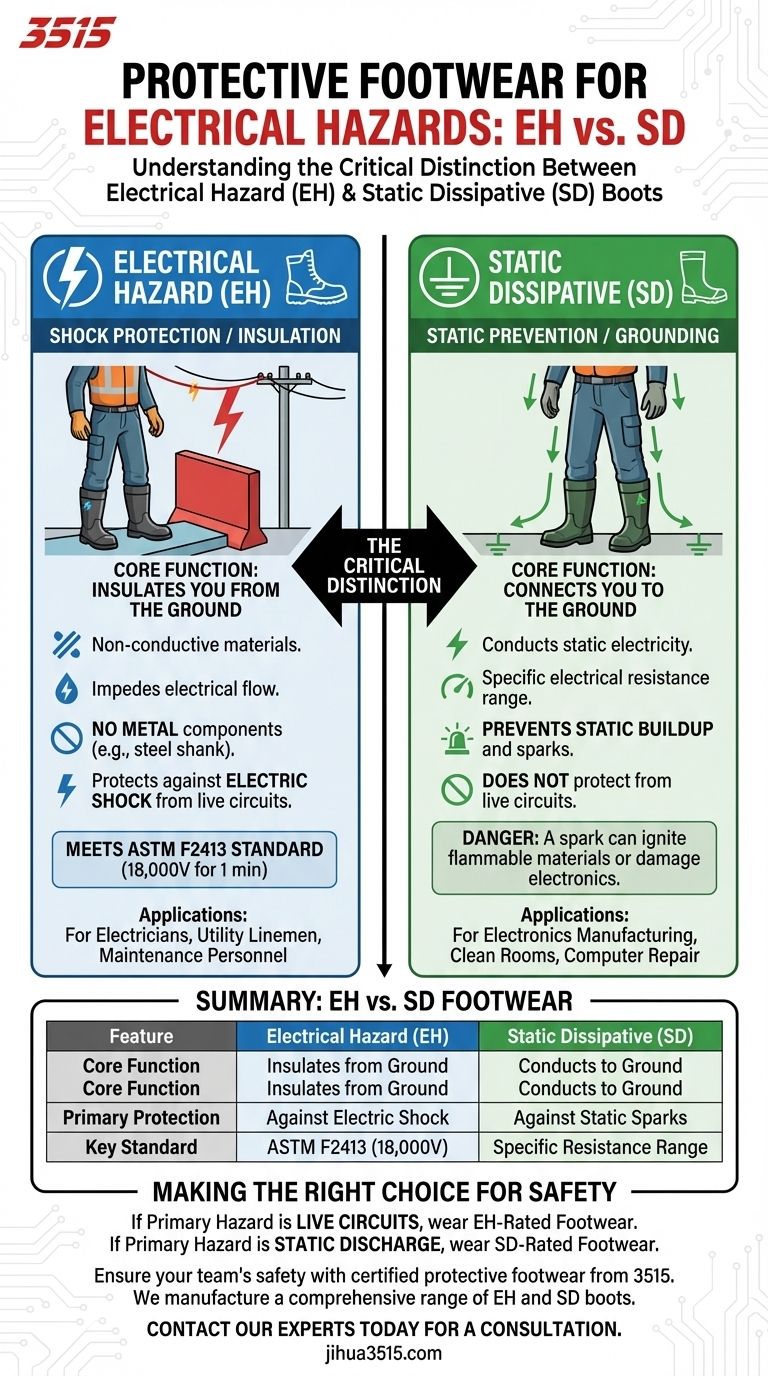
For jobs with electrical hazards, protective footwear is categorized into two primary, distinct types: Electrical Hazard (EH) rated boots designed to protect against electric shock, and Static Dissipative (SD) footwear designed to prevent the buildup of static electricity. Both are engineered for fundamentally different risks and must not be confused.
The critical distinction to understand is one of purpose: EH-rated boots insulate you from the ground to protect against shock from live currents, while SD footwear connects you to the ground to safely discharge static electricity and prevent sparks.

Understanding Electrical Hazard (EH) Rated Footwear
The Core Function: Insulation
Electrical Hazard (EH) rated boots are designed to be a secondary source of protection against accidental contact with live electrical circuits.
Their primary job is to act as an insulator, impeding the flow of electricity from the ground, through your body, and to the live wire you may have touched.
How They Are Built
EH boots are constructed with entirely non-conductive materials. The soles and heels are made from specific rubber compounds that do not conduct electricity.
Critically, they are built without any metal components, such as a steel shank or steel toe, that could compromise their insulating properties.
The ASTM Standard
A boot is only officially EH-rated if it meets the standard set by ASTM International (ASTM F2413). This certification ensures the footwear can withstand the application of 18,000 volts at 60 Hz for one minute with no current flow or leakage current in excess of 1.0 milliampere.
When to Use EH Boots
This footwear is essential for anyone who works on, near, or with live electrical equipment. This includes electricians, utility linemen, and industrial maintenance personnel.
Understanding Static Dissipative (SD) Footwear
The Core Function: Grounding
Static Dissipative (SD) footwear does the opposite of EH-rated boots. It is designed to safely conduct static electricity from your body to a properly grounded floor.
The Danger of Static Buildup
In certain environments, a tiny spark from static discharge can be catastrophic. It can damage sensitive electronic components or ignite flammable materials, dust, or gases.
How They Work
SD footwear is engineered with a specific range of electrical resistance. It's low enough to allow static to discharge safely but high enough to offer some basic resistance to electrical current, though it does not offer protection from live circuits.
When to Use SD Boots
This type of footwear is necessary for professionals working in electronics manufacturing, computer repair, clean rooms, or environments with a risk of explosion from static spark.
The Critical Distinction: EH vs. SD
Confusing these two types of footwear can have dangerous consequences. They are designed for mutually exclusive purposes.
EH is for Shock Protection
EH boots are meant to isolate you from the ground. Wearing them prevents your body from completing an electrical circuit, protecting you from shock.
SD is for Static Prevention
SD boots are meant to connect you to the ground. Wearing them prevents static from building up on your body by creating a safe path for it to dissipate.
Never Use SD Boots for Shock Protection
Wearing SD footwear while working on or near a live circuit would be extremely dangerous. It would actively facilitate the flow of electricity through your body to the ground, increasing the severity of an electric shock.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific job hazard is the only factor that should determine your choice.
- If your primary hazard is contact with live electrical circuits: You must wear footwear that is officially marked and certified as Electrical Hazard (EH) rated.
- If your primary hazard is static discharge damaging equipment or causing a fire: You must wear footwear specifically rated for Static Dissipation (SD) and ensure you are working on grounded floors.
- If you face both hazards at different times: You must switch to the appropriate footwear for the task at hand or find dual-rated boots, understanding the limitations of each rating.
Choosing the correct rated footwear is a non-negotiable step in ensuring your safety against specific and fundamentally different electrical risks.
Summary Table:
| Footwear Type | Core Function | Primary Protection | Key Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrical Hazard (EH) | Insulates the wearer from the ground | Protects against electric shock from live circuits | ASTM F2413 (18,000V, 1 min) |
| Static Dissipative (SD) | Safely conducts static to the ground | Prevents static buildup that could cause sparks or damage | Specific electrical resistance range |
Ensure your team's safety with the right protective footwear from 3515.
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of certified safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of EH and SD rated boots and shoes, designed to meet the highest safety standards for your specific electrical hazards.
Contact our experts today for a consultation on your protective footwear needs. We'll help you select the perfect solution to keep your workforce safe and productive.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Premium KPU Injection Athletic Style Safety Shoes
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
- Heavy-Duty Waterproof Nubuck Safety Boots Safety Shoes for Bulk Supply
- Premium High-Cut Waterproof Safety Boots Manufacturing & Wholesale Solutions
People Also Ask
- Why is comfort important in work shoes? Boost Health, Safety, and Productivity
- How can employers ensure their employees have the right work boots? Build a Safer, More Productive Workforce
- Why is it important for women to wear work boots in the construction industry? Essential Safety & Performance
- What maintenance steps are recommended for outsoles on work boots? Extend Boot Life & Maximize Safety
- When should boots be replaced after impact from heavy objects? The Critical 'One and Done' Rule
- What additional safety features do structural firefighting boots provide? Beyond Heat Resistance
- What are the drawbacks of pull-on work boots? A Guide to Fit, Support, and Safety
- How does an electronic Metronome standardize muscle endurance testing? Master the Pace for Safety Boot Performance



















