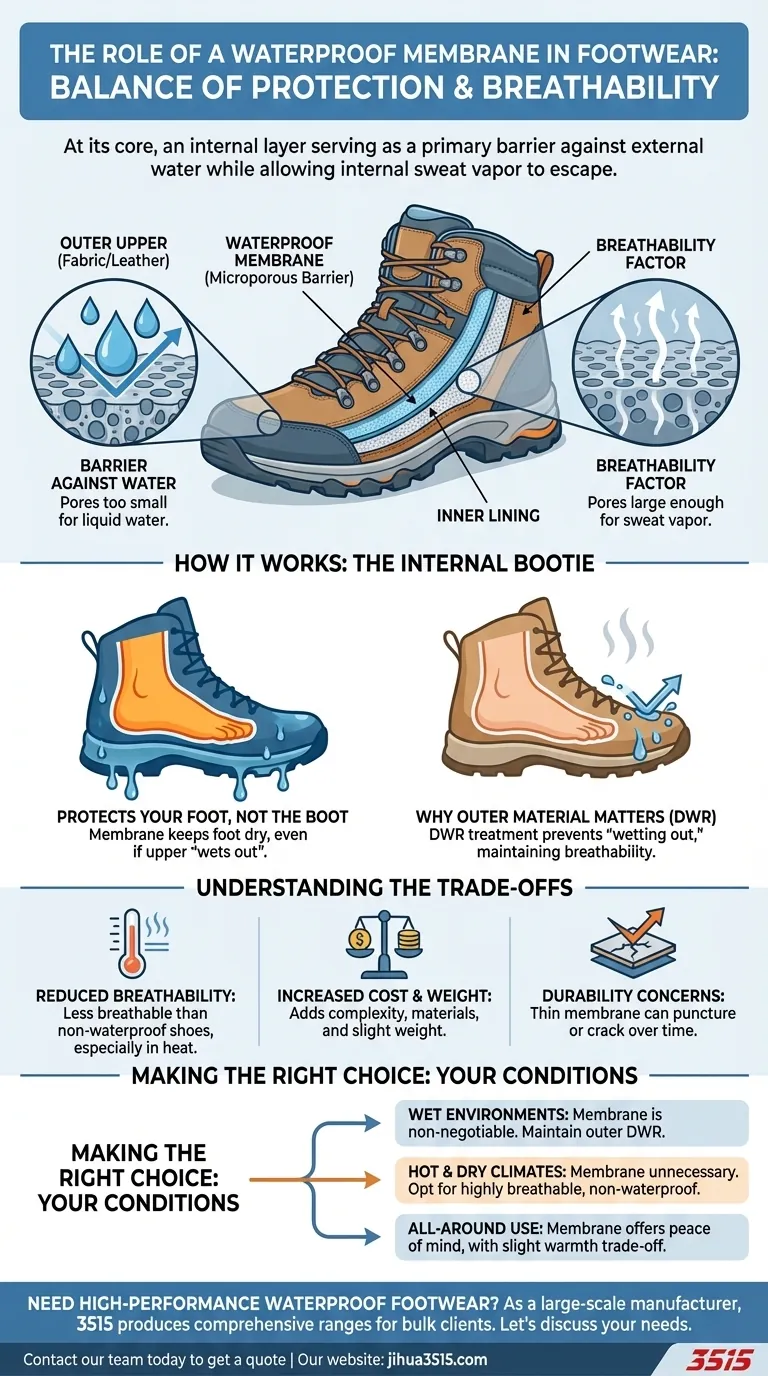
At its core, a waterproof membrane in footwear is an internal layer that serves as the primary barrier against water entering the shoe while still allowing sweat vapor to escape. It is this membrane, often made from materials like Gore-Tex, that truly makes footwear waterproof, sealing off stitch holes and the natural pores of the upper material.
The essential role of a waterproof membrane is to keep your feet dry from the outside world without trapping them in sweat. However, it's crucial to understand that the membrane protects your foot, not the shoe's outer material.

How a Waterproof Membrane Works
A waterproof membrane is a highly engineered layer, typically a thin sheet of microporous material, situated between the shoe's outer fabric (the upper) and the inner lining.
The Primary Barrier Against Water
Think of the membrane as a complete, sealed bootie inside your shoe. The pores in the membrane are thousands of times smaller than a water droplet, making it physically impossible for rain, snow, or puddle water to penetrate and reach your foot.
This is especially critical because footwear uppers are constructed from multiple pieces of material stitched together, creating tiny holes that would otherwise be easy entry points for water.
The Breathability Factor
The key innovation is that these same microscopic pores are large enough for individual water vapor molecules (your sweat) to pass through. This allows moisture from inside the shoe to escape, preventing the clammy, uncomfortable feeling that would occur if your foot were sealed in a simple plastic bag.
The Membrane vs. The Upper: A Critical Distinction
One of the most common misunderstandings is believing the waterproof membrane protects the entire boot. This is not the case; its job is to protect your foot.
Protecting Your Foot, Not the Boot
The membrane is an internal liner. While it will keep your foot dry, the outer material of the boot—whether it's leather, suede, or a synthetic fabric—can still absorb water and become saturated.
Why the Outer Material Still Matters
When the upper material gets soaked, it's known as "wetting out." This has two negative consequences. First, the boot becomes significantly heavier. Second, the waterlogged outer layer clogs the path for sweat to escape, effectively destroying the membrane's breathability.
This is why most waterproof footwear also has a Durable Water Repellent (DWR) finish on the outside and why conditioning leather is vital. These treatments help water bead up and roll off the surface, preserving breathability and the boot's integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, incorporating a waterproof membrane is not without its compromises. Understanding these will help you choose the right footwear for your needs.
Reduced Breathability
Even the most advanced membrane is less breathable than a shoe with no membrane at all. In hot, dry conditions, this can lead to warmer and sweatier feet than you would experience in a more ventilated, non-waterproof shoe.
Increased Cost and Weight
The technology and construction required to add a waterproof membrane add to the final cost of the footwear. The extra layers also contribute a small amount of additional weight.
Durability Concerns
A membrane is a thin layer. Over thousands of flexes and with internal friction from your foot, it can develop cracks or holes. Once the membrane is punctured, its waterproof integrity is permanently compromised in that spot.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting footwear with or without a waterproof membrane depends entirely on the conditions you expect to face.
- If your primary focus is maximum protection in wet environments: A waterproof membrane is non-negotiable, but you must also maintain the outer material to ensure performance.
- If your primary focus is breathability for hot and dry climates: A membrane is unnecessary and will only make your feet hotter; opt for highly breathable, non-waterproof footwear.
- If your primary focus is all-around use with occasional wet weather: A membrane provides excellent peace of mind, but be prepared for a slight warmth trade-off on dry days.
Ultimately, understanding that the membrane is a specialized internal component is the key to choosing the right footwear and caring for it properly.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Role of the Membrane |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Acts as a barrier to keep external water out while letting internal sweat vapor escape. |
| Protection Focus | Protects your foot, not the shoe's outer material. |
| Key Trade-off | Provides waterproofing at the cost of slightly reduced breathability compared to non-waterproof shoes. |
| Durability | Can be compromised if punctured; requires care of the outer material (DWR treatment) for optimal performance. |
Need high-performance waterproof footwear for your customers?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of waterproof shoes and boots for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our expertise ensures the integration of reliable membranes for superior protection and breathability.
Let's discuss your specific needs and how we can deliver quality and value.
Contact our team today to get a quote
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Lightweight Breathable Training Shoes for Wholesale & Custom OEM Manufacturing
- Durable Waterproof Rain Boots | Custom Manufacturer for Wholesale & Brands
- Custom OEM Training Shoes Wholesale Manufacturer Durable & Breathable
- Premium Wholesale Waterproof Safety Boots High Performance Protection for Industrial Markets
People Also Ask
- How does FEA contribute to footwear stiffness and strength? Precision Engineering for High-Performance Shoes
- What should be considered when choosing a waterproofing treatment for boots? Match Material & Use for Best Results
- What is a quick fix for cold feet during a winter bike ride? Master Prevention & Stay Warm
- What specific functions do IMUs perform in footwear? Unlock Precision Motion Analysis with Integrated Sensors
- Why is auditory isolation used during the psychophysical testing of foot-based thermal feedback? Ensure Data Integrity
- How does an RC network and N-channel MOSFET circuit facilitate cold start in smart footwear? Ensure System Stability.
- What is the core function of specialized orthopedic shoes for high-risk diabetic feet? Prevent Amputation with Precision
- What function does a modular drop platform serve in simulating hazards? Enhancing Gait Stability Research



















