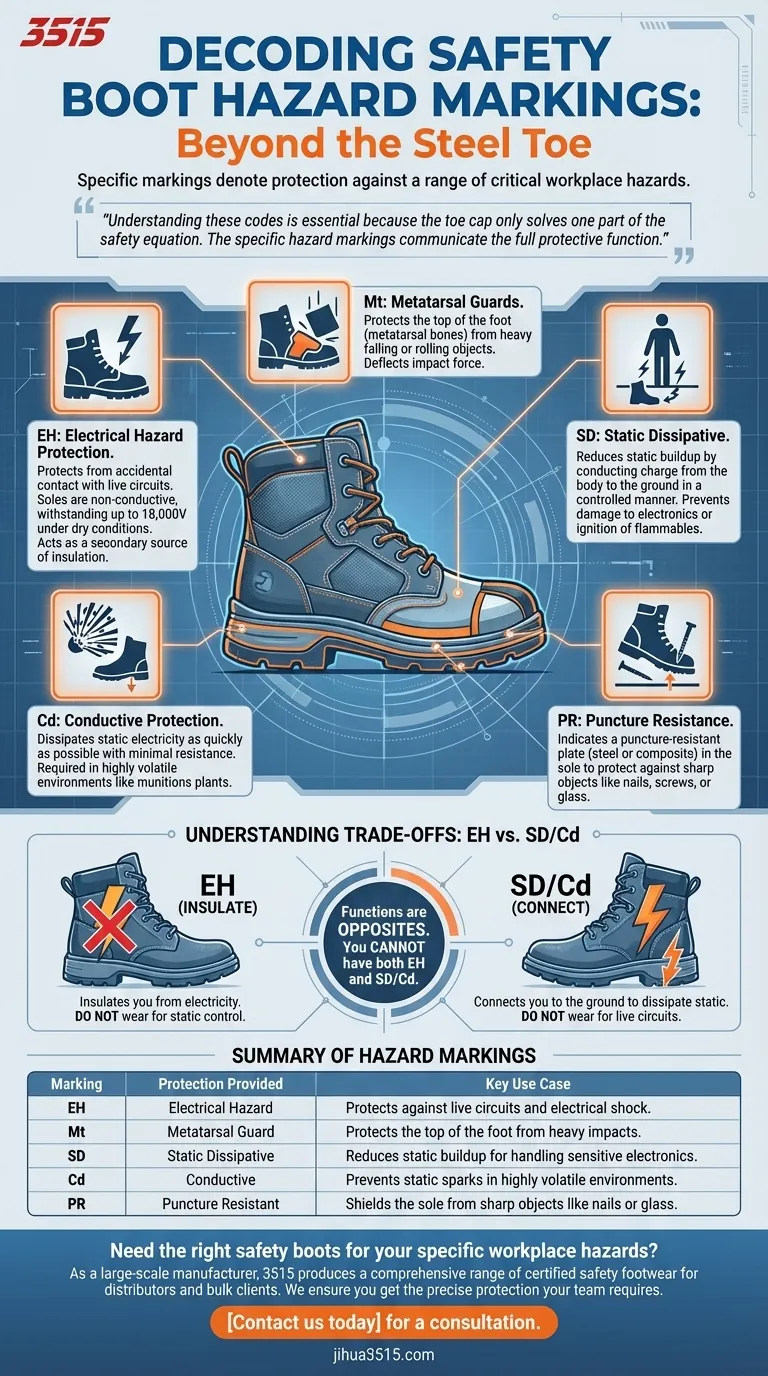
Beyond the steel toe, safety boots feature specific markings that denote protection against a range of other critical workplace hazards. The most common markings are EH for Electrical Hazard, Mt for Metatarsal protection, Cd for Conductive properties, and SD for Static Dissipative capabilities, each designed to mitigate a distinct risk.
Understanding these codes is essential because the toe cap only solves one part of the safety equation. The specific hazard markings on a boot communicate its full protective function, ensuring you match your footwear to the actual dangers of your work environment.

Decoding the Hazard Markings
A safety boot's true value is often found in the small abbreviations stamped on its tongue or side. These letters are a standardized language for safety, and knowing what they mean is non-negotiable for anyone working in a hazardous role.
EH: Electrical Hazard Protection
EH-rated footwear is designed to protect you from accidental contact with live electrical circuits. The soles and heels are made from non-conductive materials that can withstand up to a specific voltage (typically 18,000 volts at 60 Hz for one minute) under dry conditions.
These boots act as a secondary source of protection, insulating you from the ground and helping to prevent the completion of an electrical circuit through your body.
Mt: Metatarsal Guards
While the safety toe protects your toes, the Mt rating signifies an added guard that protects the top of your foot—specifically, the delicate metatarsal bones.
This feature is crucial in environments where heavy objects could be dropped or roll onto the foot, such as in heavy manufacturing, construction, or welding. The guard deflects the force of impact across a wider area.
SD: Static Dissipative
SD boots are designed to reduce the buildup of static electricity on your body. They conduct static charge from your body through the shoe and into the ground in a controlled manner.
This is critical in environments where a static spark could damage sensitive electronic equipment or, more dangerously, ignite flammable materials or explosive gases.
Cd: Conductive Protection
Cd rated boots take static control a step further than SD boots. They are designed to dissipate static electricity as quickly as possible, offering minimal electrical resistance.
This level of protection is required in highly volatile environments, such as munitions plants or facilities dealing with explosive powders, where even the slightest static buildup must be prevented.
PR: Puncture Resistance
Often marked as PR, this rating indicates a puncture-resistant plate positioned in the sole of the boot. This plate, made of steel or a composite material, protects the bottom of your foot from sharp objects like nails, screws, or glass.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
Choosing the right boot requires understanding that some protective features are mutually exclusive. Selecting the wrong type can introduce a new hazard instead of mitigating one.
EH vs. SD/Cd: A Critical Distinction
A boot cannot be both EH-rated and SD/Cd-rated. The functions are opposites.
EH boots insulate you from electricity, while SD/Cd boots connect you to the ground to dissipate static. Wearing EH boots in an environment requiring static control is dangerous, and wearing SD/Cd boots when working with live circuits is equally hazardous.
The Toe Cap is Separate
The type of safety toe—whether steel, composite, or alloy—is a separate feature from the hazard ratings. A steel toe boot is not automatically puncture-resistant or EH-rated. You must look for the specific markings (PR, EH, etc.) to ensure you have the protection you need.
Protection Has Limits
These ratings are tested under specific laboratory conditions. Real-world factors like excessive wear, moisture, or contamination can reduce a boot's protective capabilities. Regular inspection of your footwear is a critical part of your personal protective equipment (PPE) discipline.
Selecting the Right Protection for Your Environment
Your choice must be dictated by a clear assessment of your workplace risks. Use the hazard markings as your guide to ensure you have the right tool for the job.
- If you are an electrician or work near live circuits: You must have boots with an EH rating to protect against shock.
- If you work with heavy falling or rolling objects: Look for an Mt rating to protect the top of your foot from impact.
- If you handle flammable materials or sensitive electronics: You need SD or Cd boots to safely dissipate static electricity.
- If you walk on sites with nails, screws, or sharp debris: Ensure your boots have a PR rating to prevent sole punctures.
By learning to read the language of your safety footwear, you take direct control over your well-being on the job.
Summary Table:
| Hazard Marking | Protection Provided | Key Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| EH | Electrical Hazard | Protects against live circuits and electrical shock. |
| Mt | Metatarsal Guard | Protects the top of the foot from heavy impacts. |
| SD | Static Dissipative | Reduces static buildup for handling sensitive electronics. |
| Cd | Conductive | Prevents static sparks in highly volatile environments. |
| PR | Puncture Resistant | Shields the sole from sharp objects like nails or glass. |
Need the right safety boots for your specific workplace hazards?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of certified safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of safety boots and shoes, ensuring you get the precise protection—from EH and Mt to SD and PR ratings—your team requires.
Contact us today for a consultation and let us help you equip your workforce with the correct, high-quality safety footwear.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Puncture-Resistant Velcro Safety Boots for Wholesale & Custom Manufacturing
- Durable Leather Safety Boots for Wholesale & Custom OEM Manufacturing
- Custom Wholesale Leather Safety Boots Direct Factory Manufacturing
- Wholesale Safety Footwear Manufacturer for Bulk & Custom OEM Orders
- Advanced KPU Athletic Safety Shoe with Steel Toe Cap Anti-Slip Rotary Lacing System
People Also Ask
- What is puncture resistance in safety footwear? Your Guide to Essential Foot Protection
- What safety features are available in work-oriented cowboy boots? Get Certified Protection & Style
- How does toe box design differ between men's and women's work boots? Fit for a Woman's Foot Anatomy
- What are the changes to puncture resistance in the new EN ISO 20345 standard? Understand P, PL, and PS Markings
- What are the differences between steel toe, composite toe, and alloy toe Wellington boots? Choose the Right Safety Toe for Your Job



















