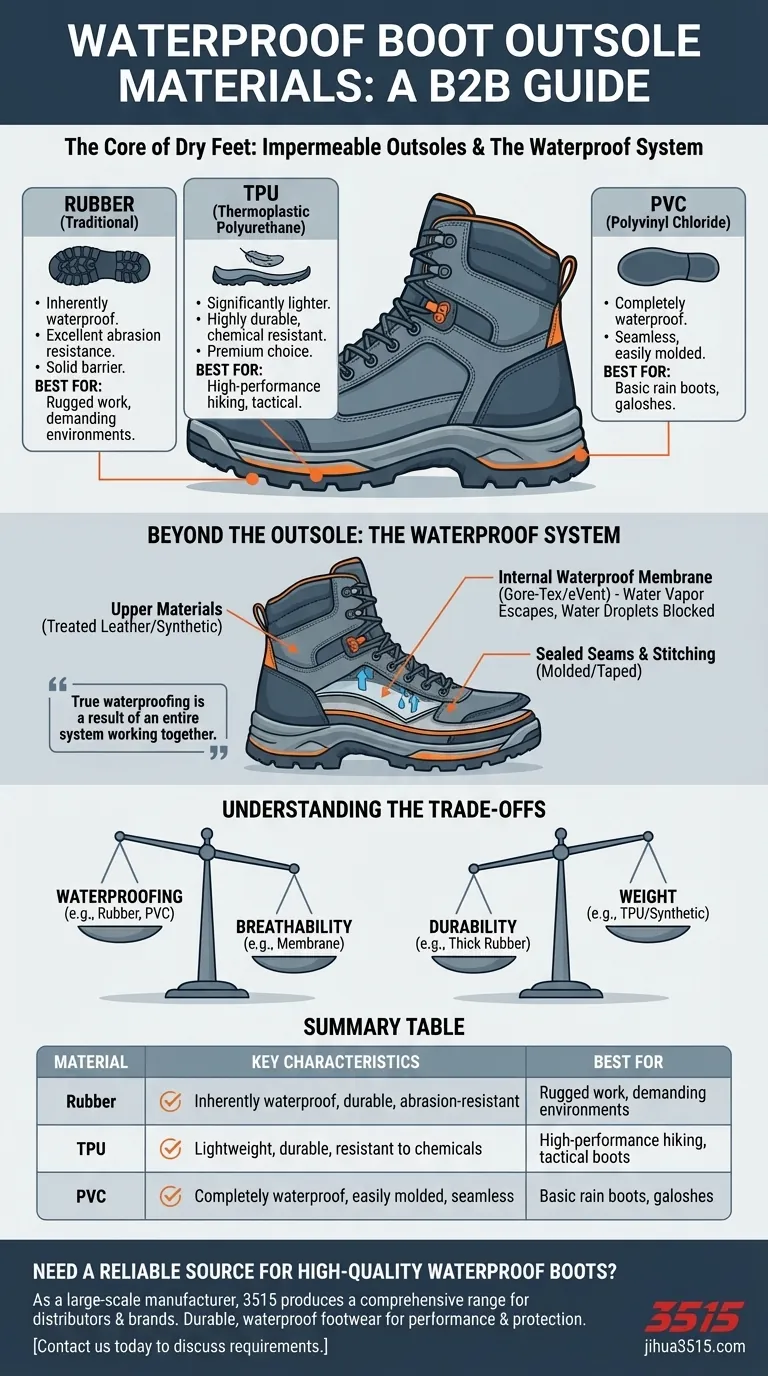
At their core, the outsoles of waterproof boots are made from solid rubber or advanced synthetic materials like TPU and PVC. These materials are chosen because they are naturally impermeable, forming a solid barrier that prevents water from seeping in from the ground up.
While a rubber or synthetic outsole provides the essential foundation, true waterproofing is a result of an entire system. The outsole, upper materials, internal membrane, and overall construction must all work together to keep your feet dry.

The Foundation: Impermeable Outsole Materials
The outsole is the first line of defense against water. Its material must be non-porous and durable enough to withstand constant abrasion without compromising its integrity.
Natural and Synthetic Rubber
Rubber is the most traditional and common material for waterproof outsoles. It is highly effective because it is inherently waterproof and offers excellent resistance to abrasions. This durability ensures the sole remains a solid barrier even after heavy use on rough terrain.
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane)
TPU is a modern synthetic alternative to rubber. It offers a key advantage in weight, being significantly lighter than traditional rubber while still providing excellent durability. TPU is also highly resistant to splitting and chemicals, making it a premium choice for high-performance boots.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
PVC is another synthetic material, often found in more basic rain boots or galoshes. It is completely waterproof and can be easily molded into a single-piece boot construction, which eliminates seams—a common failure point for water entry.
Beyond the Outsole: A System for Dry Feet
A waterproof outsole only protects the bottom of your foot. To be truly waterproof, the entire boot must be designed as a sealed system that addresses every potential point of water entry.
The Role of Upper Materials
The upper portion of the boot is typically made from treated leathers or synthetic fabrics. These materials are finished with water-repellent coatings, but their primary role is to provide structure and durability. They are the first barrier but not typically the main waterproofing component in high-performance boots.
The Importance of Waterproof Membranes
The most critical element for waterproofing in modern boots is the internal breathable waterproof membrane. Liners made from materials like Gore-Tex or eVent contain microscopic pores that are too small for water droplets to pass through, but large enough for water vapor (sweat) to escape.
This membrane is a sock-like bootie built into the boot, sitting between the outer upper material and your foot.
Construction is Critical: Seams and Stitching
Every stitch in a boot is a potential hole for water to penetrate. In truly waterproof boots, seams are either sealed with waterproof tape from the inside or eliminated altogether through molding or bonding techniques. A boot with unsealed seams will eventually leak, regardless of its materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right waterproof boot involves balancing competing factors. No single design is perfect for every situation.
Waterproofing vs. Breathability
This is the most significant trade-off. A simple, one-piece rubber boot is 100% waterproof but offers zero breathability, leading to sweaty, uncomfortable feet over time. Boots with high-tech membranes attempt to solve this by allowing sweat to escape, but even the best designs can feel warm in hot conditions.
Durability vs. Weight
Heavier materials like thick, solid rubber offer maximum durability and abrasion resistance, making them ideal for rugged work environments. Lighter materials like TPU on the outsole and synthetic fabrics on the uppers reduce fatigue, which is a major advantage for hiking or tactical use.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your boot based on a clear understanding of its entire construction, not just one feature.
- If your primary focus is absolute waterproofing for short-term wear (e.g., rain boots): Choose a boot with a single-piece molded construction made from rubber or PVC, which eliminates seams entirely.
- If your primary focus is all-day comfort in wet conditions (e.g., hiking): Prioritize a boot that combines a durable rubber or TPU outsole with a proven breathable waterproof membrane like Gore-Tex.
- If your primary focus is durability for demanding work environments: Look for a boot with a thick, abrasion-resistant rubber outsole, sealed seams, and rugged treated-leather or synthetic uppers.
Understanding how each component contributes to waterproofing empowers you to select a boot that truly meets the demands of your environment.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Rubber | Inherently waterproof, highly durable, abrasion-resistant | Rugged work, demanding environments |
| TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) | Lightweight, durable, resistant to splitting and chemicals | High-performance hiking, tactical boots |
| PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) | Completely waterproof, easily molded, seamless construction | Basic rain boots, galoshes |
Need a reliable source for high-quality waterproof boots?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of durable, waterproof boots and shoes, ensuring your customers get the performance and protection they need.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and benefit from our expertise in manufacturing.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- High Performance Fire-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots
- Factory Direct Wholesale Rain Boots Durable Waterproof & Fully Customizable
- Premium High-Cut Waterproof Safety Boots Manufacturing & Wholesale Solutions
- Durable Waterproof Rain Boots | Custom Manufacturer for Wholesale & Brands
People Also Ask
- Why can metal protective toecaps become a risk factor for dorsal foot ulcers? Learn to Prevent Pressure Point Injuries
- How do safety shoes contribute to cost savings for companies? A Strategic Investment in Risk and Cost Management
- What cultural and environmental considerations are tied to wearing shoes indoors? Balance Hygiene, Tradition, and Foot Health
- What core protection features do industrial-grade Safety Shoes provide? Key Safety Standards for Infrastructure Sites
- What are the cultural perspectives on wearing shoes in the house? A Guide to Home Etiquette & Hygiene



















