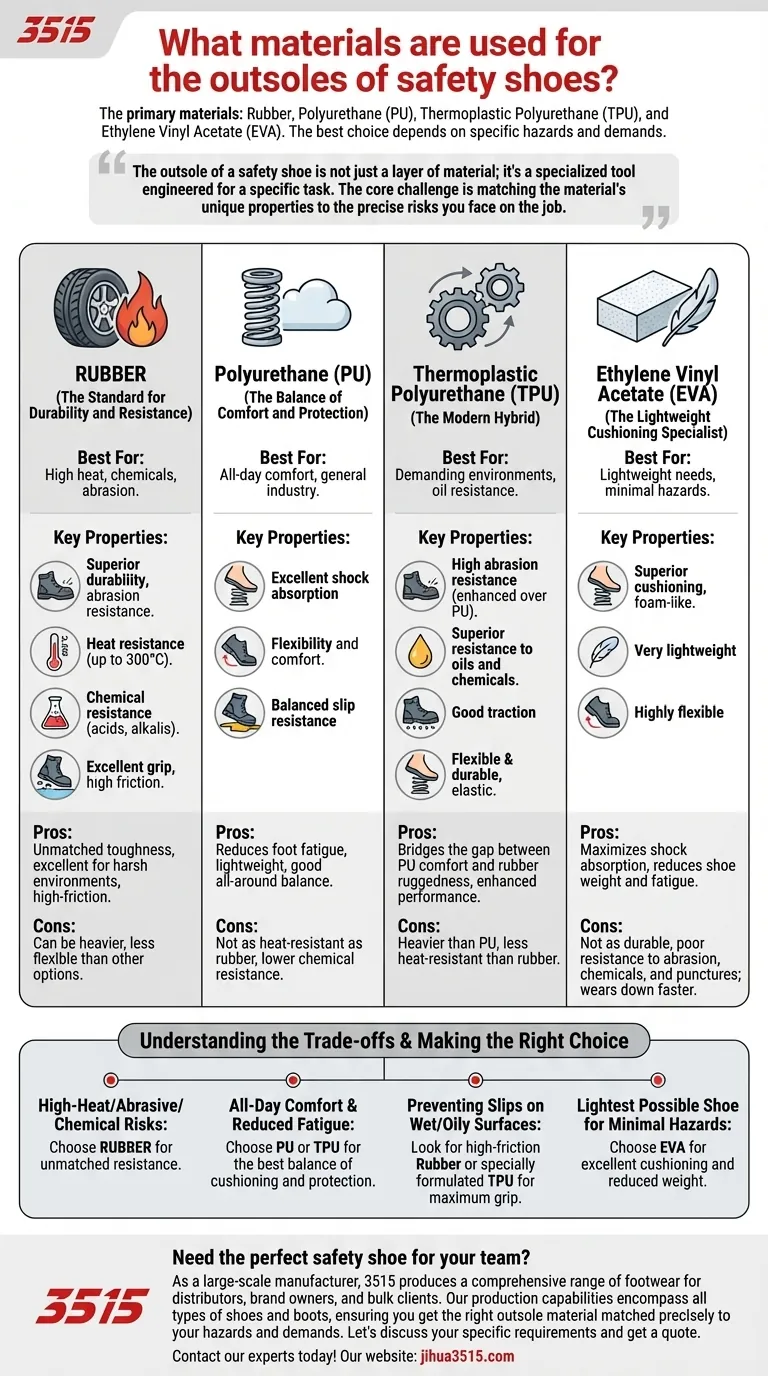
The primary materials used for safety shoe outsoles are Rubber, Polyurethane (PU), Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU), and Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA). While each of these materials provides a foundation of safety, the best choice depends entirely on the specific hazards and demands of your work environment, such as exposure to extreme heat, chemicals, or slippery surfaces.
The outsole of a safety shoe is not just a layer of material; it's a specialized tool engineered for a specific task. The core challenge is matching the material's unique properties—like heat resistance, shock absorption, or grip—to the precise risks you face on the job.

Why the Outsole Material Matters
The outsole is the shoe's single point of contact with the ground. Its composition directly dictates performance in critical areas, from preventing slips to protecting against environmental hazards. Understanding the functional differences between materials is key to ensuring your footwear provides adequate protection.
The Foundation of Safety
A safety shoe is a system of components working together, including the safety toe, upper, and midsole. However, the outsole is your primary interface with the work surface, responsible for traction, stability, and resistance to ground-based threats.
Key Performance Properties
When evaluating outsole materials, we measure them against a few core properties:
- Abrasion Resistance: How well the sole withstands wear and tear from rough surfaces.
- Slip Resistance: The material's ability to maintain grip on wet, oily, or smooth floors.
- Heat Resistance: The capacity to resist melting, cracking, or degrading at high temperatures.
- Shock Absorption: The ability to cushion impact and reduce fatigue from standing or walking on hard surfaces.
A Breakdown of Common Outsole Materials
Each material offers a distinct combination of properties, making it suitable for different applications.
Rubber: The Standard for Durability and Resistance
Rubber is a classic choice for safety footwear due to its exceptional toughness. It provides superior resistance to abrasion and can often withstand contact heat up to 300°C (572°F).
This material also holds up well against acids and alkalis, making it ideal for harsh industrial environments. Its high-friction properties deliver excellent grip, a critical feature for preventing slips and falls.
Polyurethane (PU): The Balance of Comfort and Protection
Polyurethane is known for its excellent shock-absorbing qualities and flexibility, which reduces foot fatigue during long shifts.
While not as heat-resistant as rubber, a PU outsole provides a great all-around balance of durability, slip resistance, and lightweight comfort, making it a very common choice for general construction and manufacturing work.
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU): The Modern Hybrid
TPU is an evolution of polyurethane, offering enhanced performance. It is significantly more abrasion-resistant and durable than traditional PU while retaining good flexibility and elasticity.
TPU outsoles often provide superior traction and are more resistant to oils and chemicals, bridging the gap between the comfort of PU and the ruggedness of rubber.
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA): The Lightweight Cushioning Specialist
EVA is an extremely lightweight and flexible foam-like material prized for its superior cushioning. You will often find it in the midsole of athletic shoes to provide comfort.
While sometimes used for outsoles in less demanding environments, EVA is not as durable or resistant to abrasion and chemicals as rubber or TPU. Its primary benefit is reducing shoe weight and maximizing shock absorption.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single material is perfect for every situation. Choosing an outsole always involves balancing competing priorities.
Durability vs. Comfort
The most durable materials are often the heaviest. Rubber is exceptionally tough and resistant but can be heavier and less flexible than other options. In contrast, EVA is incredibly light and cushioned but wears down much faster and offers less protection against punctures or chemicals. PU and TPU represent a middle ground, balancing longevity with all-day comfort.
Specialized vs. General-Purpose
A highly specialized outsole, such as a heat-resistant rubber sole for a foundry, is engineered for one primary purpose. While it excels in that environment, it may feel stiff or heavy for someone who walks several miles a day on a factory floor. A general-purpose PU or TPU sole may offer a better balance for more varied tasks.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select an outsole by matching the material's strengths to the primary risks of your job.
- If your primary focus is working in high-heat, abrasive, or chemical-rich environments: Rubber is the superior choice for its unmatched heat, wear, and chemical resistance.
- If your primary focus is all-day comfort and reducing fatigue on hard surfaces: Polyurethane (PU) or TPU offers the best balance of cushioning, flexibility, and reliable protection.
- If your primary focus is preventing slips on wet or oily surfaces: Look for outsoles made of high-friction rubber or a specially formulated TPU designed for maximum grip.
- If your primary focus is the lightest possible shoe for minimal-hazard areas: An EVA outsole provides excellent cushioning and reduces weight, but trades durability for comfort.
By treating your outsole as a critical piece of equipment, you can ensure your safety shoes provide the exact protection you need to perform your job safely and effectively.
Summary Table:
| Material | Best For | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Rubber | High heat, chemicals, abrasion | Superior durability, heat resistance (up to 300°C), excellent grip |
| Polyurethane (PU) | All-day comfort, general industry | Excellent shock absorption, balanced durability and flexibility |
| Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) | Demanding environments, oil resistance | High abrasion resistance, good traction, durable & flexible |
| Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) | Lightweight needs, minimal hazards | Superior cushioning, very lightweight, reduces fatigue |
Need the perfect safety shoe for your team?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of shoes and boots, ensuring you get the right outsole material—whether it's heat-resistant rubber for foundries or comfortable PU for long shifts—matched precisely to your hazards and demands.
Let's discuss your specific requirements and get a quote. Contact our experts today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
- Premium Sport Style Safety Boots for Bulk Orders
- Heavy Duty Nubuck Safety Boots Safety Shoes for Global Distribution
- Wholesale Premium Waterproof Nubuck Safety Shoes Boots
People Also Ask
- Can heavy duty work boots be worn daily outside of work? Discover Durable, All-Day Comfort
- What are the primary protective functions of composite-toe boots? A Guide to Modern Safety Footwear
- Are employers required to provide steel-toe rubber boots at no cost to employees? Yes, under OSHA rules.
- What materials are used for safety toes? Choose Steel, Composite, or Aluminum for Your Work Boots
- What are the cultural perspectives on wearing shoes in the house? A Guide to Home Etiquette & Hygiene



















