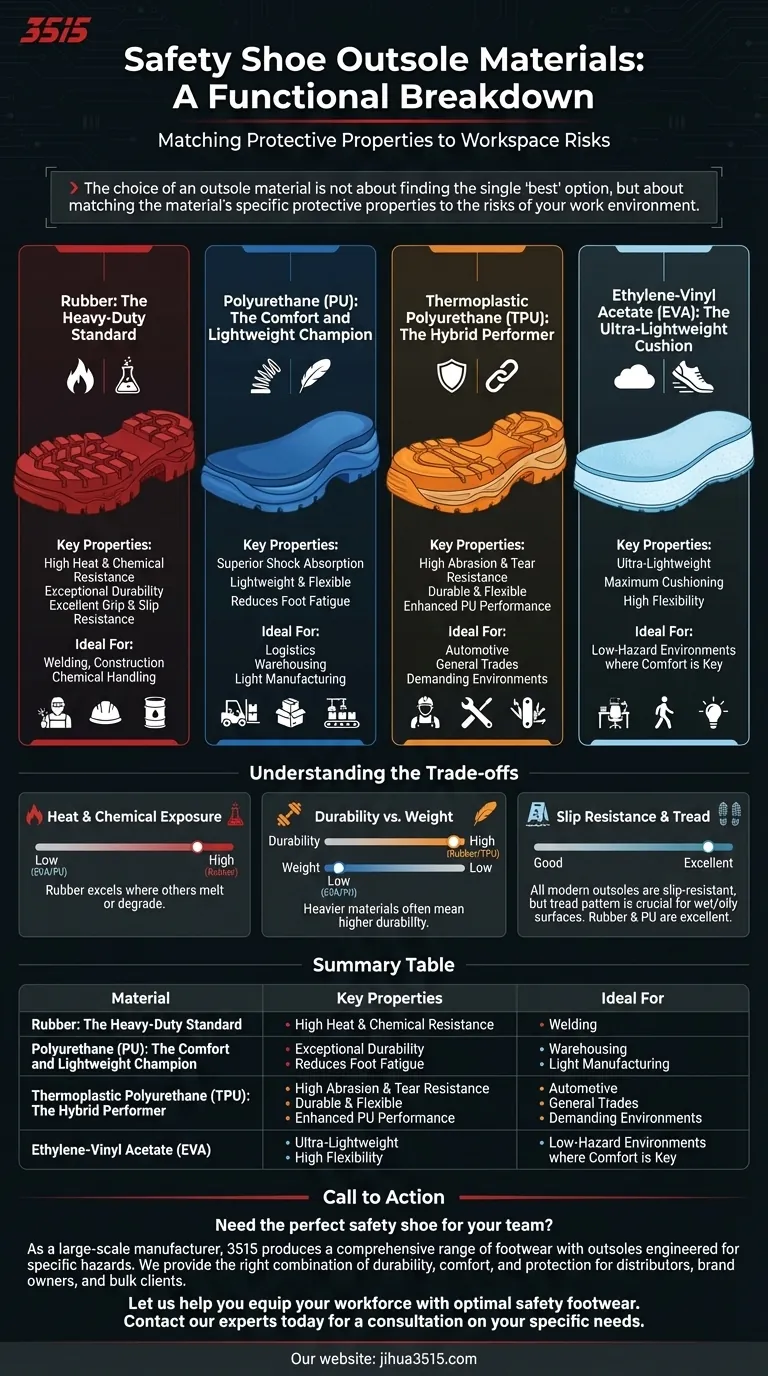
The primary materials used for safety shoe outsoles are Rubber, Polyurethane (PU), Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU), and Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA). Each material is selected for a distinct combination of properties, such as durability, flexibility, and resistance to specific workplace hazards like heat, chemicals, or slippery surfaces.
The choice of an outsole material is not about finding the single "best" option, but about matching the material's specific protective properties to the risks of your work environment. The ideal outsole for a welder is fundamentally different from one for a warehouse worker.

The Core Outsole Materials: A Functional Breakdown
Understanding the fundamental characteristics of each material is the first step in selecting the appropriate safety footwear. The outsole is the shoe's direct point of contact with the ground, making its composition critical for both safety and comfort.
Rubber: The Heavy-Duty Standard
Rubber, often a formulation like nitrile rubber, is the traditional choice for demanding environments. Its dense composition provides exceptional resistance to wear and tear.
Its primary strengths are high resistance to heat, acids, and alkalis, making it the standard for industries like welding, construction, and chemical handling. It also offers excellent grip and slip resistance.
Polyurethane (PU): The Comfort and Lightweight Champion
Polyurethane (PU) is a lighter and more flexible material than rubber. Its main advantage is superior shock absorption.
This quality significantly reduces foot fatigue during long shifts on hard surfaces, making it a popular choice for logistics, warehousing, and light manufacturing. While slip-resistant, it does not offer the same level of heat or chemical resistance as rubber.
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU): The Hybrid Performer
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) is a more advanced polymer that bridges the gap between rubber and PU. It is exceptionally durable and offers superior abrasion and tear resistance compared to conventional PU.
TPU is often used to enhance PU outsoles, providing the toughness of rubber without the associated weight. This makes it ideal for trades requiring both durability and flexibility.
Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA): The Ultra-Lightweight Cushion
EVA is a foam-like material prized for being extremely lightweight and providing excellent cushioning and flexibility.
You will often find EVA in the midsole of a shoe to provide shock absorption, but it is also used in outsoles for work environments where comfort and lightness are the absolute priorities and exposure to harsh conditions is minimal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single material excels in every category. Making an informed decision requires understanding the inherent compromises between durability, comfort, and specialized protection.
Heat and Chemical Exposure
For environments with high heat, sparks, or chemical spills, rubber is the only suitable choice. Its thermal and chemical resistance is far superior to that of PU, TPU, or EVA, which can degrade or melt under such conditions.
Durability vs. Weight
There is a direct trade-off between how much a shoe weighs and how durable it is. Rubber is the heaviest but most durable. On the other end, EVA is the lightest but least resistant to abrasion. PU and TPU occupy the middle ground, offering a balance that suits many general-purpose roles.
Slip Resistance and Tread
All modern safety outsoles are designed to be slip-resistant, but the environment matters. Rubber and PU are excellent on wet or oily surfaces. However, the material is only half the equation; the tread pattern is equally critical for channeling away liquids and gripping uneven surfaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Workplace
To select the correct outsole, start by analyzing the primary hazards and demands of your job.
- If your primary focus is protection in harsh environments (welding, chemicals, heavy construction): Choose a rubber outsole for its unmatched heat and chemical resistance.
- If your primary focus is all-day comfort on hard, flat surfaces (warehousing, logistics): A Polyurethane (PU) outsole will provide the best shock absorption and lightweight comfort to reduce fatigue.
- If your primary focus is a balance of high durability and flexibility (automotive, general trades): An outsole made with Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) offers enhanced abrasion resistance without the weight of solid rubber.
By matching the material's properties to your specific needs, you ensure your footwear provides the right protection and support.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Properties | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Rubber | High heat/chemical resistance, durable, excellent grip | Welding, construction, chemical handling |
| Polyurethane (PU) | Lightweight, superior shock absorption, comfortable | Warehousing, logistics, light manufacturing |
| Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) | High abrasion/tear resistance, durable yet flexible | Automotive, general trades, demanding environments |
| Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) | Ultra-lightweight, maximum cushioning, flexible | Low-hazard environments where comfort is key |
Need the perfect safety shoe for your team?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of footwear with outsoles engineered for specific hazards. We provide the right combination of durability, comfort, and protection for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients.
Let us help you equip your workforce with optimal safety footwear. Contact our experts today for a consultation on your specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Wholesale Safety Footwear Manufacturer for Bulk & Custom OEM Orders
- Wholesale Customizable Safety Boots Durable & Protective Footwear Manufacturing
- Customizable Anti-Smash Safety Boots for Wholesale & Private Label Manufacturing
- Premium Wholesale Wheat Nubuck Safety Boot with Rapid Lacing System
People Also Ask
- What cultural and environmental considerations are tied to wearing shoes indoors? Balance Hygiene, Tradition, and Foot Health
- What are the primary protective functions of professional Safety Boots within the automotive maintenance process?
- What are the cultural perspectives on wearing shoes in the house? A Guide to Home Etiquette & Hygiene
- How do professional construction boots improve operational efficiency? Boost Site Productivity with Advanced Footwear
- What core protection features do industrial-grade Safety Shoes provide? Key Safety Standards for Infrastructure Sites



















