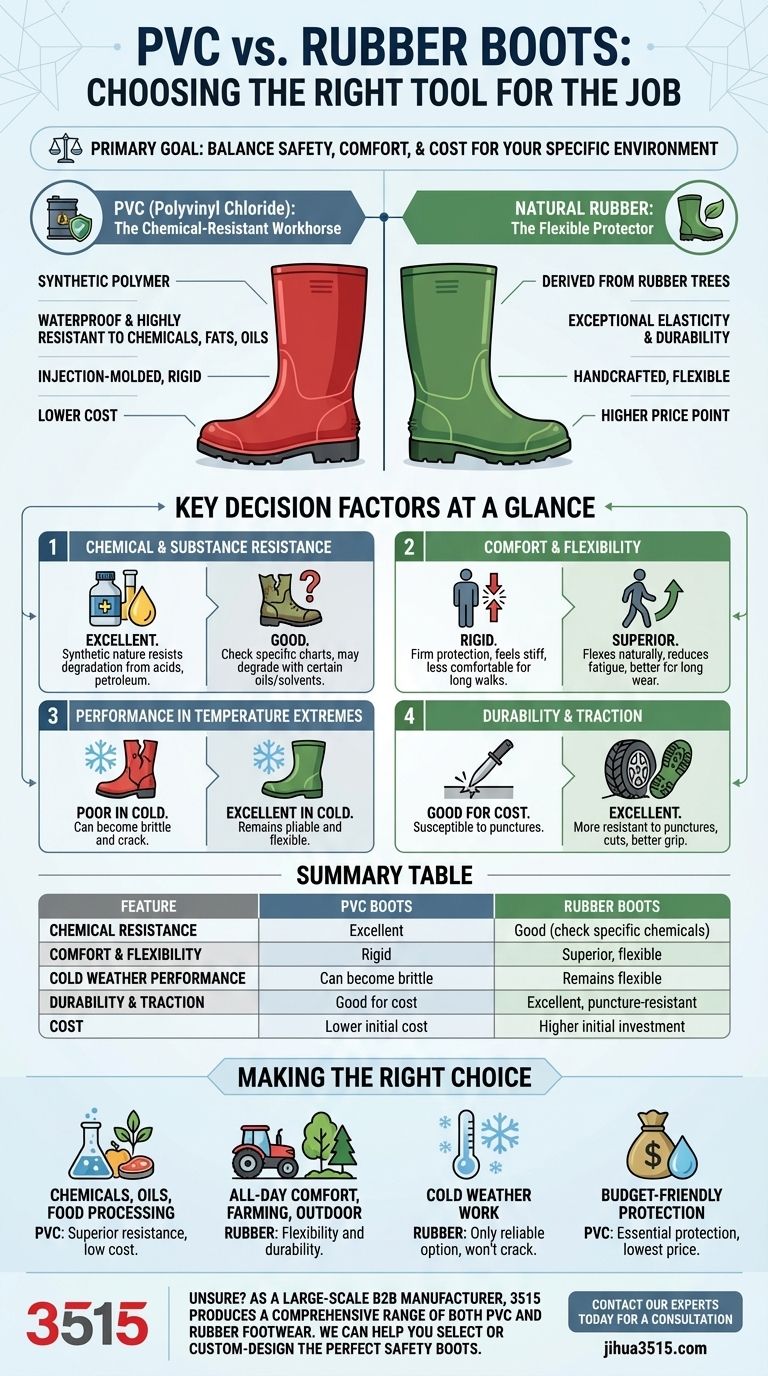
The primary goal when choosing between PVC and rubber boots is to select the material that best balances safety, comfort, and cost for your specific environment and tasks. It’s about matching the boot's properties to the unique demands you will place on it.
Your choice isn't simply between two types of boots; it's a strategic decision between two materials with distinct advantages. PVC offers superior chemical resistance at a lower cost, while rubber provides unmatched comfort, flexibility, and performance in extreme temperatures.

Understanding the Core Materials
To make an informed decision, you must first understand the fundamental properties of each material. They are not interchangeable, and one is often significantly better suited for a task than the other.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): The Chemical-Resistant Workhorse
PVC is a synthetic plastic polymer. In boot manufacturing, it's valued for being completely waterproof and highly resistant to a wide range of chemicals, fats, and oils.
This material is injection-molded, which makes production fast and keeps costs down. It is a rigid material that provides excellent protection against specific hazards.
Natural Rubber: The Flexible Protector
Natural rubber is a polymer derived from the latex of rubber trees. It is known for its exceptional elasticity, flexibility, and durability.
Rubber boots are typically handcrafted, which contributes to a higher price point. The material's natural flexibility provides superior comfort for walking long distances and remains pliable in cold temperatures.
Key Decision Factors at a Glance
Comparing the materials on key performance indicators reveals a clear pattern of strengths and weaknesses for each.
Chemical and Substance Resistance
PVC is the champion for environments with chemicals, acids, and petroleum-based products. Its synthetic nature makes it less prone to degradation from these substances.
Rubber, while waterproof, can be degraded by certain oils and solvents. Always check the manufacturer's resistance chart if chemical exposure is a primary concern.
Comfort and Flexibility
Rubber is the clear winner for comfort. It flexes naturally with your foot's movement, reducing fatigue over long periods of wear.
PVC is much more rigid. While it provides firm protection, it can feel stiff and less comfortable, especially for tasks requiring a lot of walking or kneeling.
Performance in Temperature Extremes
In cold weather, rubber maintains its flexibility and is less likely to crack. This makes it the superior choice for winter conditions or work in refrigerated environments.
PVC can become brittle and stiff in the cold, increasing the risk of the material cracking and compromising its protective barrier.
Durability and Traction
Natural rubber is more resistant to punctures, cuts, and abrasions than PVC. The outsoles on rubber boots also tend to offer better grip and traction on slippery, uneven surfaces.
PVC offers good durability for its cost but is more susceptible to being compromised by sharp objects.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither material is perfect. Your decision requires you to accept a set of compromises based on your priorities.
The PVC Compromise
When you choose PVC, you gain excellent chemical resistance and a low price point. However, you sacrifice long-term comfort, flexibility, and reliable performance in cold weather.
The Rubber Investment
By choosing rubber, you are investing in superior comfort, flexibility, and all-weather durability. The trade-off is a higher initial cost and potentially lower resistance to specific industrial chemicals.
Making the Right Choice for Your Task
Use your primary goal to guide your final decision.
- If your primary focus is working with chemicals, oils, or in food processing: PVC's superior chemical resistance and low cost make it the logical choice.
- If your primary focus is all-day comfort for farming or general outdoor use: Rubber's flexibility and durability will keep you more comfortable and better protected.
- If your primary focus is working in cold weather: Rubber is the only reliable option, as it will not become brittle and crack.
- If your primary focus is the most budget-friendly waterproof protection: PVC delivers essential protection at the lowest price point.
Ultimately, choosing the right material is choosing the right tool for the job to ensure your safety and effectiveness.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVC Boots | Rubber Boots |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Good (check specific chemicals) |
| Comfort & Flexibility | Rigid | Superior, flexible |
| Cold Weather Performance | Can become brittle | Remains flexible |
| Durability & Traction | Good for cost | Excellent, puncture-resistant |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial investment |
Still unsure which boot material is right for your team's specific hazards and environment?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of shoes and boots, including both PVC and rubber options. We can help you select or custom-design the perfect safety footwear to protect your workers and meet your budget.
Contact our experts today for a consultation and get the right boots for the job.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Wholesale Safety Footwear Manufacturer for Bulk & Custom OEM Orders
- High Performance Fire-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots
- Factory-Direct Wholesale Canvas Boots with High-Traction Rubber Soles
- Factory Direct Wholesale Rain Boots Durable Waterproof & Fully Customizable
- Premium Wholesale Waterproof Safety Boots High Performance Protection for Industrial Markets
People Also Ask
- How do composite toe work boots protect the feet? A Complete Guide to Lightweight, Metal-Free Safety
- How do safety shoes with reinforced toe protection and puncture-resistant midsoles serve as a physical barrier?
- What is the primary function of a high-precision 3D foot scanning device? Unlock Perfect Safety Shoe Sizing
- Why are standardized protective footwear and tight-fitting apparel important in gait analysis? Ensure Data Accuracy
- How do the 3R principles influence green footwear design? Master Sustainable Safety Shoe Manufacturing
- How can injury records help in identifying footwear-related dangers? Turn Data into Proactive Safety
- Why are fully covered protective shoes recommended over open-toe footwear for diabetic foot ulcers? Critical for Safety & Prevention
- How do professional-grade safety shoes contribute to the functionality of industrial load-bearing exoskeletons?



















