In simple terms, natural rubber is a highly elastic polymer derived from the milky white sap, known as latex, of the Hevea brasiliensis tree. This tree is native to tropical regions, and its latex is harvested and processed to create the versatile material used in countless everyday products.
The core concept to grasp is that natural rubber is not a synthetic, lab-created material. It is a natural biopolymer harvested directly from a specific species of tree, which is why its production is geographically concentrated in tropical climates.
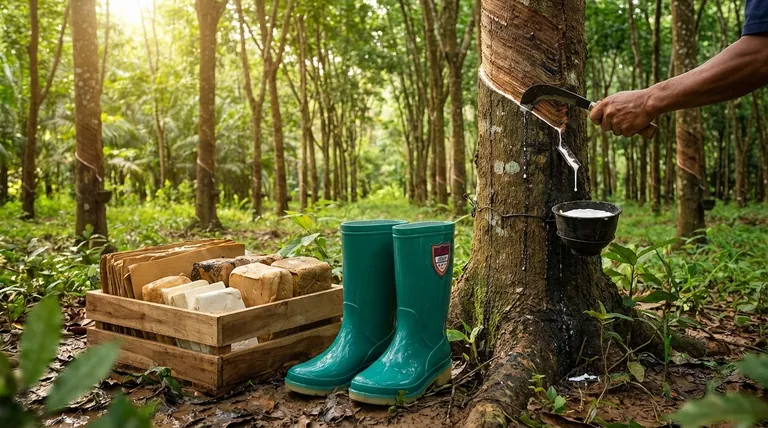

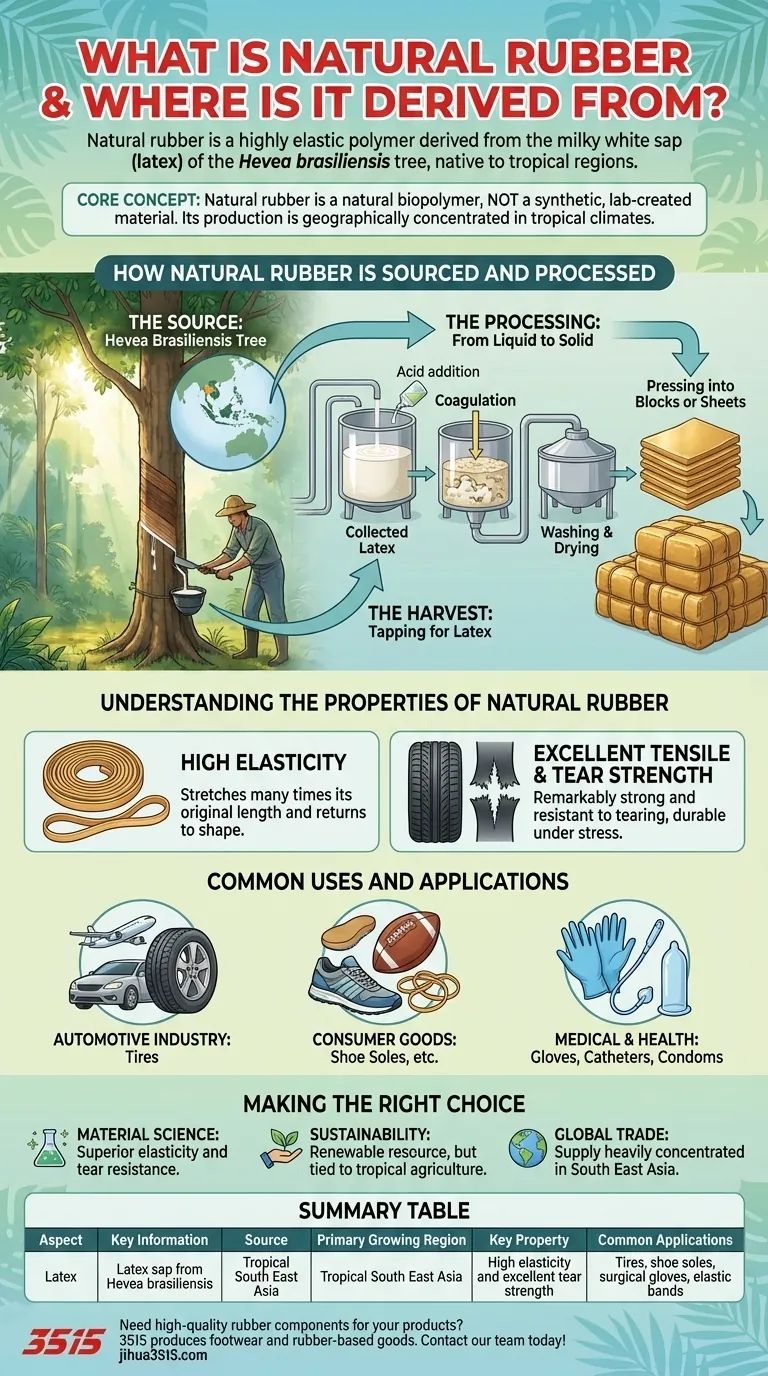
How Natural Rubber is Sourced and Processed
The journey from a tree to a finished product like a tire or a glove involves a fascinating and labor-intensive process rooted in agriculture.
The Source: The Hevea Brasiliensis Tree
The exclusive source of commercial natural rubber is the Hevea brasiliensis, or simply, the rubber tree.
These trees thrive in hot, humid climates. While originally from Brazil, the vast majority of today's commercial cultivation occurs in the tropical regions of South East Asia, with countries like Thailand and Indonesia being major producers.
The Harvest: Tapping for Latex
The harvesting process is called rubber tapping. A skilled worker makes a precise, angled incision into the bark of the rubber tree.
This cut severs the latex vessels but does not harm the tree's growth. The milky white latex sap then oozes out of the incision and is collected in a cup attached to the tree.
The Processing: From Liquid to Solid
The collected latex is a liquid mixture of rubber particles suspended in water. This raw latex is then processed to remove excess water and impurities.
It is coagulated, often using an acid, which causes the rubber particles to clump together. The resulting solid mass is then washed, dried, and pressed into blocks or sheets, ready to be shipped and manufactured into final goods.
Understanding the Properties of Natural Rubber
The molecular structure of natural rubber gives it a unique combination of physical properties that make it highly valuable.
High Elasticity
This is its most defining characteristic. Natural rubber can be stretched to many times its original length and will return to its original shape once the force is removed.
Excellent Tensile and Tear Strength
Natural rubber is remarkably strong and resistant to tearing. This durability is why it is a critical component in applications that undergo significant stress, such as vehicle tires.
Common Uses and Applications
The unique properties of natural rubber make it indispensable in numerous industries and consumer products.
Automotive Industry
The most significant use of natural rubber is in the manufacturing of tires for cars, trucks, and aircraft due to its strength and heat resistance.
Consumer Goods
It is found in a wide variety of items, including shoe soles, footballs, and elastic bands.
Medical and Health Products
Its elasticity and barrier properties make it ideal for products like surgical gloves, catheters, and condoms.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the origin of natural rubber helps clarify its role in global supply chains and material science.
- If your primary focus is material science: Recognize that natural rubber is a biopolymer with superior elasticity and tear resistance compared to many synthetic alternatives.
- If your primary focus is sustainability: Understand that natural rubber is a renewable resource, but its cultivation is linked to tropical agriculture and can have environmental impacts.
- If your primary focus is global trade: Acknowledge that the world's supply of this critical material is heavily concentrated in the specific climates of South East Asia.
Ultimately, natural rubber is a remarkable gift from nature, transformed by human ingenuity into a cornerstone of modern industry.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Information |
|---|---|
| Source | Latex sap from the Hevea brasiliensis tree |
| Primary Growing Region | Tropical South East Asia (e.g., Thailand, Indonesia) |
| Key Property | High elasticity and excellent tear strength |
| Common Applications | Tires, shoe soles, surgical gloves, elastic bands |
Need high-quality rubber components for your products?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of footwear and other rubber-based goods for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our expertise in material science ensures we deliver durable, elastic, and reliable products that meet your exact specifications.
Let us help you leverage the superior properties of natural rubber in your next project. Contact our team today to discuss your manufacturing needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Factory Direct Wholesale Rain Boots Durable Waterproof & Fully Customizable
- Factory-Direct Wholesale Canvas Boots with High-Traction Rubber Soles
- Wholesale Leather Work Boots with Customizable Wedge Sole for Brands
- Durable Goodyear Welt Leather Work Boots for Wholesale & Private Label
- Durable Leather Work Boots for Wholesale & Custom Manufacturing
People Also Ask
- What materials are used in snow boots and rain boots? A Guide to Waterproof Footwear
- What are the characteristics of rubber as a rain boot material? Discover Its Durability & Flexibility
- What are rain boots made of? Discover the best materials for ultimate waterproof protection.
- What alternatives exist for extreme wet conditions beyond waterproof hiking boots? Discover the Best Footwear for Saturated Terrain
- What factors should be considered when choosing rain boots? Find the Perfect Boot for Your Needs



















