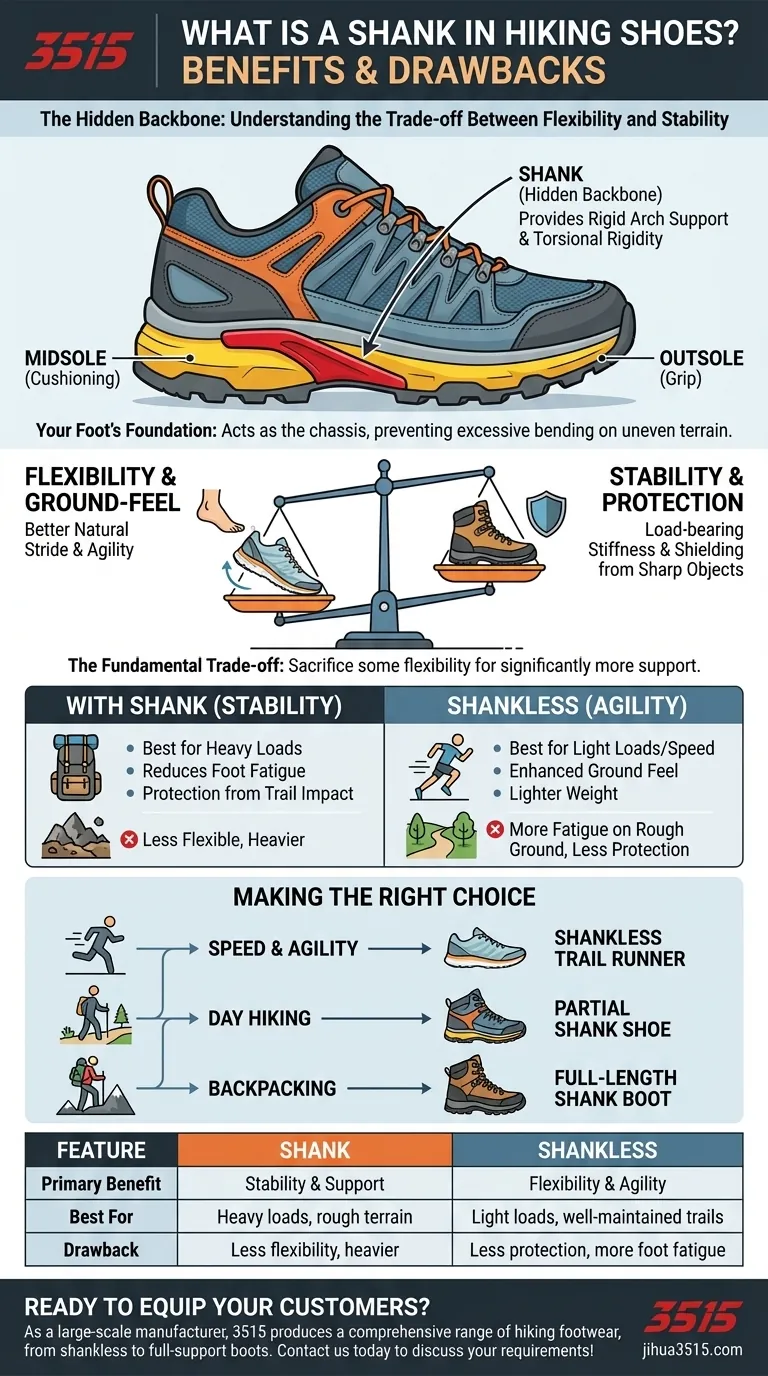
In hiking footwear, the shank is the hidden backbone of the shoe. It is a stiff, load-bearing insert, typically made of steel, plastic, or a composite material, that is placed between the shoe's midsole and outsole. Its primary job is to add rigidity and support to the arch of your foot, preventing the shoe from bending excessively on uneven or sharp terrain.
The presence of a shank represents a fundamental trade-off in hiking footwear: you sacrifice some flexibility and ground-feel in exchange for significantly more stability and protection. Understanding this balance is the key to choosing the right shoe for your specific needs on the trail.

The Role of the Shank: Your Foot's Foundation
A shoe's performance on a long hike is determined by more than just its tread and cushioning. The internal structure, particularly the shank, dictates how the shoe supports your foot under stress.
What is a Shank?
A shank is a supportive piece integrated into the sole's construction. It adds torsional rigidity, meaning it resists twisting forces, which helps keep your foot on a stable platform.
Think of it as the chassis of the shoe. While the outsole provides grip and the midsole provides cushioning, the shank provides the structural integrity.
The Primary Benefit: Stiffness and Support
The main reason to have a shank is for load-bearing stiffness. When you're carrying a backpack, your feet are under immense pressure. The shank helps distribute that weight and prevents your arch from collapsing under the load.
This stiffness also reduces foot fatigue on long hikes. By supporting your foot's natural arch, the shank lessens the strain on the muscles and tendons in your feet, allowing you to walk further with greater comfort.
Protection from the Trail
While not its only purpose, a shank does offer a layer of protection from below. It helps shield your foot from bruising caused by stepping on sharp rocks or gnarled roots.
Some shoes also include a plate, which is a thinner, more flexible insert designed specifically for this kind of point-impact protection. A shoe can have a shank, a plate, or both.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Shank vs. Shankless
Choosing a shoe with or without a shank is not about which is universally "better," but which is better for a specific purpose.
The Case for a Shank: Stability and Endurance
Footwear with a shank excels on rough, unpredictable terrain. The added rigidity provides a solid platform, which is critical for maintaining balance and preventing your foot from contorting over rocks and roots.
This makes shanks essential for hikers carrying heavy backpacks or those prone to foot fatigue. The support is a non-negotiable feature for serious trekking and multi-day trips.
The Case for No Shank: Flexibility and Agility
Shankless shoes, such as many trail runners, are significantly lighter and more flexible. This allows for a more natural stride and a better "ground feel," which some hikers prefer on well-maintained trails.
Their agility and lightness make them excellent for fast hiking, day trips with a light pack, or for experienced ultralight backpackers who prioritize speed.
The Downside of Too Much Flex
The main drawback of a shankless shoe appears on challenging ground. Without that rigid support structure, you will feel every sharp rock and root underfoot, which can become painful over time.
This excessive flexibility can also lead to faster foot fatigue, as the small muscles in your feet have to work much harder to stabilize every step, especially when carrying weight.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision ultimately depends on the type of hiking you do. Use your primary activity as your guide to select the right level of stiffness and support.
- If your primary focus is speed and agility on well-maintained paths: A flexible, shankless trail runner will provide the lightness and ground-feel you need.
- If your primary focus is day hiking on moderate trails: A hiking shoe with a partial shank offers an excellent balance of protective support and comfortable flexibility.
- If your primary focus is backpacking with a heavy load: A hiking shoe or boot with a full-length shank is essential for providing the necessary stiffness and reducing foot fatigue.
Choosing footwear with the right amount of stiffness is the first step toward a more comfortable and stable experience on the trail.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Shank | Shankless |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Benefit | Stability & Support | Flexibility & Agility |
| Best For | Heavy loads, rough terrain | Light loads, well-maintained trails |
| Drawback | Less flexibility, heavier | Less protection, more foot fatigue |
Ready to find the perfect hiking footwear for your needs? As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of hiking shoes and boots for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of footwear, from shankless trail runners to full-support backpacking boots, ensuring you get the right balance of stability, protection, and comfort. Let us help you equip your customers for the trail. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Durable Rubber Sole Outdoor Shoes Wholesale & Custom Manufacturing
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Durable Waterproof Rain Boots | Custom Manufacturer for Wholesale & Brands
- Wholesale Safety Footwear Manufacturer for Bulk & Custom OEM Orders
- Wholesale Durable Breathable Safety Boots Custom OEM Manufacturer
People Also Ask
- Are trekking shoes worth it? Essential for Safety and Comfort on the Trail
- What are the characteristics of heavy-duty hiking boots? Ultimate Guide for Rugged Terrain
- What are some alternatives to hunting boots? Hiking, Rubber & Tactical Boots Explained
- What protective role does the sole structure of toe spring shoes play? Master Complex Terrain and Prevent Falls
- What are the disadvantages of vulcanized soles? Lack of Support & Durability Explained



















