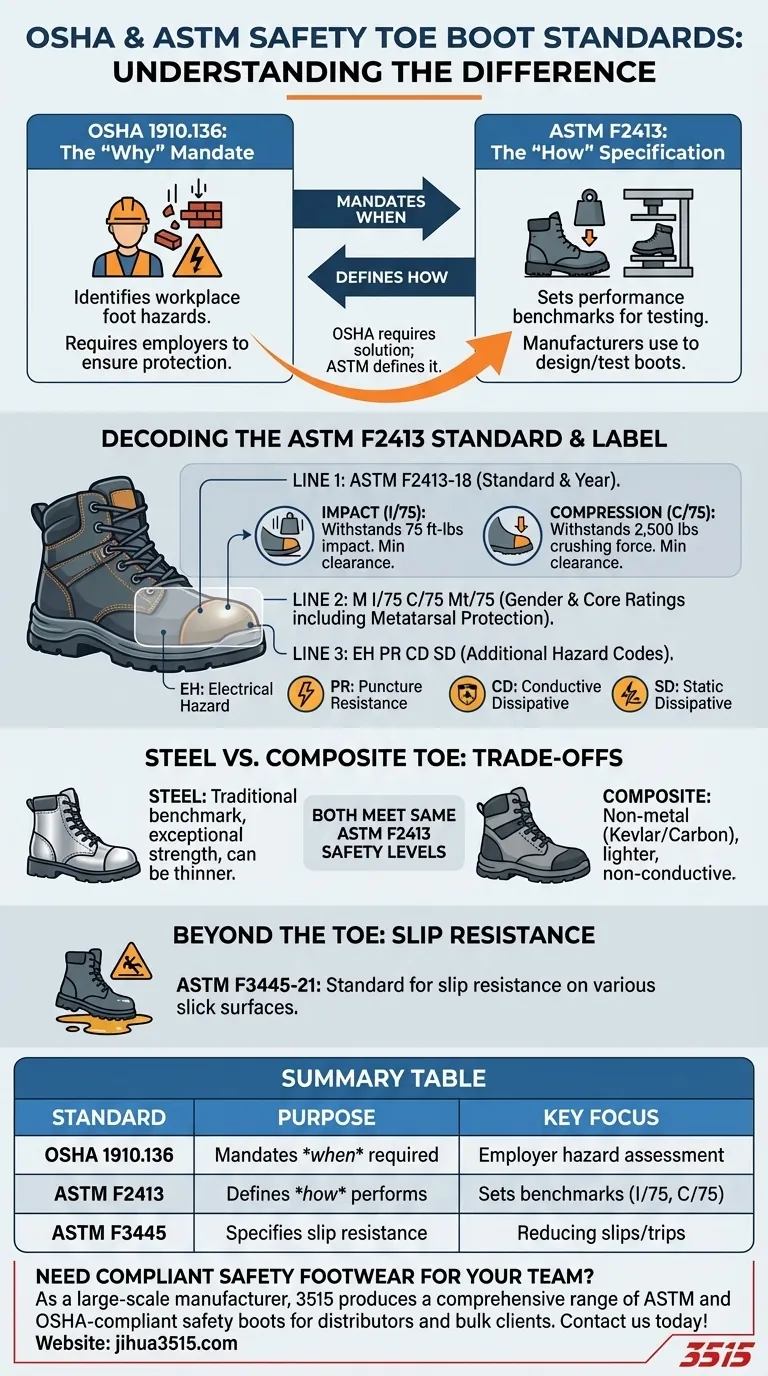
The fundamental difference is that OSHA mandates when you need protective footwear, while ASTM defines how that footwear must perform. OSHA’s standard (1910.136) requires employers to ensure workers use protective footwear in hazardous areas, but it's the ASTM standard (F2413) that provides the specific performance benchmarks for impact resistance, compression, and other critical safety features that boots must meet to be considered compliant.
In short, OSHA identifies the hazard, and ASTM sets the standard for the solution. To be compliant, your safety toe boots must meet the specific performance criteria outlined in the ASTM F2413 standard, which is what satisfies the general requirement set by OSHA.

The Role of OSHA vs. ASTM: A Critical Distinction
To select the right footwear, you must understand the two organizations' complementary roles. One creates the rule, and the other creates the test for the rule.
OSHA 1910.136: The "Why" Mandate
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) requires employers to assess their workplaces for foot hazards.
Under OSHA standard 1910.136, if hazards are present from falling or rolling objects, sharp objects that could pierce the sole, or electrical dangers, the employer must ensure employees use appropriate protective footwear.
OSHA does not design or test boots; it simply mandates their use when necessary.
ASTM F2413: The "How" Specification
The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) develops the technical standards. ASTM F2413 is the "Standard Specification for Performance Requirements for Protective (Safety) Toe Cap Footwear."
This is the document manufacturers use to design and test their boots. It establishes the minimum requirements for performance in a series of controlled laboratory tests.
Decoding the ASTM F2413 Standard
All compliant safety footwear has a label, typically on the tongue, that acts as a code for its specific protections. Understanding this code is essential.
The Core Requirements: Impact and Compression
Every safety toe boot must pass two fundamental tests:
- Impact (I): The boot must withstand an impact of 75 foot-pounds. This test measures the clearance remaining inside the toe cap after a heavy weight is dropped on it. The rating is I/75.
- Compression (C): The boot must withstand a compressive force of 2,500 pounds. This tests the toe cap's ability to resist crushing from a slow, heavy force. The rating is C/75.
For both tests, the boot must maintain a minimum interior clearance after the event: 0.500 inches for men's footwear and 0.468 inches for women's.
How to Read the Safety Boot Label
The label is formatted in specific lines to be read easily.
Line 1: ASTM F2413-18
This identifies that the boot meets the performance standards of ASTM F2413, with "-18" indicating the year of the standard's revision (2018).
Line 2: M I/75 C/75 Mt/75
This line identifies the gender (M for Male, F for Female) and the core ratings. In this example, it meets the I/75 and C/75 standards. It also indicates Metatarsal (Mt) protection, which guards the delicate bones on top of the foot.
Line 3: EH PR
This line lists any additional hazard protections the boot offers. Common codes include:
- EH: Electrical Hazard protection against accidental contact with live electrical circuits.
- PR: Puncture Resistance, indicating a plate in the sole to protect against sharp objects.
- CD: Conductive Dissipative, to reduce the buildup of static electricity.
- SD: Static Dissipative, for more controlled static discharge.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Steel vs. Composite Toe
Both traditional steel and modern composite materials can meet the same ASTM F2413 standards. The choice between them is a matter of trade-offs, not a difference in certified safety levels.
Steel Toe: The Traditional Standard
Steel has been the industry benchmark for decades. It provides exceptional impact and compression resistance and can often be made slightly thinner in the toe cap profile.
Composite Toe: The Modern Alternative
Composite toes are made from non-metal materials like Kevlar, carbon fiber, or plastic. They are significantly lighter, do not conduct heat or cold, and will not set off metal detectors. A composite toe boot with an I/75 C/75 rating offers the exact same level of certified protection as its steel counterpart.
Beyond the Toe: Other Critical Standards
While the toe cap gets the most attention, other hazards are just as critical.
ASTM F3445: The Standard for Slip Resistance
Slips, trips, and falls are among the most common workplace injuries. ASTM F3445-21 is a newer standard that specifically sets performance requirements for the slip resistance of footwear soles.
A boot that is compliant with this standard has passed rigorous testing on various wet, oily, and soapy surfaces, providing a much higher degree of confidence in its traction.
Making the Right Choice for Your Job
Your specific work environment dictates the combination of standards you need.
- If your primary focus is construction or heavy industry: Prioritize boots with I/75, C/75, and ideally Mt/75 (Metatarsal) ratings for maximum protection from falling and rolling objects.
- If your primary focus is electrical work: An EH (Electrical Hazard) rating is non-negotiable, and a composite toe is often preferred to ensure no conductive materials are in the boot.
- If your primary focus is working on wet or oily surfaces: Look for a boot that explicitly states compliance with ASTM F3445 for proven slip resistance, in addition to its safety toe rating.
- If you work outdoors in extreme temperatures: A composite toe boot will provide better insulation, keeping your feet more comfortable without sacrificing certified impact protection.
Understanding these standards transforms your safety footwear from a simple requirement into a calculated tool for personal protection.
Summary Table:
| Standard | Purpose | Key Focus |
|---|---|---|
| OSHA 1910.136 | Mandates when protective footwear is required | Employer responsibility for hazard assessment |
| ASTM F2413 | Defines how footwear must perform | Sets performance benchmarks (e.g., I/75, C/75) |
| ASTM F3445 | Specifies slip resistance requirements | Reduces risk of slips, trips, and falls on slick surfaces |
Need Compliant Safety Footwear for Your Team?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of ASTM and OSHA-compliant safety boots and shoes for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. We ensure every pair meets the precise performance criteria your workforce needs, from impact and compression resistance to electrical hazard and slip resistance protection.
Let us help you equip your team with the right safety solution.
Contact us today to discuss your requirements and receive a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Premium KPU Athletic Safety Shoes for Wholesale
- Premium KPU Injection Athletic Style Safety Shoes
- Custom Safety Shoe Manufacturer for Wholesale & OEM Brands
- Wholesale Leather Safety Boots with Customizable Protective Toe
- Wholesale Durable Breathable Safety Boots Custom OEM Manufacturer
People Also Ask
- What should women consider when choosing safety footwear for their work environment? Get the Right Fit and Protection
- What additional consideration is mentioned if protective footwear is electric shock resistant? Employer's Financial Responsibility
- What should users know about the transition period between the old and new EN ISO 20345 standards? A Guide to Compliance
- How does devulcanized recycled rubber benefit outsoles for safety shoes? Boost Performance and Sustainability
- What are the specific functional requirements for safety shoes used in high-load clinical environments? Top 8 Features
- Why is durability a core technical requirement for safety shoes in economic uncertainty? Secure Long-Term Value
- Why is a heat flux intensity of 20 kW/m² applied to fire safety boots? Ensuring Superior Thermal Protection
- What is a composite toe boot and what materials is it made from? Lighter, Safer Footwear for Modern Work



















