At its core, the shoe sole manufacturing process creates two or three primary components that are later fused into a single unit. These are the insole, which sits inside the shoe; the outsole, which makes contact with the ground; and often a midsole, which is layered between them to provide cushioning and structure.
The specific components and materials of a shoe sole are not arbitrary; they are engineered to deliver a specific outcome. Understanding the function of the insole, midsole, and outsole is key to understanding the shoe's overall performance, comfort, and durability.
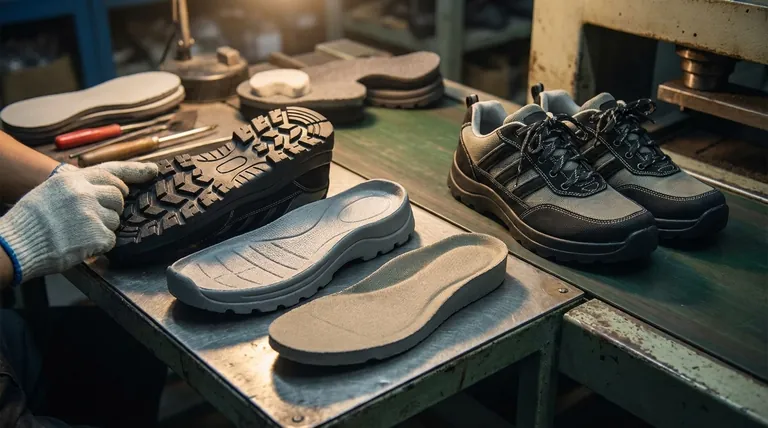

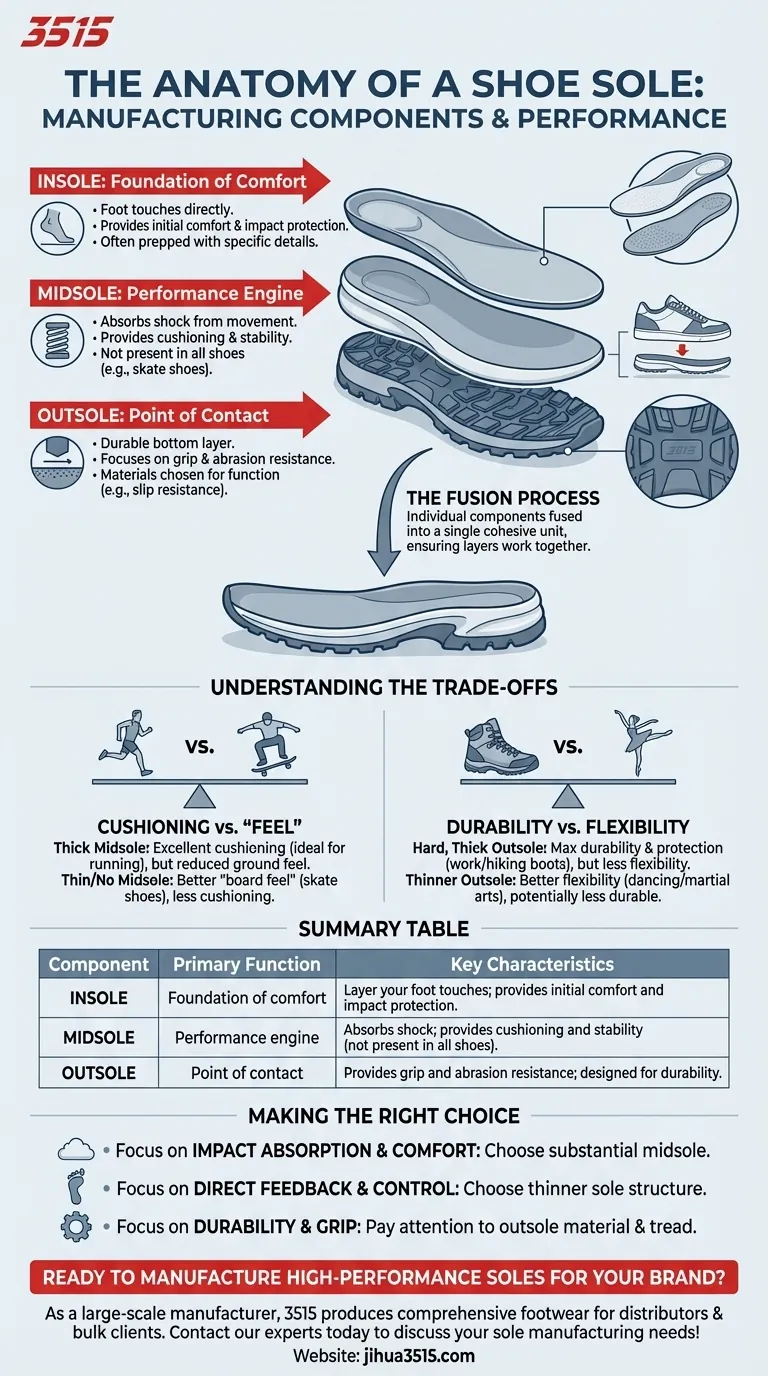
The Anatomy of a Shoe Sole
A shoe sole is a system of layers, each with a distinct and vital job. The complexity of this system is dictated entirely by the shoe's intended purpose, from a simple sandal to a high-performance athletic sneaker.
The Insole: The Foundation of Comfort
The insole is the layer your foot directly touches. Its primary role is to provide initial comfort and some impact protection.
During manufacturing, this component is often prepped with specific details, such as coloring for the heel area, before being joined with the other layers.
The Midsole: The Performance Engine
The midsole is the crucial, often hidden, layer responsible for cushioning and stability. It absorbs the shock from walking, running, and jumping.
This component is not present in all shoes. For example, some skate shoes omit a distinct midsole to provide better "board feel," prioritizing direct feedback from the ground over maximum cushioning.
The Outsole: The Point of Contact
The outsole is the durable bottom layer of the shoe that contacts the ground. Its design focuses on grip and resistance to abrasion.
Materials are chosen for specific functions, such as the excellent slip resistance required for safety shoes used in environments with oil, water, or chemicals. It's also where logos and background colors are often applied during manufacturing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The combination of these components creates a series of trade-offs that define how the shoe feels and performs. The manufacturer's choices directly impact the end user.
Cushioning vs. "Feel"
A thick, soft midsole provides excellent cushioning, which is ideal for running. However, this same feature reduces the wearer's direct feel for the ground, a trade-off a skateboarder might not want.
Durability vs. Flexibility
A hard, thick outsole offers maximum durability and protection, perfect for a work or hiking boot. This comes at the cost of flexibility, which would be a major drawback in a shoe designed for dancing or martial arts.
The Fusion Process
The final step in manufacturing is to fuse these individual components—the prepared insole, the performance-tuned midsole, and the durable outsole—into a single, cohesive sole unit. This bonding process ensures the layers work together as intended.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
By understanding how these components function, you can better select footwear that aligns with your specific needs.
- If your primary focus is impact absorption and comfort: Look for shoes with a substantial midsole designed for cushioning.
- If your primary focus is direct feedback and control: Choose shoes with a thinner sole structure, which may have a minimal or non-existent midsole.
- If your primary focus is durability and grip: Pay closest attention to the material composition and tread pattern of the outsole.
Ultimately, recognizing the role of each layer empowers you to look beyond style and evaluate a shoe based on its fundamental engineering.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Insole | Foundation of comfort | Layer your foot touches; provides initial comfort and impact protection. |
| Midsole | Performance engine | Absorbs shock; provides cushioning and stability (not present in all shoes). |
| Outsole | Point of contact | Provides grip and abrasion resistance; designed for durability. |
Ready to manufacture high-performance soles for your brand?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of shoes and boots, ensuring the perfect balance of cushioning, durability, and flexibility for your target market.
Contact our experts today to discuss your sole manufacturing needs and get a custom solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Durable Rubber-Soled Utility Shoes for Wholesale & Custom Brand Manufacturing
- Wholesale Modern Comfort Shoes with Dial Closure for Private Label & Bulk Orders
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Wholesale Durable Camouflage Canvas Shoes with High-Traction Cleated Rubber Sole
- Premium Safety Shoes with Rotating Buckle Safety Sneakers
People Also Ask
- What were traditional shoe soles made from before rubber? The History of Leather Soles
- What are the advantages of rubber soles in sneakers? Unmatched Grip, Durability & Comfort
- What causes white marks on rubber boots, and how can they be removed? A Guide to 'Blooming' & Boot Care
- How do rubber soles affect a shoe's appearance? Defining Your Shoe's Style and Formality
- How do rubber and TPR soles compare in terms of water resistance? A Guide to Grip and Performance



















