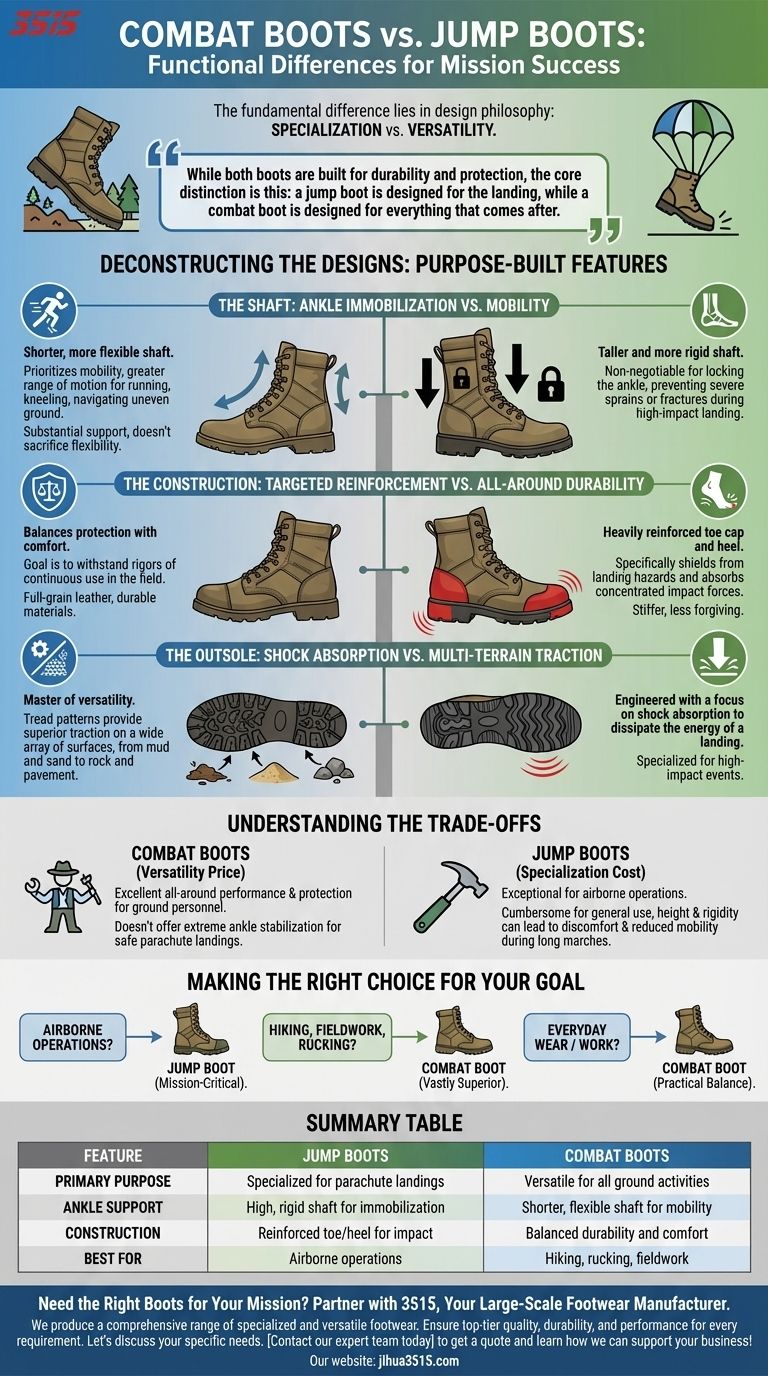
The fundamental difference between combat boots and jump boots lies in their design philosophy: specialization versus versatility. Jump boots are highly specialized tools designed to provide maximum ankle support and protection for the single, critical event of a parachute landing. Combat boots are versatile, general-purpose footwear engineered for durability, flexibility, and comfort across a wide variety of terrains and ground-based activities.
While both boots are built for durability and protection, the core distinction is this: a jump boot is designed for the landing, while a combat boot is designed for everything that comes after.

Deconstructing the Designs: Purpose-Built Features
The functional differences between these two boot types are not arbitrary; they are direct results of their intended missions. Each component is engineered to solve a different primary problem.
The Shaft: Ankle Immobilization vs. Mobility
Jump boots feature a distinctly taller and more rigid shaft, typically extending well above the ankle. This design is non-negotiable for its purpose: to lock the ankle in place and prevent severe sprains or fractures during the high-impact, unpredictable force of a parachute landing.
Combat boots, in contrast, have a shorter, more flexible shaft. This design prioritizes mobility, allowing the wearer a greater range of motion for running, kneeling, and navigating uneven ground. The support is substantial but doesn't sacrifice the flexibility needed for prolonged marching.
The Construction: Targeted Reinforcement vs. All-Around Durability
Jump boots are heavily reinforced at the toe cap and heel. This isn't just for general protection but specifically to shield the foot from landing hazards and absorb impact forces concentrated in those areas. The overall construction is stiffer and less forgiving.
While combat boots also feature reinforced toes and durable materials like full-grain leather, their construction balances protection with comfort. The goal is to withstand the rigors of continuous use in the field, not just a single, violent impact.
The Outsole: Shock Absorption vs. Multi-Terrain Traction
Both boot types have aggressive outsoles for grip. However, a jump boot's sole is often engineered with a focus on shock absorption to dissipate the energy of a landing.
A modern combat boot's outsole is a master of versatility, with tread patterns designed to provide superior traction on a wide array of surfaces, from mud and sand to rock and pavement.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these boots means accepting a specific set of compromises. The strengths of one design are the inherent weaknesses of the other for a given task.
The Cost of Specialization (Jump Boots)
The very features that make jump boots exceptional for airborne operations make them cumbersome for general use. Their height and rigidity can lead to discomfort and reduced mobility during long marches. They are a specialized tool, and using them outside their intended context is inefficient.
The Price of Versatility (Combat Boots)
A combat boot is the quintessential jack-of-all-trades. It provides excellent all-around performance and protection for ground personnel. However, it does not offer the extreme level of ankle stabilization required to safely mitigate the unique risks of a parachute landing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be dictated entirely by your primary mission or activity.
- If your primary focus is airborne operations: The jump boot is the only appropriate choice; its protective design is mission-critical.
- If your primary focus is hiking, fieldwork, or rucking: The combat boot is vastly superior, offering the necessary flexibility and comfort for long-duration movement.
- If your primary focus is everyday wear or work: The combat boot provides a far more practical balance of durability, support, and all-day comfort.
Ultimately, you must match the engineering of the boot to the demands of your environment.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Jump Boots | Combat Boots |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Specialized for parachute landings | Versatile for all ground activities |
| Ankle Support | High, rigid shaft for immobilization | Shorter, flexible shaft for mobility |
| Construction | Reinforced toe/heel for impact | Balanced durability and comfort |
| Best For | Airborne operations | Hiking, rucking, fieldwork |
Need the Right Boots for Your Mission? Partner with 3515, Your Large-Scale Footwear Manufacturer.
As a leading manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of specialized and versatile footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Whether you need purpose-built jump boots or durable combat boots, our production capabilities ensure top-tier quality, durability, and performance for every requirement.
Let's discuss your specific needs. Contact our expert team today to get a quote and learn how we can support your business!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Wholesale Waterproof Tactical Boots Custom Suede & High-Traction Soles
- Durable Leather High-Ankle Tactical Boots for Wholesale & Custom Manufacturing
- Durable Leather Tactical Boots Wholesale & Custom Manufacturing for Brands
- Wholesale Durable Mid-Cut Tactical Boots for Custom & Private Label Brands
- High-Traction Suede Tactical Boots Wholesale & Custom Manufacturing
People Also Ask
- What boots do navy SEALs run in? Discover the Mission-Driven Footwear Philosophy
- What improvements does the high-traction outsole offer in modern jungle boots? Unlock Superior Grip & Versatility
- What are the drawbacks of jungle boots without a side zipper? A Guide to Trade-offs in Boot Design
- What are the key components of military boot anatomy that affect fit? Unlock Perfect Comfort & Performance
- How should excess dirt be removed from military boots? A Step-by-Step Guide to Proper Care
- What distinguishes desert boots from chukka boots? The Sole & Formality Breakdown
- Who is authorized to wear combat boots with specific berets or in certain roles? Understanding U.S. Army Uniform Exceptions
- How do military boots protect the feet from harm? An Inside Look at Protective Footwear Design



















