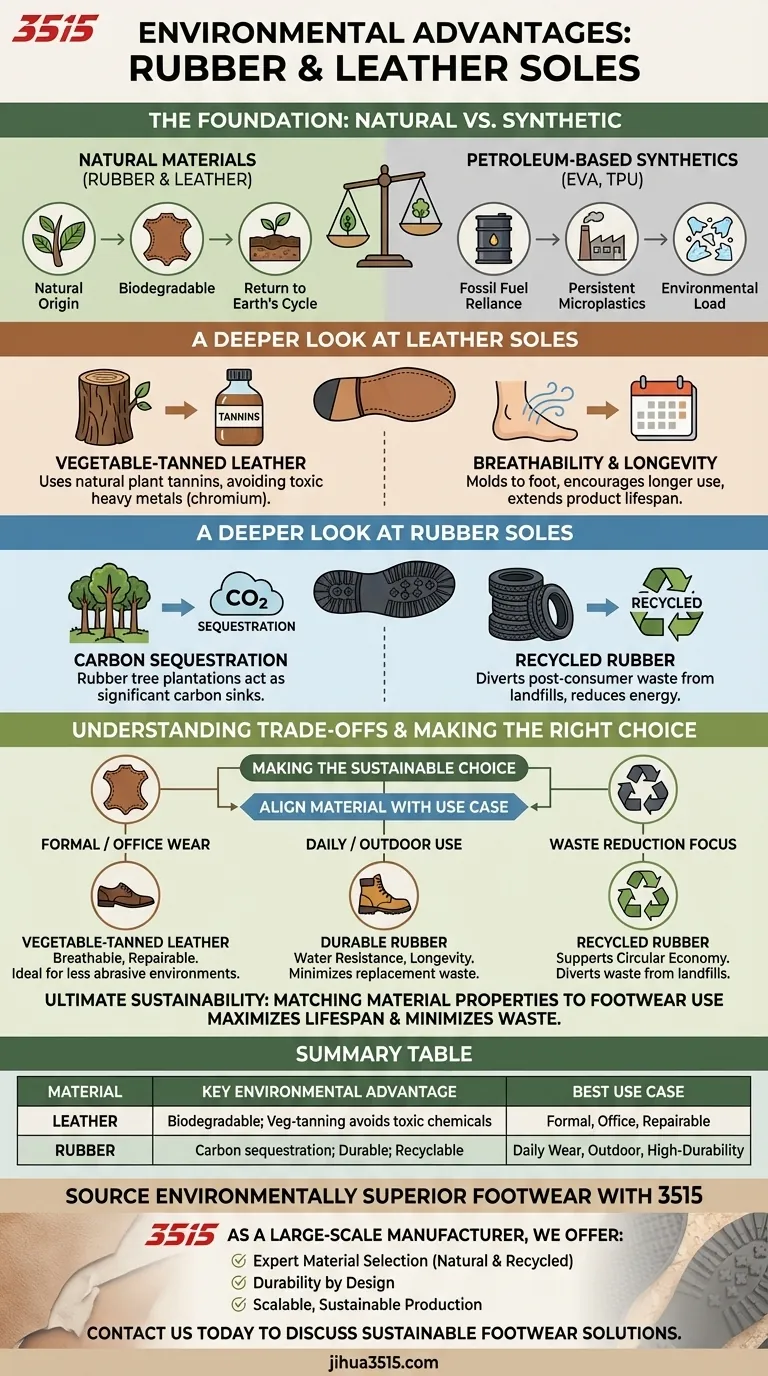
From a purely environmental perspective, rubber and leather stand out as sole materials because they are natural and biodegradable, capable of re-entering the earth's natural cycle. Unlike synthetic plastics, vegetable-tanned leather avoids many toxic chemicals, while natural rubber production can sequester atmospheric carbon, and using recycled rubber actively reduces landfill waste.
The core advantage of rubber and leather soles lies in their natural origin, which offers a more sustainable path than petroleum-based synthetics. However, their true environmental benefit is only realized when the material's specific properties are matched to the footwear's intended use, maximizing durability and lifespan.

The Foundation: Why Natural Materials Matter
Choosing a sole made from a natural material like rubber or leather is a fundamental step away from a reliance on fossil fuels, which are the primary feedstock for common synthetic soles like EVA and TPU.
Biodegradability and the Natural Cycle
Both rubber and leather are organic materials. When their useful life is over, they have the ability to decompose and return to the earth, a stark contrast to synthetic plastics that break down into persistent microplastics.
Reducing Chemical Inputs
Opting for natural materials can reduce the environmental load from industrial chemical processes. This is especially true when specific, cleaner production methods are chosen by the manufacturer.
A Deeper Look at Leather Soles
Leather soles are most associated with high-quality, formal, and welted footwear. Their environmental credentials hinge almost entirely on how the leather is processed.
The Critical Role of Tanning
The most significant environmental factor for leather is the tanning method. Vegetable-tanned leather uses natural tannins from tree bark and plants, avoiding the heavy metals and toxic chemicals associated with mainstream chromium tanning.
Breathability and Longevity
Leather's natural breathability and ability to mold to the wearer's foot create a custom, comfortable fit. This comfort encourages longer use, extending the product's life and reducing the cycle of consumption and waste.
A Deeper Look at Rubber Soles
Rubber soles are prized for their durability and versatility. Their environmental story includes benefits that begin right at the source.
Carbon Sequestration
Natural rubber is harvested as latex from the Hevea brasiliensis tree. These rubber tree plantations act as significant carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere and helping to mitigate climate change.
The Power of Recycled Rubber
A major environmental advantage is the use of recycled rubber. Sourcing rubber from post-consumer waste, such as old tires, diverts massive amounts of material from landfills and reduces the energy and contamination associated with waste management.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither material is a perfect solution. An objective assessment requires acknowledging the functional and environmental compromises of each.
Performance Dictates Lifespan
The most sustainable choice is one that lasts. A leather sole worn daily on wet, abrasive pavement will fail quickly, creating waste. In this scenario, a durable rubber sole is the far more sustainable option because it will not need to be replaced.
The Reality of "Biodegradable"
While these materials are biodegradable, the conditions in a modern, compacted landfill are not ideal for decomposition. The primary benefit remains avoiding the creation of permanent microplastics that pollute ecosystems.
Production vs. Use
The environmental impact of production must be weighed against the product's lifespan. Vegetable tanning is better, but still resource-intensive. A highly durable rubber sole may have a lower overall impact than a less-durable leather sole if it lasts three times as long.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To make a truly sustainable decision, align the material's strengths with your primary use case.
- If your primary focus is formal or office wear: A vegetable-tanned leather sole offers a sustainable, breathable, and repairable option ideal for less abrasive environments.
- If your primary focus is durability for daily and outdoor use: A natural or recycled rubber sole provides the water resistance and longevity needed to minimize waste and replacement.
- If your primary focus is actively reducing waste: Prioritize footwear made with recycled rubber soles to support a circular economy and divert waste from landfills.
Ultimately, the most environmentally sound sole is one that is perfectly suited to its purpose, ensuring the longest possible lifespan for your footwear.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Environmental Advantage | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Leather | Biodegradable; vegetable-tanning avoids toxic chemicals | Formal, office, and repairable footwear |
| Rubber | Carbon sequestration; durable; recyclable | Daily wear, outdoor, and high-durability footwear |
Ready to source environmentally superior footwear?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of footwear with rubber and leather soles for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. We help you align your product line with sustainability goals by offering:
- Expert Material Selection: Choose from natural, vegetable-tanned leathers and recycled rubber compounds.
- Durability by Design: Our production capabilities ensure the right sole is matched to the product's use, maximizing lifespan.
- Scalable, Sustainable Production: Benefit from our expertise in manufacturing all types of shoes and boots with a lower environmental footprint.
Contact us today to discuss how we can bring sustainable, high-quality footwear to your market.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Durable Rubber Sole Outdoor Shoes Wholesale & Custom Manufacturing
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Custom OEM Training Shoes Wholesale Manufacturer Durable & Breathable
- Durable Waterproof Rain Boots | Custom Manufacturer for Wholesale & Brands
- Durable Moc-Toe Wedge Work Boots | Wholesale Manufacturing for Brands
People Also Ask
- What were traditional shoe soles made from before rubber? The History of Leather Soles
- What technical requirements are essential for outsoles in pivoting sports? Boost Grip and Lateral Stability
- Why are rubber-soled shoes considered multi-weather footwear? Unlock All-Season Traction & Protection
- What are some alternatives to hunting boots? Hiking, Rubber & Tactical Boots Explained
- What are the characteristics of heavy-duty hiking boots? Ultimate Guide for Rugged Terrain



















