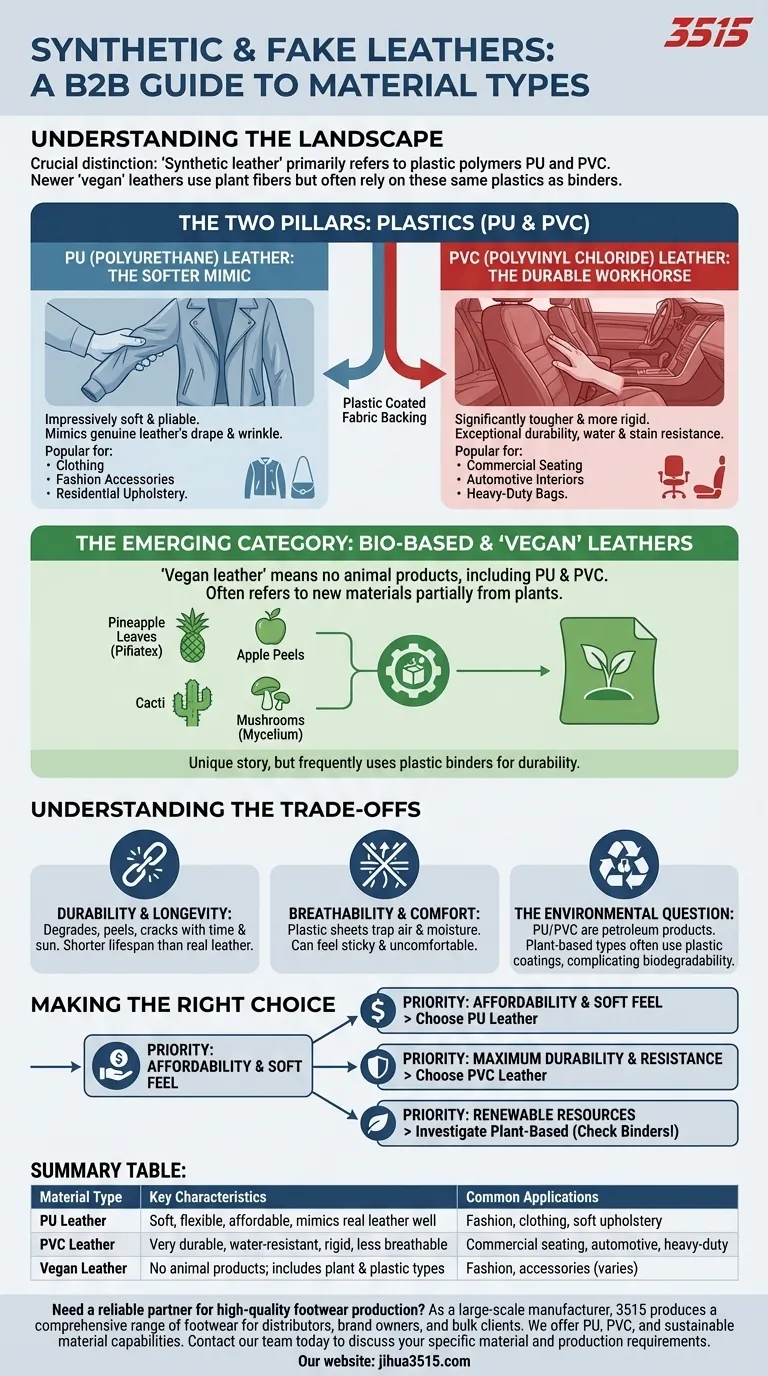
When choosing an alternative to traditional leather, it's crucial to understand that not all "fake" leathers are created equal. The most common types are plastic-based materials like Polyurethane (PU) and Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), which are designed to mimic leather's appearance, alongside a newer, diverse category of materials marketed as "vegan" or plant-based leather.
The core distinction to grasp is that "synthetic leather" typically refers to two main plastic polymers: PU for a softer, more flexible feel, and PVC for tougher, more durable applications. Newer "vegan" leathers often use plant fibers but still frequently rely on these same plastics as binders.

The Two Pillars of Synthetic Leather: Plastics
For decades, the vast majority of leather alternatives have been derived from two specific types of plastic coated onto a fabric backing. Their distinct properties make them suitable for different applications.
PU (Polyurethane) Leather: The Softer Mimic
PU leather is made by applying a coating of polyurethane to a backing fabric, such as cotton or polyester. This method allows the material to be impressively soft and pliable.
Its flexible nature allows it to wrinkle and drape in a way that more closely resembles genuine leather. Because of this, PU is a popular choice for clothing, fashion accessories, and softer residential upholstery.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) Leather: The Durable Workhorse
PVC leather is constructed with multiple layers of polyvinyl chloride and plasticizers over a fabric base. This layered structure makes it significantly tougher and more rigid than PU.
While it feels more "plastic" and does not breathe, its primary advantages are exceptional durability and resistance to water and stains. You will often find PVC in high-traffic commercial seating, automotive interiors, and bags requiring maximum resilience.
The Emerging Category: Bio-Based & "Vegan" Leathers
The term "vegan leather" has gained significant traction, but it's a marketing label, not a technical classification. It's an umbrella term that requires closer inspection.
What "Vegan Leather" Really Means
At its simplest, vegan leather means a material that contains no animal products. This definition includes both the traditional plastic-based PU and PVC leathers.
However, the term is now more commonly used to describe a new generation of materials made partially from plants. These are often positioned as more sustainable alternatives.
Common Plant-Based Sources
These innovative materials use organic matter as a base, which is then typically processed and combined with a polymer binder (often polyurethane) to create a durable sheet.
Popular examples include leathers derived from pineapple leaves (Piñatex), apple peels, cacti, and mushrooms (mycelium). They offer a unique story but share many practical trade-offs with their fully plastic cousins.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a leather alternative involves balancing cost, appearance, and performance. Each material comes with inherent limitations that are critical to understand.
Durability and Longevity
Unlike genuine leather which develops a patina over time, synthetic leathers degrade. They are prone to peeling, cracking, and delaminating, especially with sun exposure and frequent use. Their lifespan is significantly shorter than that of real leather.
Breathability and Comfort
This is a major performance gap. Both PU and especially PVC are essentially plastic sheets that do not allow air or moisture to pass through. In clothing or on furniture, this can lead to a sticky, sweaty, and uncomfortable feeling.
The Environmental Question
While "vegan" implies ethical or environmental superiority, the reality is complex. PU and PVC are petroleum products that do not biodegrade and can release harmful chemicals during production.
Even plant-based leathers often rely on plastic coatings and binders to achieve durability, which complicates their end-of-life and environmental footprint.
Making the Right Choice for Your Needs
To select the correct material, you must first define your priority.
- If your primary focus is affordability and a soft feel: PU leather offers the closest appearance to real leather for items like jackets and fashion accessories at a low cost.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and water resistance: PVC-based leather is the toughest and easiest-to-clean option, ideal for high-wear applications.
- If your primary focus is using renewable resources: Investigate specific plant-based leathers, but be sure to research the binders and coatings they use to understand their full environmental impact.
Understanding these material differences allows you to look past marketing terms and choose the right leather alternative based on performance, longevity, and principle.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| PU Leather | Soft, flexible, affordable, mimics real leather well | Fashion accessories, clothing, soft upholstery |
| PVC Leather | Very durable, water-resistant, rigid, less breathable | Commercial seating, automotive interiors, heavy-duty bags |
| Vegan Leather | No animal products; includes plant-based & plastic types | Fashion, accessories (varies by specific material) |
Need a reliable partner for high-quality footwear production?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Whether your design calls for the soft feel of PU, the rugged durability of PVC, or innovative sustainable materials, we have the production capabilities to bring your vision to life.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific material and production requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Factory Direct Wholesale Leather Comfort Shoes with Dial Closure
- Wholesale Leather Business Casual Shoes with Dial Closure - Manufacturer of Comfort Dress Sneakers
- Custom Manufactured Air Cushion Leather Business Shoes for Wholesale
- Classic Leather Derby Dress Shoes Wholesale & Custom Manufacturing
- Wholesale Comfort Leather Business Shoes with Dial Lacing System
People Also Ask
- What is the importance of understanding different types of leather for shoes? A Guide to Quality & Durability
- How should business casual shoes be maintained? A Proactive System for Longevity & Style
- How does top-grain leather differ from full-grain? Choose the Right Leather for Your Products
- What should be known about genuine leather for shoes? Don't Be Misled by the Label
- How does leather compare to other shoe materials in terms of durability and comfort? A Material Guide for Footwear



















