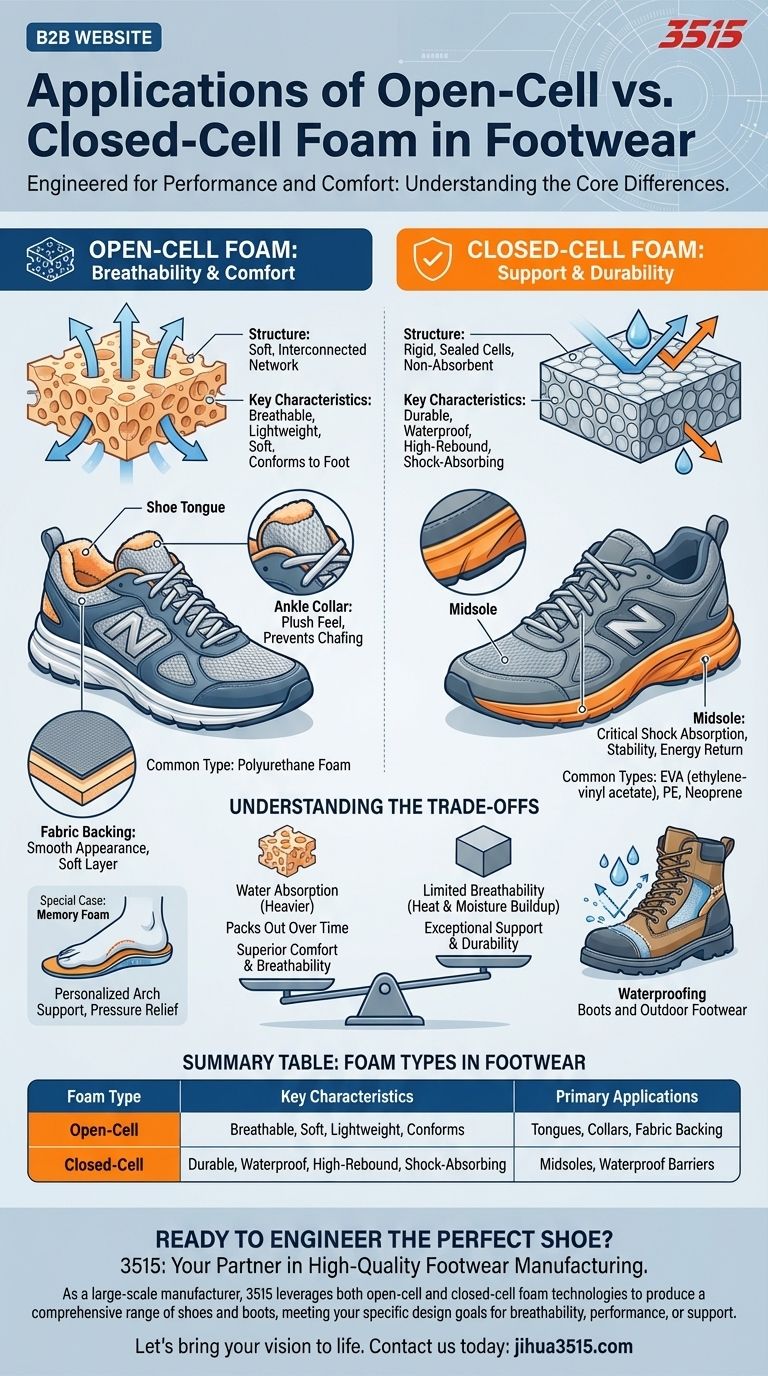
In footwear design, the choice between open-cell and closed-cell foam is a critical engineering decision that dictates a shoe's performance and feel. Open-cell foam is primarily used for breathable comfort in areas like the shoe's tongue and collar, while dense, closed-cell foam provides structural support, shock absorption, and waterproofing in components like the midsole.
The fundamental difference lies in structure: open-cell foam is a breathable sponge built for comfort, while closed-cell foam is a durable, non-absorbent barrier built for performance and protection.
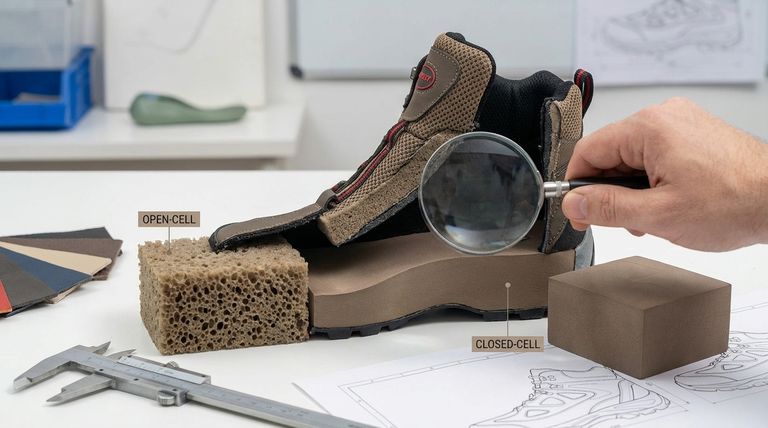

The Role of Open-Cell Foam: Breathability and Comfort
Open-cell foam functions like a soft, interconnected network of tiny pockets. Its structure allows air, moisture, and vapor to pass through easily.
How Open-Cell Foam Works
The cells within this foam are not fully sealed, creating a sponge-like material. This makes it exceptionally soft, lightweight, and breathable. The most common type used in shoes is polyurethane foam.
Application: Tongues and Collars
The plush, cushioned feel in a shoe's tongue and ankle collar comes from open-cell foam. Its softness prevents chafing and conforms to the unique shape of your foot, providing immediate comfort.
Application: Fabric Backing
This foam is often bonded to the back of upper materials. It provides a soft layer against the foot and helps fabrics, especially thin textiles, maintain a smooth, wrinkle-free appearance.
The Power of Closed-Cell Foam: Support and Durability
Closed-cell foam is defined by its sealed, individual gas-filled cells. This structure makes the material far more rigid, durable, and resistant to water.
How Closed-Cell Foam Works
Because its cells are not interconnected, gas cannot escape when compressed. This gives the foam high-rebound properties and prevents it from absorbing liquid. Common types include EVA (ethylene-vinyl acetate), PE (polyethylene), and neoprene.
Application: Midsoles
The midsole is the engine of a performance shoe, and it is almost always made from closed-cell foam like EVA. Its dense structure provides critical shock absorption, stability, and energy return with every step.
Application: Waterproofing
The non-absorbent nature of closed-cell foam makes it an ideal material for creating a waterproof barrier in boots and outdoor footwear, keeping the foot dry from external moisture.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect; the choice of foam always involves balancing competing priorities. Understanding these compromises is key to evaluating a shoe's design.
Open-Cell: Comfort vs. Water Absorption
While incredibly comfortable and breathable, open-cell foam will act like a sponge when exposed to water, becoming heavy and slow to dry. Over time and with repeated compression, it can also "pack out" and lose its cushioning.
Closed-Cell: Support vs. Breathability
The same structure that makes closed-cell foam durable and waterproof also means it is not breathable. This is why it's used for structural components like the midsole, not for parts that wrap directly around the foot where heat and moisture management are critical.
The Case of Memory Foam
Memory foam is a specific type of high-density open-cell polyurethane foam. It excels at adapting to the user's specific foot shape, providing personalized arch support and pressure relief, making it a popular choice for insoles and comfort-oriented shoes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
By understanding these materials, you can better assess if a shoe is truly designed for your specific needs.
- If your primary focus is all-day comfort and breathability: Look for shoes with a generously padded tongue and collar, which signals a focus on open-cell foam for cushioning.
- If your primary focus is athletic performance and durability: The composition and design of the closed-cell foam midsole is the most important factor for support and longevity.
- If your primary focus is pain relief or custom support: Consider shoes that specifically feature memory foam insoles or liners for their unique, adaptive properties.
Understanding these materials empowers you to look beyond marketing and choose footwear based on genuine engineering and its intended function.
Summary Table:
| Foam Type | Key Characteristics | Primary Applications in Footwear |
|---|---|---|
| Open-Cell | Breathable, soft, lightweight, conforms to foot shape | Shoe tongues, ankle collars, fabric backing for comfort |
| Closed-Cell | Durable, waterproof, high-rebound, shock-absorbing | Midsoles for support, athletic performance, waterproof barriers |
Ready to engineer the perfect shoe?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of shoes and boots, leveraging both open-cell and closed-cell foam technologies to meet your specific design goals—whether you prioritize breathable comfort, athletic performance, or durable support.
Let’s bring your vision to life. Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how we can deliver high-quality, tailored footwear solutions for your market.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Durable Rubber-Soled Utility Shoes for Wholesale & Custom Brand Manufacturing
- Advanced KPU Athletic Safety Shoe with Steel Toe Cap Anti-Slip Rotary Lacing System
- Premium KPU Injection Athletic Style Safety Shoes
- Wholesale Safety Footwear Manufacturer for Bulk & Custom OEM Orders
People Also Ask
- How do specialized foot sensors function in gait assessments? High-Precision Data for Ataxia Gait Analysis
- What role do high-strength fixation straps play in isokinetic testing? Unlock Data Purity and Accurate Muscle Assessment
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of artificial leather? A Guide to Making the Right Material Choice
- What are the notable qualities of brand fabrics? Engineered for Superior Durability & Performance
- Why is it necessary to configure a voltage divider for Hull Piezoelectric Energy Harvesters? Protect Your DAQ Equipment
- What role does computer-aided gait analysis software play in processing footwear data? Accelerating Design Innovation
- How have boots evolved from their original purpose? From Utility to Status Symbol
- What outfit can help men stand out and draw attention? The Power of a Blazer



















