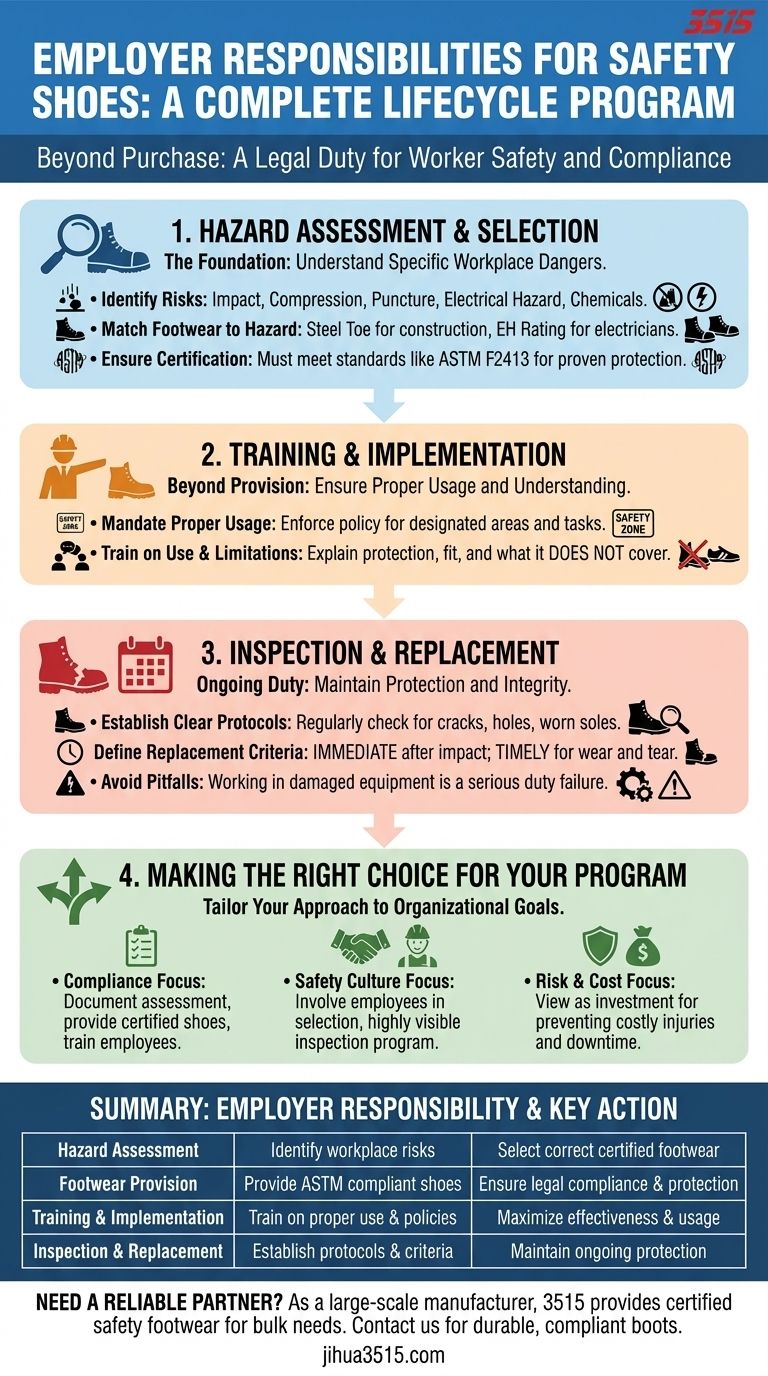
An employer's responsibility for safety shoes is a comprehensive legal duty that extends far beyond the initial purchase. It involves a complete safety lifecycle, including assessing workplace risks, providing certified and appropriate footwear, training employees on its use and limitations, and actively managing its inspection and replacement.
The core responsibility is not merely to provide safety shoes, but to implement and manage a complete protective footwear program. This transforms the task from a simple transaction into an ongoing commitment to worker safety and regulatory compliance.

The Foundation: Hazard Assessment and Selection
The entire safety footwear program rests on a thorough understanding of the specific dangers present in your work environment. Providing the wrong type of shoe can be as dangerous as providing none at all.
Conducting a Thorough Hazard Assessment
Before any footwear is selected, employers must perform a detailed hazard assessment. This process identifies the specific risks employees face that necessitate protective footwear.
Key hazards include impact from falling objects, compression from rolling equipment, punctures from sharp objects on the ground, and exposure to electrical currents, chemicals, or extreme temperatures.
Matching Footwear to the Specific Hazard
The results of the assessment directly dictate the type of footwear required. A "one-size-fits-all" approach is rarely compliant or effective.
For example, a construction site may require shoes with steel toes for impact protection and puncture-resistant soles. An electrician, however, needs footwear with an electrical hazard (EH) rating to protect against shock.
Ensuring Proper Certification
Employers must provide footwear that meets established safety standards. In the United States, this typically means complying with standards set by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), such as ASTM F2413.
Certified footwear is clearly marked, indicating the specific hazards it is designed to protect against. This certification is a non-negotiable proof of protection.
Beyond Provision: Training and Implementation
Providing the correct equipment is only half the responsibility. Employees must understand how and when to use it, as well as its limitations.
Mandating Proper Usage
Employers must create and enforce a policy requiring employees to wear protective footwear in all designated areas or during all specified tasks. This policy should be clearly communicated to every worker.
Training on Use and Limitations
Effective training covers more than just telling employees to wear the shoes. It must explain what the footwear protects against and, just as importantly, what it does not protect against.
Employees should also be instructed on how to properly put on and take off their footwear to ensure maximum protection and comfort.
The Ongoing Duty: Inspection and Replacement
Protective footwear is not a permanent solution; it is equipment that degrades over time and after incidents. A program is only effective if it includes clear protocols for maintenance and replacement.
Establishing Clear Inspection Protocols
Employers are responsible for ensuring footwear remains in good condition. This involves training employees to inspect their shoes regularly for signs of wear and tear.
Look for issues like cracks, holes, worn-out soles, or an exposed protective toe cap. Any damage compromises the shoe's protective capabilities.
Defining Replacement Criteria
A clear replacement policy is essential. Footwear should be replaced immediately if it sustains a significant impact or compression, even if no damage is visible.
Furthermore, shoes should be replaced when they show signs of excessive wear, as their structural integrity may be compromised. Establishing a general timeframe for replacement based on work conditions is also a best practice.
The Pitfall of Neglecting Damaged Equipment
Allowing an employee to work in damaged safety shoes is a serious failure of an employer's duty. It creates a false sense of security and exposes both the worker and the company to significant risk.
Making the Right Choice for Your Program
A compliant and effective safety footwear program is a critical component of any workplace safety plan. Your specific approach should be tailored to your primary organizational goals.
- If your primary focus is basic legal compliance: Ensure you perform and document a hazard assessment, provide certified ASTM-compliant footwear at no cost to employees, and train them on its use.
- If your primary focus is building a proactive safety culture: Go beyond compliance by involving employees in the selection process to improve comfort and fit, and implement a highly visible and easy-to-use inspection and replacement program.
- If your primary focus is minimizing long-term risk and cost: View the footwear program as an investment, understanding that proper maintenance and timely replacement prevent costly injuries, downtime, and potential litigation.
Ultimately, a well-managed safety footwear program is a fundamental investment in the well-being of your people and the resilience of your organization.
Summary Table:
| Employer Responsibility | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Hazard Assessment | Identify workplace risks (impact, puncture, electrical, etc.) | Select the correct type of certified footwear |
| Footwear Provision | Provide ASTM F2413 compliant shoes at no cost to employees | Ensure basic legal compliance and protection |
| Training & Implementation | Train on proper use, limitations, and mandatory wear policies | Maximize effectiveness and correct usage |
| Inspection & Replacement | Establish protocols for regular checks and timely replacement | Maintain ongoing protection and program integrity |
Need a reliable partner for your safety footwear program?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of certified safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. We help you meet your employer responsibilities with durable, compliant boots and shoes tailored to your specific workplace hazards.
Contact us today to discuss your bulk procurement needs and ensure your workforce is fully protected.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Premium Waterproof High-Cut Industrial Safety Boots for Wholesale and Bulk Orders
- Wholesale Premium Waterproof Nubuck Safety Shoes Boots
- Wholesale Durable 6-Inch Work Boots | Custom & Private Label Manufacturer
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Advanced KPU Athletic Safety Shoe with Steel Toe Cap Anti-Slip Rotary Lacing System
People Also Ask
- What do the slip resistance certifications SRA, SRB, and SRC indicate? Choose the Right Safety Footwear
- Why is laboratory-grade pressure testing equipment indispensable? Ensure High-Performance Safety Footwear Standards
- What are penetration-resistant insoles in safety footwear? Steel vs. Textile for Ultimate Protection
- Why are composite toe boots suitable for FIFO workers and frequent travelers? Unlock Hassle-Free Travel & Superior Safety
- How does the structured support design in safety shoes protect high-risk individuals? Optimize Foot Health & Safety
- How do integrated sensor systems contribute to the objective measurement of wearable industrial products? Unlock Verifiable Performance and Safety.
- Can composite toe shoes be used after an accident? No, Here's the Critical Safety Rule
- How is abrasion resistance tested in motorcycle boots? Learn the CE EN 13634 Safety Standards



















