Under specific conditions, yes. Prolonged barefoot walking, particularly on unyielding hard surfaces, can directly contribute to the formation and acceleration of foot deformities like bunions and hammertoes. It achieves this by forcing your foot into an unstable and mechanically unsound position, which over time, places progressive stress on the joints of the forefoot.
The fundamental issue is not walking barefoot, but walking barefoot on modern hard, flat surfaces. This environment forces the foot to over-flatten and pronate excessively, destabilizing the forefoot and creating the precise mechanical stresses that lead to conditions like bunions and hammertoes.

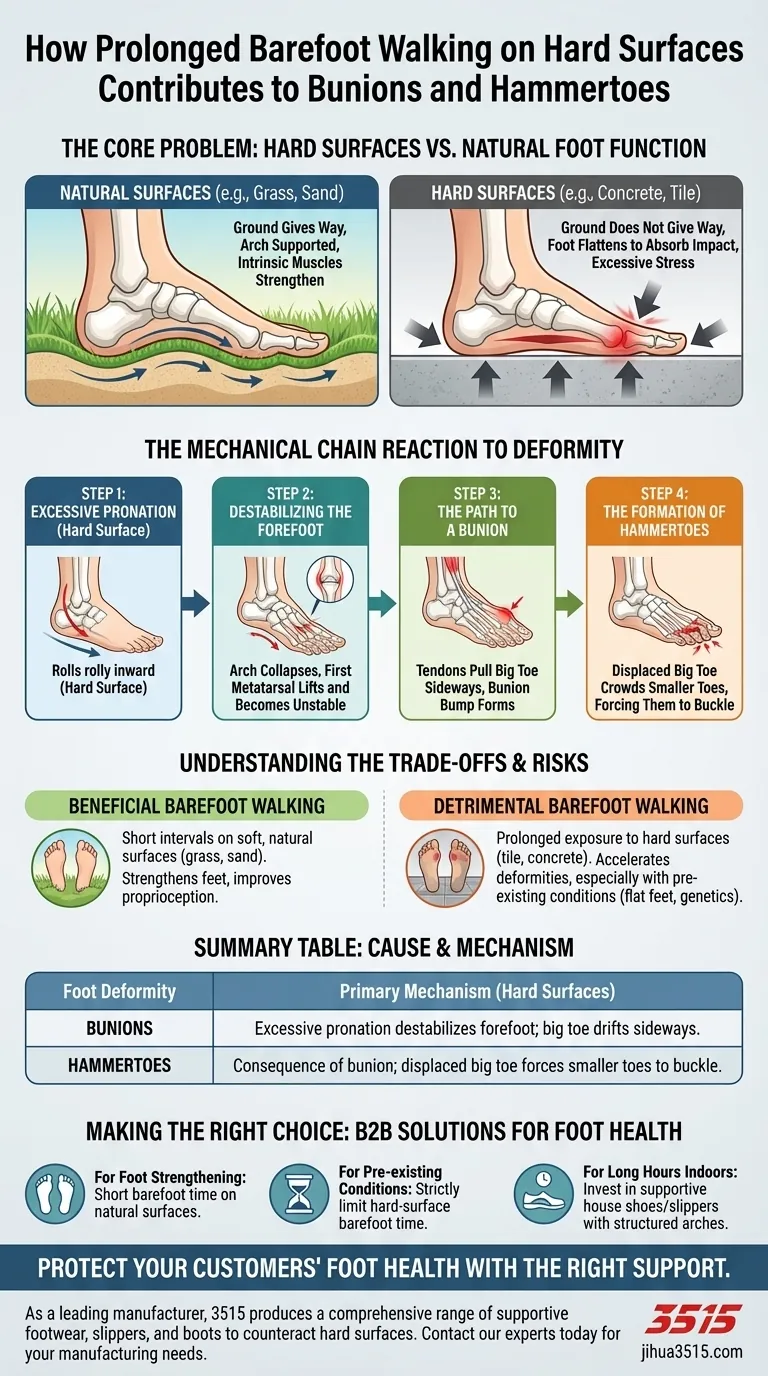
The Core Problem: Hard Surfaces vs. Natural Foot Function
To understand why this happens, we must first appreciate the environment our feet were designed for versus the one they now inhabit.
How Your Foot is Designed to Work
Your foot's arch is a natural shock absorber. On soft, uneven surfaces like soil or sand, the ground gives way, and your foot can adapt, strengthening the small intrinsic muscles that support its structure.
The Impact of Hard, Flat Surfaces
Modern surfaces like concrete, tile, and hardwood do not give way. When you walk on them barefoot, your foot is forced to absorb all the impact. To do this, it flattens out dramatically with every step.
The Mechanical Chain Reaction to Deformity
This constant flattening on hard surfaces sets off a predictable chain reaction that leads to structural changes in the foot.
Step 1: Excessive Pronation
Pronation is the natural inward rolling motion of your foot as you walk. However, on hard surfaces, this motion becomes excessive and prolonged. The arch collapses more than it should, for longer than it should.
Step 2: Destabilizing the Forefoot
This excessive pronation turns your foot from a rigid lever into an unstable structure. Crucially, it causes the bone behind the big toe (the first metatarsal) to lift and become unstable.
Step 3: The Path to a Bunion
With the first metatarsal unstable, the powerful tendons pulling on the big toe can no longer hold it straight. Instead, they begin to pull it sideways, towards the second toe. The characteristic "bunion bump" is the head of that unstable metatarsal bone pushing out from the side of the foot.
Step 4: The Formation of Hammertoes
Hammertoes are often a direct consequence of a developing bunion. As the big toe drifts sideways, it crowds the smaller toes, especially the second toe. This pressure can force the smaller toes to buckle at their middle joint, creating the classic "hammer" shape.
Understanding the Trade-offs
It's critical to note that the issue is nuanced. Not all barefoot walking is detrimental to your foot health.
The Myth of "Always Bad"
Walking barefoot on soft, natural surfaces like grass or sand can be highly beneficial. It helps strengthen the small muscles in your feet and improves your sense of balance and body awareness (proprioception).
The Role of Pre-existing Conditions
The negative effects are significantly worse for individuals who already have faulty biomechanics, such as flat feet or a genetic predisposition to bunions. For these people, walking barefoot on hard floors acts as a powerful accelerant for these conditions.
Duration and Surface Are Key
The primary risk comes from prolonged exposure to hard surfaces. Walking from the bedroom to the bathroom barefoot is not the issue. The problem arises from spending hours every day walking or standing on tile, concrete, or hardwood floors without any support.
Making the Right Choice for Your Foot Health
You can mitigate the risks by matching your footwear (or lack thereof) to your environment and personal biomechanics.
- If your primary focus is strengthening your feet: Enjoy barefoot time in short intervals on soft, natural surfaces like grass or sand.
- If you have existing foot pain, flat feet, or a family history of bunions: Strictly limit barefoot time on hard surfaces and consider supportive footwear even inside the home.
- If you spend long hours at home on hard floors: Invest in a pair of supportive house shoes or slippers with a structured arch to neutralize the harmful forces.
Ultimately, understanding the interplay between your foot's mechanics and your environment is the key to preventing long-term structural problems.
Summary Table:
| Foot Deformity | Primary Cause from Barefoot Walking | Key Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Bunions | Prolonged walking on hard, flat surfaces | Excessive pronation destabilizes the forefoot, causing the big toe to drift sideways. |
| Hammertoes | Often a consequence of a developing bunion | The displaced big toe crowds and forces the smaller toes to buckle at the joints. |
Protect your customers' foot health with the right support. As a leading manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of supportive footwear, slippers, and boots designed to counteract the harmful effects of hard surfaces. Whether you are a distributor, brand owner, or bulk client, we can help you provide products that promote proper foot mechanics and prevent deformities. Contact our experts today to discuss your manufacturing needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Premium KPU Athletic Safety Shoes for Wholesale
- Custom Safety Shoe Manufacturer for Wholesale & OEM Brands
- Wholesale Breathable Training Shoes Custom Athletic Footwear Manufacturer
- Durable Rubber-Soled Utility Shoes for Wholesale & Custom Brand Manufacturing
- Wholesale Leather Safety Boots with Customizable Protective Toe
People Also Ask
- Why are ultrasonic sensors typically utilized as core detection components in smart obstacle-avoidance boots?
- What are the core advantages of smart wearable plantar pressure monitoring systems? Unleash Real-World Gait Analysis
- How do shape memory polymers improve movement analysis accuracy? The Key to Precision in Wearable Footwear
- Why is it critical to place infrared markers at the 2nd-3rd metatarsal head? Key for Precise Foot Motion Analysis
- How does virtual sampling technology reduce environmental impact in footwear R&D? Transition to Green Footwear Design
- How does Surface Electromyography (EMG) contribute to shoe design? Engineer Peak Performance with Data-Driven Biomechanics
- What is the primary function of an optical 3D motion capture system? Mastering High-Precision Gait Evaluation
- What are the primary reasons for selecting high-grade thermoplastic polyolefin foam? Enhance Orthotic Precision & Comfort



















