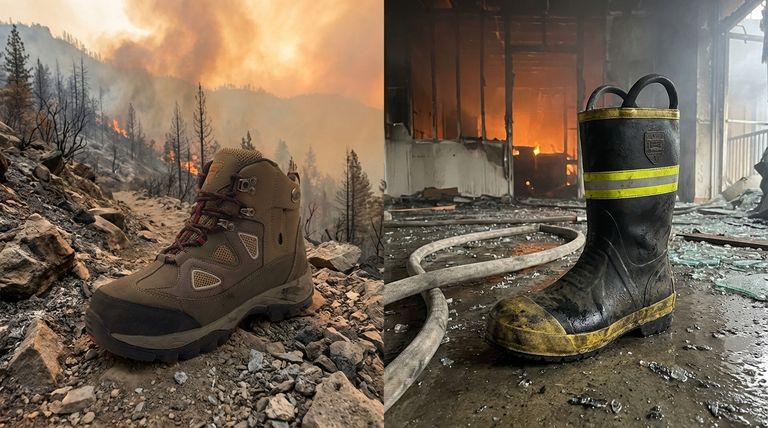
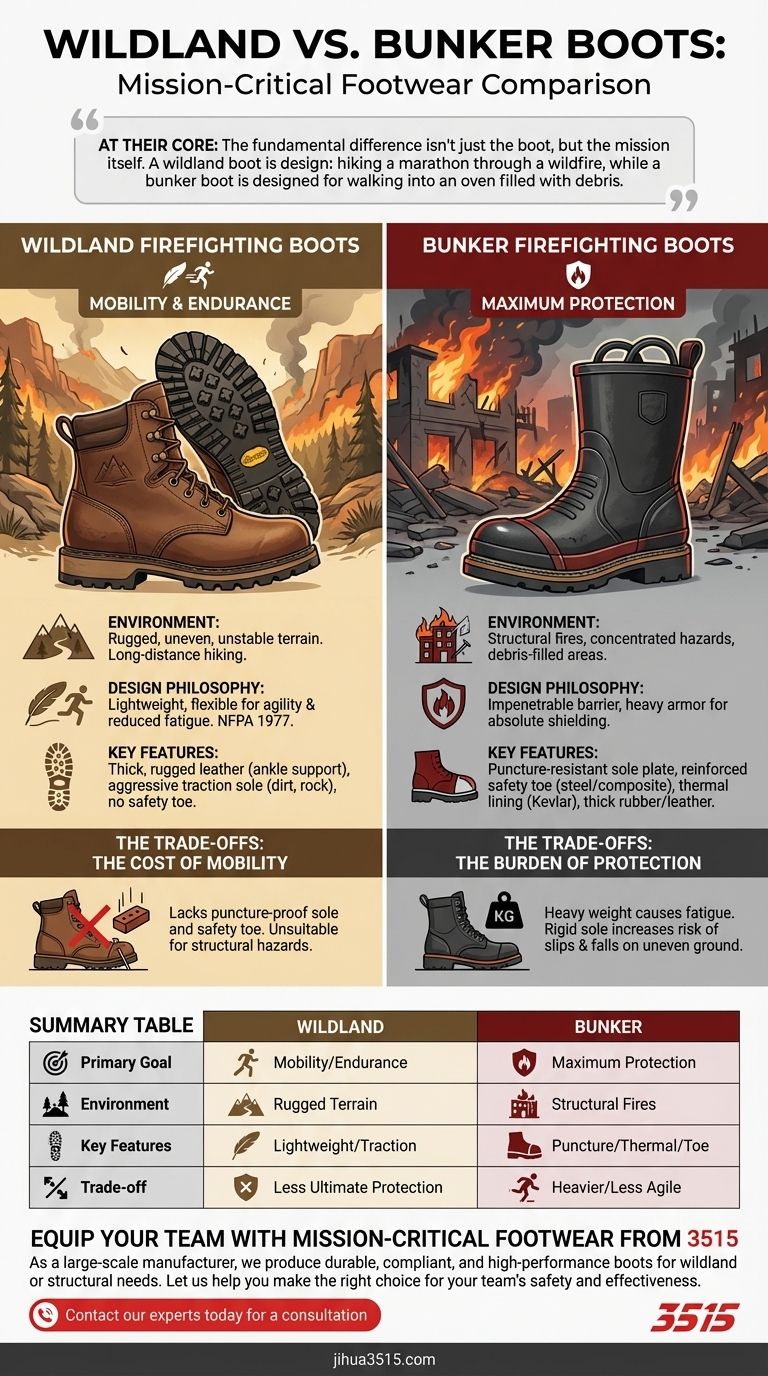
At their core, wildland firefighting boots are engineered for mobility and endurance over rugged terrain, while traditional bunker boots are built as heavy armor for maximum protection in structural fires. Wildland boots are essentially specialized, heavy-duty hiking boots designed to resist heat and support the foot over long distances, whereas bunker boots prioritize shielding firefighters from extreme heat, falling objects, and puncture hazards in urban environments.
The fundamental difference isn't just the boot, but the mission itself. A wildland boot is designed for hiking a marathon through a wildfire, while a bunker boot is designed for walking into an oven filled with debris.

The Tale of Two Battlefields
The design of each boot is a direct response to its intended environment. The hazards faced on a remote mountainside are fundamentally different from those inside a burning building.
The Wildland Environment: Unpredictable Terrain
Wildland firefighters operate on steep, uneven, and often unstable ground for extended periods. They cover miles on foot, carrying heavy packs.
Their primary threats are ambient heat from the fire, sharp rocks, and the physical exhaustion and potential for injury that comes with hiking on difficult terrain for 12-hour shifts.
The Structural Environment: Concentrated Hazards
Structural firefighters face extreme, concentrated hazards in a small area. They operate on surfaces that may be slick with water, littered with nails and glass, or at risk of collapse.
Their greatest threats are intense radiant heat, direct flame contact, punctures from debris, impacts from falling objects, and exposure to water and hazardous chemicals.
Design Philosophy: Mobility vs. Armor
Because the environments are so different, the boots are engineered with opposing priorities. One values agility and stamina; the other values absolute protection.
Wildland Boots: Built for the Hike
The construction of a wildland boot, which must meet NFPA 1977 standards, focuses on durability and support for movement.
They are typically made of thick, rugged leather to provide ankle support and resist abrasions.
Their soles, often made by Vibram, are designed for aggressive traction on dirt, rock, and ash, much like a high-end hiking boot.
The design prioritizes being lightweight and somewhat flexible to reduce fatigue and allow for a natural stride over long distances.
Bunker Boots: Built for the Breach
Bunker boots are focused on creating an impenetrable barrier between the firefighter and the hazardous environment.
They are often made of thick rubber or treated leather with integrated Kevlar linings for thermal and cut protection.
Key features include puncture-resistant sole plates and reinforced safety toes (steel or composite) to guard against nails and crushing impacts.
Their primary function is to offer the highest possible resistance to extreme heat and direct flame contact, making them much heavier and more rigid than their wildland counterparts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither boot is inherently "better"; they are specialized tools, and using the wrong one can be ineffective and dangerous.
The Cost of Mobility
A wildland boot's flexibility and lighter weight come at the cost of ultimate protection. It lacks a puncture-proof sole and a safety toe, making it completely unsuitable for a structural fire where nails and falling debris are common.
The Burden of Protection
A bunker boot's heavy armor is a significant liability in a wildland setting. The weight would cause rapid fatigue, and the stiff, flat sole is poorly suited for navigating steep or uneven ground, dramatically increasing the risk of slips, falls, and ankle injuries.
Making the Right Choice for Your Mission
The correct boot is always the one designed for the specific hazards you will face.
- If your primary focus is wildland firefighting: You need a boot that provides superior traction, ankle support, and lightweight durability for long hours on unpredictable terrain.
- If your primary focus is structural firefighting: You must have a boot that offers maximum thermal protection and guards against punctures and impacts in hazardous, man-made environments.
Ultimately, choosing the right footwear is a critical decision that directly impacts a firefighter's safety and operational effectiveness.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Wildland Boots (NFPA 1977) | Bunker Boots (Structural) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Mobility & Endurance | Maximum Protection |
| Environment | Rugged, uneven terrain | Structural fires, debris-filled areas |
| Key Features | Lightweight, flexible, hiking boot traction | Puncture-resistant sole, safety toe, thermal lining |
| Trade-off | Less ultimate protection | Heavier, less agile |
Equip Your Team with Mission-Critical Footwear from 3515
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of professional-grade footwear. Whether you are a distributor, brand owner, or bulk client requiring specialized boots for wildland or structural firefighting, our production capabilities ensure durability, compliance, and performance.
Let us help you make the right choice for your team's safety and effectiveness.
Contact our experts today for a consultation to discuss your specific needs and explore our full product catalog.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Wholesale Safety Footwear Manufacturer for Bulk & Custom OEM Orders
- Wholesale Customizable Safety Boots Durable & Protective Footwear Manufacturing
- Durable Rubber Sole Outdoor Shoes Wholesale & Custom Manufacturing
- Heavy Duty Nubuck Safety Boots Safety Shoes for Global Distribution
People Also Ask
- Are water-resistant and water-repellent boots the same? A Guide to Choosing the Right Footwear
- Why are packer boots considered an investment? Unlock Decades of Durability & Performance
- Why is proper fit crucial for firefighters' footwear? Avoid Injury and Boost Performance
- Why is it important to dry winter boots after use? Protect Your Feet & Extend Boot Life
- How do specialized industrial work boots or training shoes help reduce occupational burnout? Improve Worker Resilience
- What are some top choices for durable and stylish engineer boots? Discover the best for long-term wear.
- Why are slip-resistant soles important in mining boots? Prevent Slips and Falls in Hazardous Conditions
- Are zippers common in cowboy boots? The Truth About Authentic vs. Modern Western Boots



















