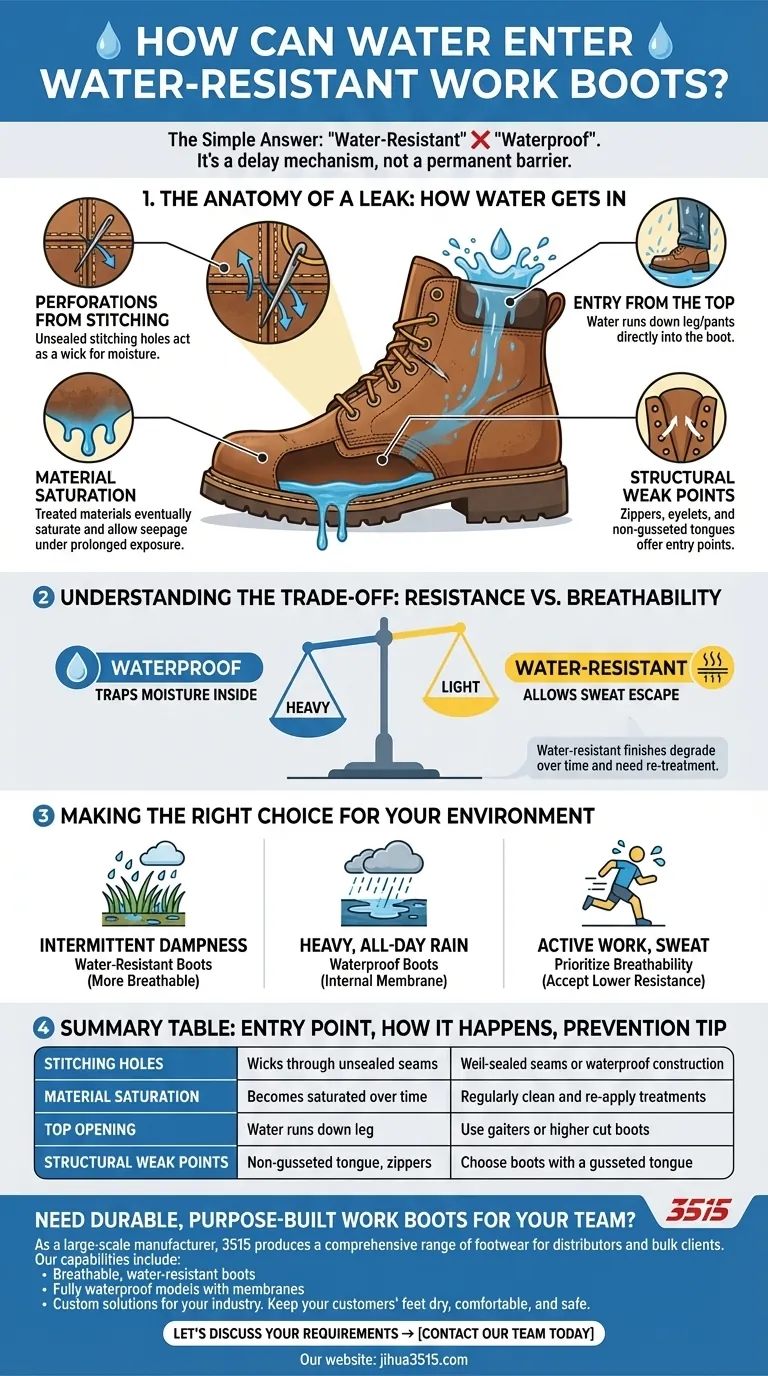
The simple answer is that "water-resistant" is not waterproof. Water can penetrate work boots through unsealed stitching holes created during manufacturing, by saturating the leather or fabric after prolonged exposure, or by simply entering through the top opening of the boot.
The core issue lies in a misunderstanding of the term "water-resistant." It signifies a material's ability to delay water penetration from splashes or light rain, not a permanent, impenetrable barrier designed for submersion or heavy, sustained downpours.
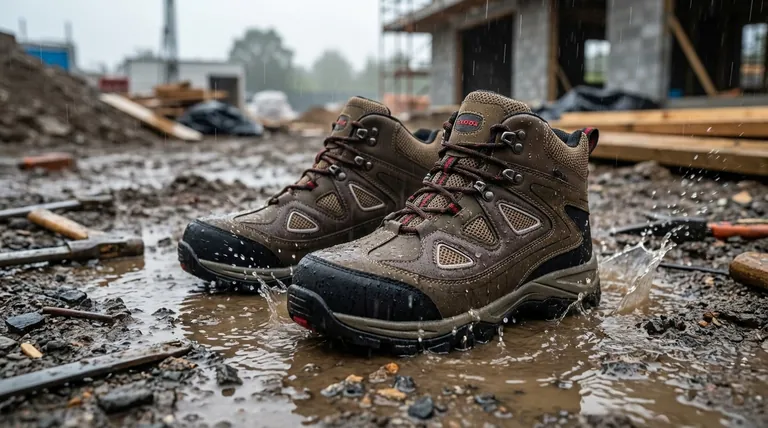

The Anatomy of a Leak: How Water Gets In
Even a brand-new pair of water-resistant boots has inherent vulnerabilities. Understanding these points of failure is key to managing expectations and choosing the right footwear for the job.
Perforations from Stitching
Every stitch required to assemble a boot creates a tiny hole in the water-resistant material. While manufacturers often try to seal these seams, a perfect seal is not always achieved.
The thread itself can act as a wick, drawing moisture through these holes and into the boot's interior over time.
Material Saturation
Water-resistant materials, like treated leather or coated fabrics, work by repelling water up to a certain point. They are not impermeable.
Under sustained rain or prolonged contact with wet surfaces, the material will eventually become saturated. Once saturated, its ability to resist water is gone, and moisture will begin to seep through.
Entry from the Top
The most common and overlooked entry point has nothing to do with the boot's construction. Water can simply run down your leg or rain pants and drain directly into the top of the boot.
Structural Weak Points
Features like zippers, eyelets, and the tongue area can also be points of entry. A boot with a "gusseted" tongue—one that is attached to the upper along the sides—offers far more protection than a standard, separate tongue.
Understanding the Trade-off: Resistance vs. Breathability
The distinction between water-resistant and waterproof isn't just marketing; it reflects a fundamental design compromise between keeping water out and letting sweat escape.
Why Aren't All Boots Waterproof?
Creating a truly waterproof boot, like a classic rubber wellington, requires a non-porous barrier. This barrier is excellent at stopping water from getting in, but it also traps all moisture inside.
For active work, this means your feet get wet from sweat, leading to blisters, discomfort, and cold in the winter.
The Role of Water-Resistant Finishes
Most water-resistant boots rely on a combination of tightly woven materials or treated leather and a topical coating. These finishes degrade over time with wear, abrasion, and dirt.
This is why a pair of boots that was effective when new may seem to fail after a few months of hard use. They often require cleaning and re-treatment to maintain their resistance.
The Limits of the Technology
As stated, water-resistant footwear is designed to handle incidental and brief exposure to moisture. It should not be submerged for more than a few seconds.
It provides protection when walking through damp grass or getting caught in a brief shower, but it is not intended for standing in puddles or working in a constant downpour.
Making the Right Choice for Your Environment
To keep your feet dry, you must match the boot's technology to the specific challenges of your worksite.
- If your primary focus is working in damp fields or intermittent light rain: A well-maintained, high-quality water-resistant boot is often sufficient and will be more breathable and comfortable.
- If your primary focus is standing in water or working in heavy, all-day rain: You must seek out boots explicitly labeled "waterproof," which typically include an internal waterproof membrane liner.
- If your primary focus is preventing wet feet from your own sweat: Prioritize boots with maximum breathability and understand that this will come at the cost of water resistance.
Ultimately, choosing the right boot is about accurately assessing your daily environment and selecting the tool built for that specific task.
Summary Table:
| Entry Point | How Water Gets In | Prevention Tip |
|---|---|---|
| Stitching Holes | Acts as a wick through unsealed seams. | Look for well-sealed seams or waterproof construction. |
| Material Saturation | Treated leather/fabric becomes saturated over time. | Regularly clean and re-apply water-repellent treatments. |
| Top Opening | Water runs down your leg into the boot. | Use gaiters or boots with a higher cut. |
| Structural Weak Points | Zippers, eyelets, or a non-gusseted tongue. | Choose boots with a gusseted tongue for better protection. |
Need Durable, Purpose-Built Work Boots for Your Team?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of shoes and boots, including:
- Breathable, water-resistant boots for comfort in damp conditions.
- Fully waterproof models with internal membranes for wet environments.
- Custom solutions tailored to your specific industry needs.
We help you provide the right footwear to keep your customers' feet dry, comfortable, and safe, boosting their productivity and satisfaction.
Let's discuss your requirements → Contact Our Team Today
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
- Wholesale Premium Waterproof Nubuck Safety Shoes Boots
- Premium Wholesale Waterproof Safety Boots High Performance Protection for Industrial Markets
- Durable Waterproof Rain Boots | Custom Manufacturer for Wholesale & Brands
People Also Ask
- What are the primary protective functions of composite-toe boots? A Guide to Modern Safety Footwear
- What materials are used for safety toes? Choose Steel, Composite, or Aluminum for Your Work Boots
- What are the cultural perspectives on wearing shoes in the house? A Guide to Home Etiquette & Hygiene
- How do safety shoes contribute to cost savings for companies? A Strategic Investment in Risk and Cost Management
- Can heavy duty work boots be worn daily outside of work? Discover Durable, All-Day Comfort



















