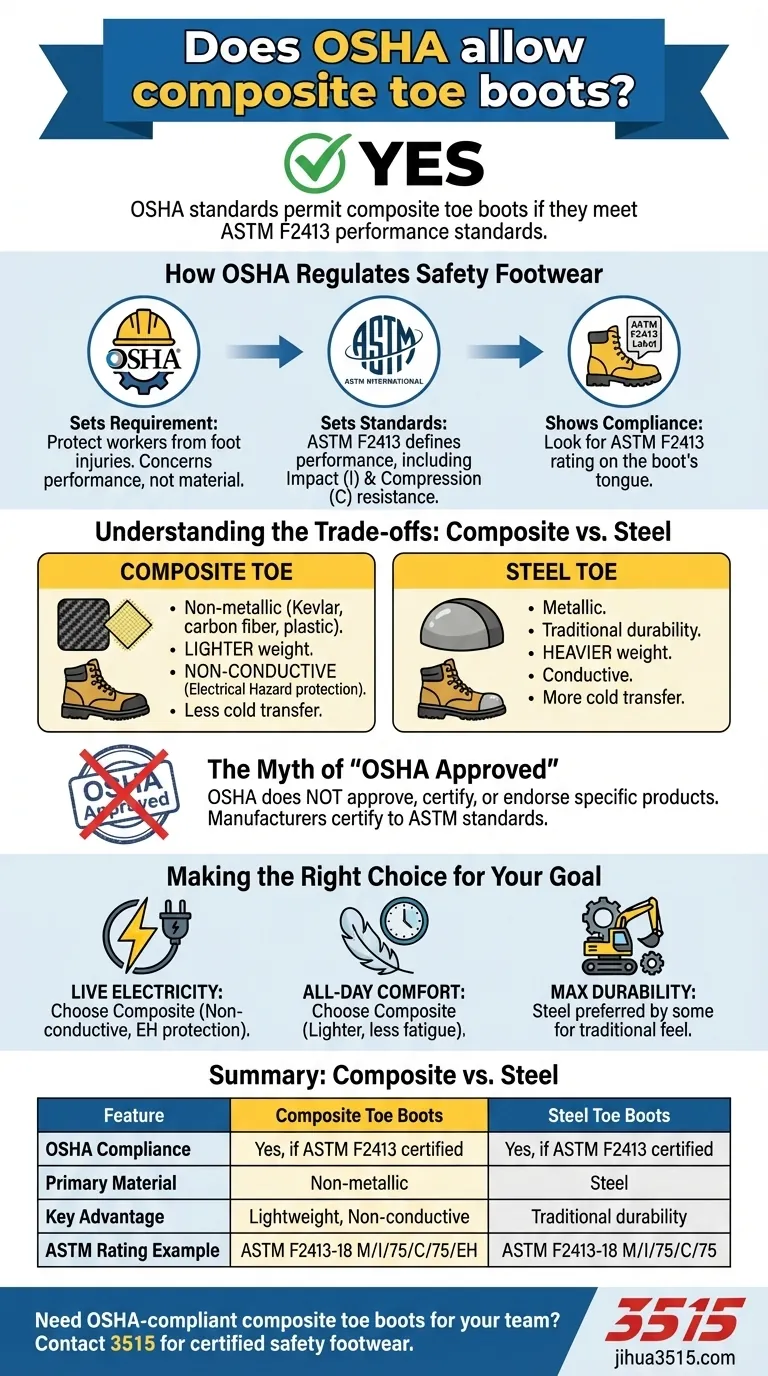
Yes, OSHA standards permit the use of composite toe boots. However, the critical detail is that OSHA does not approve specific materials, but rather sets performance standards that protective footwear must meet. As long as a composite toe boot meets the required ASTM International standard for impact and compression resistance, it is considered OSHA-compliant.
The core issue is not about the material of the toe cap—be it composite, steel, or alloy—but about its certified performance. OSHA requires that safety footwear meets the specific hazard protection standards laid out by ASTM F2413, making the boot's official rating the only thing that matters for compliance.

How OSHA Regulates Safety Footwear
Understanding the relationship between OSHA and ASTM is key to selecting the right protective footwear and ensuring you are truly compliant and safe.
OSHA Sets the Requirement, Not the Material
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) mandates that employers protect workers from foot injuries. The relevant regulation requires protective footwear in workplaces where there is a danger of foot injuries due to falling or rolling objects, or objects piercing the sole.
Critically, OSHA does not specify what material the protective toe cap must be made from. Their concern is performance, not construction.
The Role of ASTM Standards
To define what constitutes adequate performance, OSHA defers to standards developed by ASTM International. The primary standard for safety footwear is ASTM F2413.
This standard establishes the minimum requirements for the design, performance, testing, and classification of protective footwear. It includes tests for impact resistance (I) and compression resistance (C) for the toe area.
Reading the Safety Label
Compliant boots will have a label, typically on the tongue, that specifies the ASTM standard it meets. A typical label will read something like: ASTM F2413-18 M/I/75/C/75/EH.
- ASTM F2413-18: Indicates the boot meets the 2018 version of the standard.
- M/I/75: Identifies it's for a male (M) and the toe cap meets the highest impact rating (75 foot-pounds).
- C/75: Means the toe cap meets the highest compression rating (75, or 2,500 pounds).
- EH: Indicates the boot provides Electrical Hazard protection, a common feature of composite toe boots.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a boot isn't just about compliance; it's about matching the boot's features to your specific work environment. Both composite and steel toe caps that meet the same ASTM rating offer equivalent protection against impact and compression. The differences lie in their secondary characteristics.
Why Choose Composite Toe?
Composite toe caps are made from non-metallic materials like Kevlar®, carbon fiber, or plastic. This construction gives them a key advantage in certain environments.
Because they do not conduct electricity, they are the preferred choice for electricians and engineers working in environments with live electrical hazards. They are also lighter than steel and do not transfer cold as readily in winter conditions.
The Myth of "OSHA Approved"
It is a common misconception that OSHA "approves" specific brands or models of equipment. OSHA does not approve, certify, or endorse any products.
Instead, manufacturers are responsible for ensuring their products meet the required standards. A boot that is certified to meet ASTM F2413 is what OSHA requires for compliance. Look for the ASTM rating, not an "OSHA Approved" stamp.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your job's specific hazards should always dictate your choice of footwear.
- If your primary focus is working around live electricity: Composite toe is the clear choice, as it provides electrical hazard (EH) protection without conducting electricity.
- If your primary focus is all-day comfort and mobility: Composite toe is often preferred for its lighter weight, which can reduce fatigue over a long shift.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability in heavy industrial settings: While both meet the standard, some users prefer the traditional feel and perceived resilience of a steel toe for extreme physical work.
Ultimately, selecting the right boot begins with understanding the specific risks of your job and verifying the footwear has the corresponding ASTM certification.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Composite Toe Boots | Steel Toe Boots |
|---|---|---|
| OSHA Compliance | Yes, if ASTM F2413 certified | Yes, if ASTM F2413 certified |
| Primary Material | Non-metallic (e.g., Kevlar®, carbon fiber) | Steel |
| Key Advantage | Lightweight, non-conductive (ideal for electrical hazards) | Traditional durability |
| ASTM Rating Example | ASTM F2413-18 M/I/75/C/75/EH | ASTM F2413-18 M/I/75/C/75 |
Need OSHA-compliant composite toe boots for your team? As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of certified safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our boots meet ASTM F2413 standards and are designed for comfort, durability, and hazard protection. Let us help you equip your workforce with the right safety solution—contact us today for custom orders and bulk pricing!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Premium KPU Injection Athletic Style Safety Shoes
- Wholesale Safety Footwear Manufacturer for Bulk & Custom OEM Orders
- High Performance Fire-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots
- Wholesale Anti-Smash & Puncture-Proof Safety Shoes Custom Manufacturing for Brands
People Also Ask
- Is it normal to wear shoes in the house? A Guide to Hygiene, Comfort & Culture
- How do safety shoes contribute to cost savings for companies? A Strategic Investment in Risk and Cost Management
- What cultural and environmental considerations are tied to wearing shoes indoors? Balance Hygiene, Tradition, and Foot Health
- What are the cultural perspectives on wearing shoes in the house? A Guide to Home Etiquette & Hygiene
- What are the differences between steel toe, composite toe, and alloy toe Wellington boots? Choose the Right Safety Toe for Your Job



















