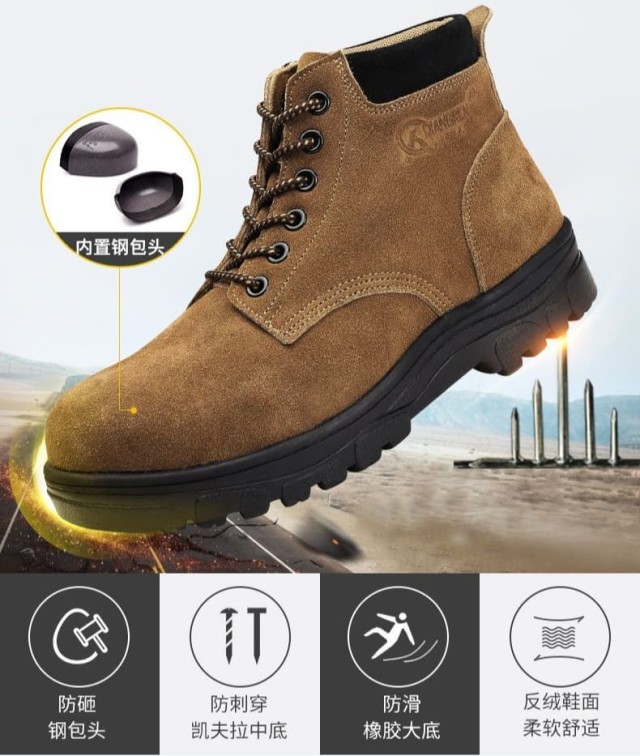
When every step in an oilfield presents potential hazards—from heavy falling objects to electrical currents—your boots become the first line of defense. This guide breaks down the critical safety standards (OSHA, ASTM, ANSI) that govern oilfield work boots, their real-world impact on injury prevention, and how to select compliant footwear that keeps workers protected.
Oilfield Boot Safety Standards Decoded
The Role of OSHA in Hazardous Environments
OSHA sets the baseline for workplace safety but doesn’t prescribe specific boot designs. Instead, it mandates that employers provide footwear meeting ASTM standards when hazards like electrical exposure or crushing risks exist (29 CFR 1910.136). Key takeaways:
- Enforcement through inspections: OSHA verifies compliance during site visits, emphasizing employer-employee collaboration on PPE programs.
- Beyond minimums: While OSHA requirements are foundational, leading operators often exceed them—for example, selecting boots with additional metatarsal guards.
ASTM F2413-18: What Specific Protections Does It Mandate?
This benchmark standard covers six protective features, with two being non-negotiable for oilfields:
- Impact/Compression Resistance: Steel or composite toe caps must withstand forces equivalent to a 2,500-pound object dropped from 1 foot.
- Electrical Hazard (EH) Protection: Boots must insulate against 18,000 volts for 1 minute without current transfer, using non-conductive materials in soles and shanks.
Did you know? EH-rated boots often omit metal components entirely, replacing them with fiberglass or engineered composites to prevent conductivity.
ANSI/ISEA 75: Testing for Slip Resistance and Durability
Oilfield boots must pass rigorous slip-resistance tests simulating wet, oily surfaces. ANSI/ISEA 75 grades traction performance, with top-tier boots maintaining grip even on angled metal surfaces—a common scenario in drilling platforms.
Selecting Compliant Boots for Oilfield Work
Key Features to Verify
- Toe Caps: Steel (traditional) vs. composite (lighter, non-metallic). Both meet ASTM F2413-18 but differ in weight and thermal conductivity.
- Puncture Resistance: Outsoles should deflect sharp objects like rebar or nails, tested per ASTM F2413-18’s PR rating.
- Slip-Resistant Outsoles: Look for ANSI/ISEA 75-compliant lugs or tread patterns designed for oily conditions.
How to Interpret Certification Labels
Labels like "ASTM F2413-18 EH" indicate electrical hazard protection, while "I/75" denotes impact resistance. Confused? Prioritize boots listing:
- ASTM F2413-18 (base standard)
- EH (electrical hazard)
- MT (metatarsal protection, if applicable)
Real-World Impact of Compliance
Case Study: Reduced Injuries in Offshore Drilling Operations
A 2022 analysis of Gulf Coast rigs showed a 40% drop in foot injuries after switching to ASTM/ANSI-compliant boots with metatarsal guards. Most incidents involved previously overlooked hazards like pipe rolling.
Common Oilfield Accidents Prevented by Proper Footwear
- Crush Injuries: Toe caps meeting ASTM compression standards reduce broken bone risks by over 50%.
- Electrical Burns: EH-rated boots prevent currents from grounding through the body.
- Slips and Falls: ANSI-tested slip resistance cuts fall-related injuries by approximately 30% on slick surfaces.
Ready to Equip Your Team with Certified Safety Footwear?
3515 partners with distributors and bulk buyers to deliver OSHA, ASTM, and ANSI-compliant boots engineered for oilfield hazards. From electrical hazard protection to slip-resistant designs, our range combines regulatory adherence with real-world durability. [Contact 3515] to discuss your procurement needs—because every worker deserves protection that meets the highest standards.
Related Products
- Wholesale Customizable Suede Safety Boots - Puncture-Proof with Velcro Closure
- Puncture-Resistant Velcro Safety Boots for Wholesale & Custom Manufacturing
- Customizable Anti-Smash Safety Boots for Wholesale & Private Label Manufacturing
- Durable Leather Moc Toe Work Boots for Wholesale & Custom Manufacturing
- Durable Moc-Toe Wedge Work Boots | Wholesale Manufacturing for Brands
Related Articles
- How Safety Work Boots Engineer Protection: Features and Standards for Targeted Hazard Mitigation
- Steel Toe Work Boots: Balancing Safety and Comfort for Demanding Jobs
- Matching Men’s Work Shoe Safety Technologies to Workplace Hazards
- How to Choose Work Boots That Match Your Job's Safety Demands
- How to Choose Work Boots That Balance Safety, Comfort, and Durability for Your Job