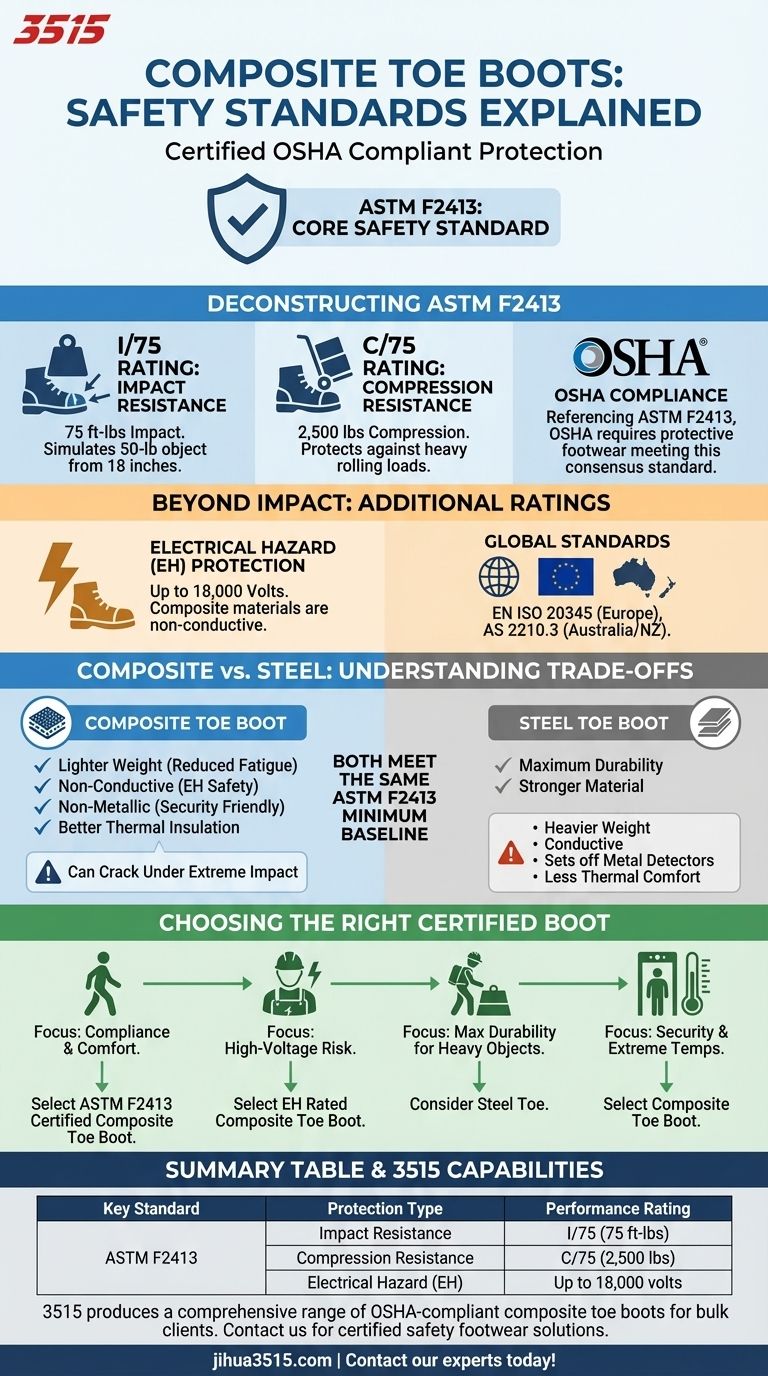
At their core, composite toe boots are certified to meet the same foundational safety standard as their steel toe counterparts: ASTM F2413. This is the primary American specification for protective footwear, ensuring verified resistance against both impact and compression. Many boots also carry additional ratings for hazards like electrical shock under this same standard.
The critical takeaway is that certified composite toe boots are fully compliant with OSHA requirements because they meet the same ASTM F2413 impact and compression standards as steel toe boots. The choice between them is not about meeting a minimum safety baseline, but about matching the specific material properties to your workplace hazards and needs.

Deconstructing the Core Safety Standard: ASTM F2413
To understand if a boot is truly safe, you must understand the standard it's tested against. For footwear in the United States, that standard is ASTM F2413.
What is ASTM F2413?
This is the Standard Specification for Performance Requirements for Protective (Safety) Toe Cap Footwear. The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) develops the standard, and OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) references it as the benchmark for workplace compliance.
The "I/75" Rating: Impact Resistance
A boot with an I/75 rating means its protective toe cap has been tested to withstand an impact of 75 foot-pounds. This simulates a 50-pound object being dropped from a height of approximately 18 inches.
The "C/75" Rating: Compression Resistance
A C/75 rating indicates the toe cap can withstand a compressive load of 2,500 pounds before it cracks or breaks. This protects the foot from heavy rolling objects, like a cart or barrel.
The Role of OSHA
OSHA mandates that employers ensure their employees use protective footwear in hazardous environments. Instead of creating its own footwear specification, OSHA requires that the footwear meets a consensus standard like ASTM F2413. A boot certified to this standard is therefore OSHA-compliant.
Beyond Impact: Additional Safety Ratings
The ASTM standard covers more than just the toe cap. A certified boot will have a label detailing its specific protections.
Electrical Hazard (EH) Protection
This is a key area where composite materials excel. Boots with an EH rating are tested to protect the wearer from open electrical circuits of up to 18,000 volts. Because composite materials are non-conductive, they are a natural fit for this protection.
Global Safety Standards
While ASTM F2413 is the US standard, composite toe boots also comply with international equivalents. The two most common are EN ISO 20345 for Europe and AS 2210.3 for Australia and New Zealand, which have similar performance requirements.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Composite vs. Steel
Both composite and steel toe boots must pass the same ASTM I/75 and C/75 tests to be sold as safety footwear. The difference lies in their material properties and performance at the extremes.
Meeting the Minimum Standard
Any boot you purchase with an ASTM F2413 rating, whether composite or steel, provides a proven, certified level of protection for most common workplace hazards.
Performance at the Extremes
While both meet the 75 foot-pound impact test, steel is a stronger material. In an accident involving an impact far exceeding the standard, a steel toe is more likely to bend, whereas a composite toe is more likely to crack or shatter.
Material Durability and Comfort
Composite materials are much lighter than steel, reducing foot fatigue over a long shift. They also do not conduct heat or cold, making them far more comfortable in extreme temperature environments.
The Non-Metallic Advantage
Since they contain no metal, composite toe boots will not set off metal detectors. This is a significant advantage for workers in security-sensitive facilities, such as airports, nuclear plants, or government buildings.
How to Choose the Right Certified Boot
Your choice should be guided by a clear understanding of your specific work environment and daily tasks.
- If your primary focus is compliance and all-around comfort: A composite toe boot certified to ASTM F2413 is an excellent, OSHA-compliant choice that reduces fatigue.
- If you work with or near high-voltage electricity: An Electrical Hazard (EH) rated composite toe boot is the safest and most logical option.
- If your work involves a constant, high risk of extremely heavy falling or rolling objects: You might consider a steel toe for maximum potential durability, even though both meet the same base standard.
- If you pass through metal detectors or work in extreme temperatures: Composite toe boots provide a clear advantage in comfort and convenience.
Ultimately, selecting certified safety footwear is a critical decision based on a sober assessment of your daily risks.
Summary Table:
| Key Standard | Protection Type | Performance Rating |
|---|---|---|
| ASTM F2413 | Impact Resistance | I/75 (75 ft-lbs) |
| ASTM F2413 | Compression Resistance | C/75 (2,500 lbs) |
| ASTM F2413 | Electrical Hazard (EH) | Up to 18,000 volts |
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of OSHA-compliant composite toe boots for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of safety footwear with certified ASTM F2413 protection.
Let us help you select the perfect safety footwear solution for your workforce. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and receive a customized quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Performance Fire-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots
- Premium High-Cut Waterproof Safety Boots Manufacturing & Wholesale Solutions
- Heavy-Duty Waterproof Nubuck Safety Boots Safety Shoes for Bulk Supply
- Premium Wholesale Waterproof Safety Boots High Performance Protection for Industrial Markets
- Puncture-Resistant Velcro Safety Boots for Wholesale & Custom Manufacturing
People Also Ask
- What is a packer boot for? The Ultimate Footwear for Ranchers and Riders
- Why is heat-resistant protective footwear required for high-temp construction? Essential Safety for Steam Pipe Ops
- Why should extreme heat be avoided when drying work boots? Protect Your Investment & Safety
- Are heavy duty work boots suitable for extreme weather? Key Features for Ultimate Protection
- Are water-resistant and water-repellent boots the same? A Guide to Choosing the Right Footwear
- What are the benefits of insulated work boots? Stay Warm & Safe in Extreme Conditions
- What makes chemical-resistant boots suitable for certain environments? Essential Protection for Hazardous Work
- Why are composite toe work boots better for extreme weather? Insulate Against Heat and Cold



















