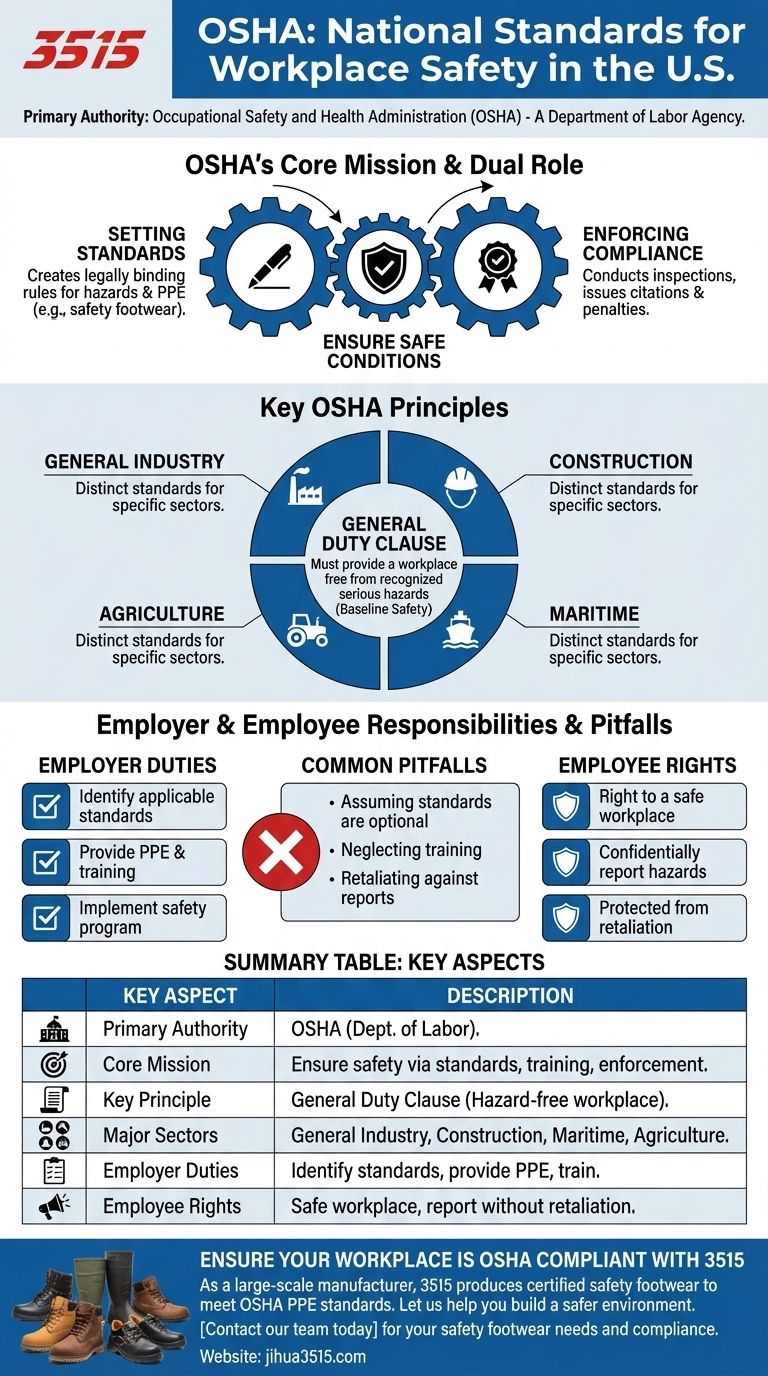
In the United States, the primary authority for workplace safety is the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, universally known as OSHA. As an agency within the Department of Labor, OSHA is responsible for both creating and enforcing the national standards that protect employees from workplace hazards.
OSHA's core mission is to ensure safe and healthful working conditions by setting legally binding standards and providing training, outreach, education, and assistance to both employers and employees.

The Dual Role of OSHA: Setting and Enforcing
OSHA's function is not merely to publish a list of rules. The agency's power lies in its comprehensive approach, which combines standard-setting with active enforcement to ensure compliance.
Creating the Standards
OSHA develops detailed safety standards tailored to different industries and specific hazards. These are not suggestions; they are legal requirements.
A clear example is the mandate for Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). OSHA standards define when employers must provide PPE, such as safety footwear, respirators, or gloves, at no cost to workers.
Enforcing Compliance
To ensure these rules are followed, OSHA is empowered to conduct workplace inspections. These can be triggered by employee complaints, serious accidents, or proactive programming for high-hazard industries.
If an inspection reveals violations, OSHA can issue citations and financial penalties to the employer, creating a powerful incentive for compliance.
Understanding Key OSHA Principles
Simply knowing OSHA exists is not enough. To truly grasp its impact, you must understand the core principles that guide its authority and application in the workplace.
The General Duty Clause
Perhaps the most critical concept is OSHA's General Duty Clause. This is a catch-all requirement stating that every employer must provide a workplace that is "free from recognized hazards that are causing or are likely to cause death or serious physical harm."
This clause empowers OSHA to act even if no specific standard applies to a particular situation, ensuring a baseline level of safety across all industries.
Industry-Specific Focus
OSHA recognizes that a factory has different risks than a construction site. Therefore, it maintains distinct sets of standards for four primary sectors: General Industry, Construction, Maritime, and Agriculture.
An employer must identify which standards apply to their specific operations to ensure they are meeting their legal obligations.
Common Pitfalls and Employer Responsibilities
Misunderstanding OSHA's scope and requirements can lead to significant risk for both employers and employees. Navigating compliance means avoiding common mistakes.
Assuming Standards are Optional
Many standards may seem like common sense, but they are legal mandates. Relying on an informal safety culture instead of implementing specific OSHA requirements is a frequent and costly error.
Neglecting Employee Training
Providing safety equipment is only half the battle. Employers are also required to train workers on how to properly use that equipment and how to recognize the hazards it protects against.
Retaliating Against Reports
Employees have a legally protected right to report safety concerns to their employer or directly to OSHA. It is illegal for an employer to retaliate against a worker for exercising their safety rights.
How to Apply This to Your Role
Understanding OSHA is the first step toward proactive safety management. Your next steps depend on your specific role within the workplace.
- If you are an employer: Your primary responsibility is to identify all applicable OSHA standards for your industry and implement a formal, documented safety program.
- If you are an employee: You have the right to a safe work environment and can confidentially report hazards to OSHA without fear of reprisal.
Ultimately, OSHA provides the framework for a culture of safety where every worker has the right to return home unharmed.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Authority | Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) |
| Core Mission | Ensure safe working conditions via standards, training, and enforcement. |
| Key Principle | The General Duty Clause requires a workplace free from recognized hazards. |
| Major Sectors | General Industry, Construction, Maritime, Agriculture. |
| Employer Duties | Identify applicable standards, provide PPE, and train employees. |
| Employee Rights | Right to a safe workplace and to report hazards without retaliation. |
Ensure Your Workplace is OSHA Compliant
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of certified safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Proper Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), like our industrial boots and shoes, is a fundamental part of meeting OSHA standards and protecting your workforce.
Let us help you build a safer environment. Our production capabilities encompass all types of safety shoes and boots designed to meet rigorous requirements.
Contact our team today to discuss your safety footwear needs and ensure compliance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable Slip-On Safety Shoes Direct from the Factory for Wholesale
- Wholesale Customizable Suede Safety Boots - Puncture-Proof with Velcro Closure
- Wholesale Durable Camo Canvas Shoes with High-Traction Rubber Soles
- Durable Mid-Cut Tactical Boots for Wholesale & Private Label
- Wholesale Durable Mid-Cut Tactical Boots for Custom & Private Label Brands
People Also Ask
- What is the industrial value of applying specialized coating materials and high-spec packaging in premium footwear?
- How does suede differ from leather? A Guide to Choosing the Right Material
- What are the care steps for footwear made of smooth leather? A 3-Step Guide to Longevity
- How should synthetic leather riding boots be cared for? Simple Steps for Long-Lasting Performance
- What is the role of flame atomization technology in detecting heavy metals in leather? Fast & Reliable Footwear Analysis
- How does a high-precision 3D scanning system assist in determining RMM? Master Precise Foot Biomechanics
- What technical challenge does the Bi-LSTM address in fall-detection? Enhancing Temporal Accuracy in Motion Sensing
- What is the significance of 'No leg, no horse'? Protecting Your Horse's Most Critical Asset

















