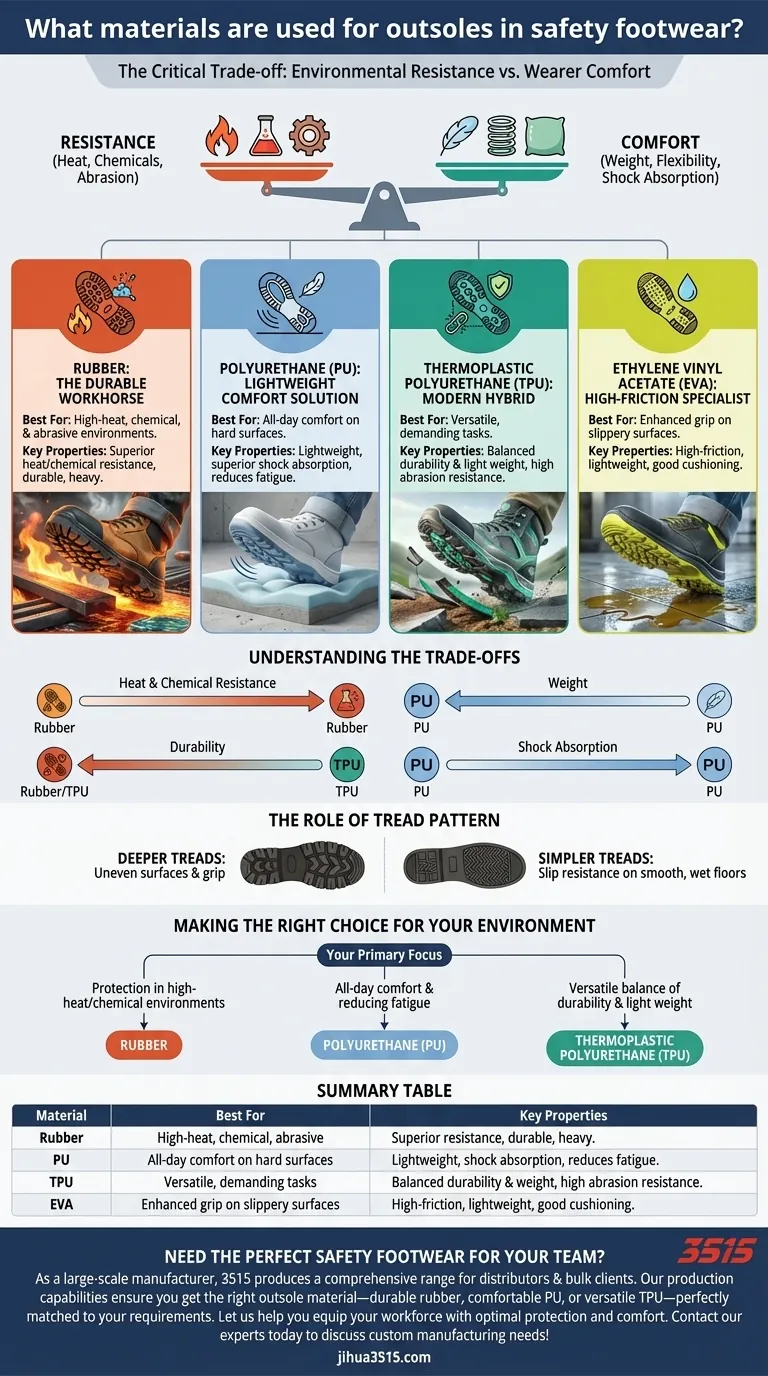
In safety footwear, the outsole is most commonly made from one of three primary materials: Rubber, Polyurethane (PU), or Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU). Each material is selected for a distinct profile of properties, including resistance to heat and chemicals, durability, and shock absorption, to match the demands of a specific work environment.
The choice of an outsole material is not about finding the "best" one, but about understanding the critical trade-off between environmental resistance (heat, chemicals, abrasion) and wearer comfort (weight, flexibility, shock absorption).

The Core Outsole Materials Explained
The material making direct contact with the ground dictates much of a safety boot's performance. Understanding the fundamental differences between these materials is key to selecting the right footwear.
Rubber: The Durable Workhorse
Rubber, particularly nitrile rubber, is a traditional and highly effective choice for safety outsoles. It is renowned for its exceptional durability and resistance.
Its primary advantage is its high resistance to heat, abrasions, acids, and alkalis. This makes it the standard for harsh industrial environments where contact with hot surfaces or corrosive chemicals is a risk.
Polyurethane (PU): The Lightweight Comfort Solution
Polyurethane (PU or PUR) is a modern polymer valued for its comfort-oriented properties. Its main benefits are its light weight and superior shock absorption.
This makes PU outsoles ideal for workers who spend long hours on their feet, as they significantly reduce fatigue. They also provide excellent slip resistance on common surfaces.
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU): The Modern Hybrid
TPU is an advanced material that offers a blend of the best qualities of rubber and PU. It is both lightweight and extremely durable.
A key feature of TPU is its high resistance to splitting and abrasion, often outperforming other materials in longevity. It provides a great balance for general-purpose safety footwear.
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA): The High-Friction Specialist
While less common as a primary outsole in heavy-duty safety boots, EVA is frequently used for its high-friction properties and cushioning.
It is exceptionally lightweight and enhances grip, making it a valuable material for creating non-slip footwear, especially for wet or oily indoor surfaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single outsole material is perfect for every application. The right choice always involves balancing competing priorities based on your specific workplace hazards and tasks.
Heat and Chemical Resistance vs. Weight
The most significant trade-off is often between protection and comfort. Rubber offers the highest level of heat and chemical resistance but is typically the heaviest option.
Conversely, Polyurethane is significantly lighter, reducing foot fatigue, but it does not withstand high heat or aggressive chemicals as effectively as rubber.
Durability vs. Shock Absorption
While both are durable, TPU and rubber excel in abrasion and cut resistance, making them suitable for rough terrain and demanding physical work.
PU offers better cushioning and shock absorption. This feature is critical for preventing joint stress on hard, flat surfaces like concrete floors but may come at the expense of ultimate abrasion resistance.
The Role of Tread Pattern
The material itself is only half the story. The tread pattern molded into the outsole is equally critical for performance.
Deeper, more aggressive treads are designed for grip on uneven or loose surfaces, while simpler patterns may be optimized for slip resistance on smooth, wet floors.
Making the Right Choice for Your Environment
Your daily tasks and work environment should be the ultimate guide in selecting an outsole material.
- If your primary focus is protection in high-heat or chemical environments: Rubber is the superior choice for its unmatched resistance.
- If your primary focus is all-day comfort and reducing fatigue on hard floors: Polyurethane (PU) offers the best combination of light weight and shock absorption.
- If your primary focus is a versatile balance of durability and light weight for varied tasks: Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) provides an excellent all-around solution with high resistance to splitting.
Choosing the right outsole material is a foundational step in ensuring both your safety and your functional comfort on the job.
Summary Table:
| Material | Best For | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Rubber | High-heat, chemical, and abrasive environments | Superior heat/chemical resistance, durable, heavy |
| Polyurethane (PU) | All-day comfort on hard surfaces | Lightweight, excellent shock absorption, reduces fatigue |
| Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) | Versatile, demanding tasks | Balanced durability and light weight, high abrasion resistance |
| Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) | Enhanced grip on slippery surfaces | High-friction, lightweight, good cushioning |
Need the Perfect Safety Footwear for Your Team?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of shoes and boots, ensuring you get the right outsole material—be it durable rubber, comfortable PU, or versatile TPU—perfectly matched to your specific safety and comfort requirements.
Let us help you equip your workforce with optimal protection and comfort.
Contact our experts today to discuss your custom manufacturing needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
- Advanced KPU Athletic Safety Shoe with Steel Toe Cap Anti-Slip Rotary Lacing System
- Premium Grain Leather Safety Boots for Bulk Supply
- Heavy-Duty Waterproof Nubuck Safety Boots Safety Shoes for Bulk Supply
People Also Ask
- Is safety-toe as good as steel toe? Choose the Right Protection for Your Job
- How long can you wear safety boots? The Lifespan is Determined by Wear, Not Time
- What cultural and environmental considerations are tied to wearing shoes indoors? Balance Hygiene, Tradition, and Foot Health
- Do snake bite boots work? Your Ultimate Guide to Effective Snake Bite Protection
- What are OSHA approved shoes? Understanding the Correct Standards for Workplace Safety



















