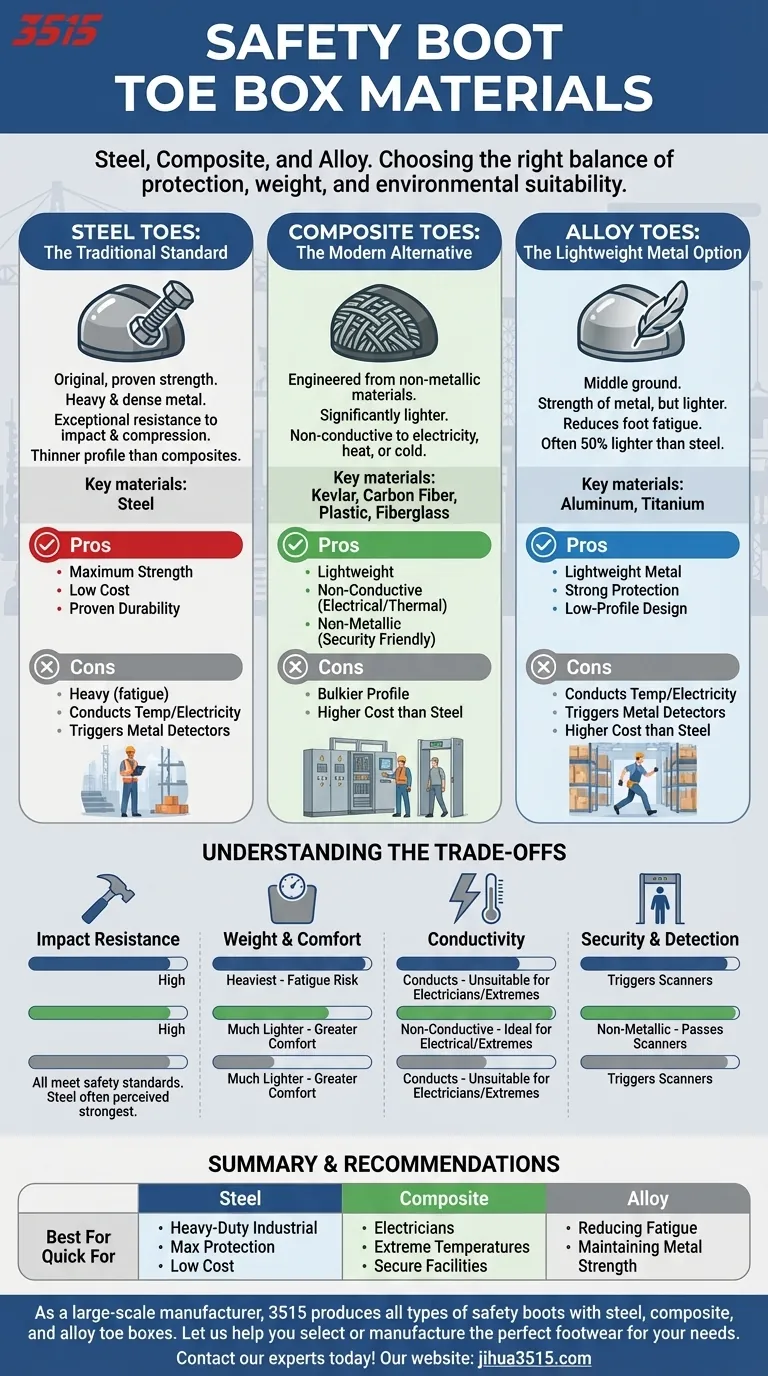
When selecting safety footwear, the material of the protective toe box is a critical decision. The three primary materials used to protect your feet from impact and compression are steel, composite materials like carbon fiber or fiberglass, and lighter metal alloys such as aluminum. Each material is engineered to meet specific safety standards but offers a distinct set of advantages and disadvantages depending on your work environment.
The core decision is not about which material is "best" overall, but which offers the right balance of protection, weight, and environmental suitability for your specific job. Steel provides maximum strength at a low cost, while composite and alloy offer lighter, non-conductive alternatives.

The Three Core Types of Safety Toes
Understanding the fundamental properties of each material is the first step toward making an informed choice. The material of the toe cap directly impacts the boot's weight, comfort, and suitability for different hazards.
Steel Toes: The Traditional Standard
Steel is the original material for safety toes and remains a common choice due to its proven strength. It is a heavy and dense metal that offers exceptional resistance to impact and compression.
Because of its strength, a steel toe cap can be made relatively thin, resulting in a less bulky boot profile compared to some non-metal alternatives.
Composite Toes: The Modern Alternative
Composite toes are engineered from non-metallic materials, including Kevlar, carbon fiber, plastic, or fiberglass. They have become a popular modern alternative to steel.
Their primary advantage is that they are significantly lighter and do not conduct electricity, heat, or cold, making them ideal for a wide range of specialized environments.
Alloy Toes: The Lightweight Metal Option
Alloy toes, typically made from materials like aluminum or titanium, offer a middle ground between steel and composite. They provide the strength of a metal cap but are considerably lighter than steel.
This makes them a good choice for workers who want to reduce foot fatigue without moving to a non-metallic option. They are often just as strong as steel but can be up to 50% lighter.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right safety toe involves weighing the benefits and drawbacks of each material against the demands of your workplace. The key factors are protection, weight, conductivity, and cost.
Impact and Compression Resistance
All safety toes—whether steel, composite, or alloy—must meet the same regulatory safety standards for impact and compression resistance.
However, steel is often perceived as the strongest on a pound-for-pound basis. It can withstand very high impacts without shattering.
Weight and All-Day Comfort
Steel is the heaviest option, which can lead to fatigue over long shifts.
Alloy and composite toes are much lighter, directly contributing to greater comfort and less strain on your legs and back throughout the day.
Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
This is a critical differentiator. Steel and alloy are metals and will conduct temperature and electricity. This makes them unsuitable for electricians or those working in extremely hot or cold environments.
Composite toes are non-conductive, providing a crucial layer of protection against electrical hazards and offering superior insulation against temperature extremes.
Security and Detection
For those who frequently pass through metal detectors, the choice is clear. Steel and alloy toes will trigger security scanners.
Composite toes are non-metallic and will not set off detectors, saving time and hassle for professionals in secure facilities like airports or power plants.
Making the Right Choice for Your Work Environment
Your daily tasks and workplace hazards should be the ultimate guide for your decision.
- If your primary focus is maximum protection at the lowest cost: Steel toes offer the traditional, time-tested solution for heavy-duty construction and industrial sites.
- If your primary focus is working around electricity or in extreme temperatures: Composite toes are the superior choice, as they provide protection without conducting electricity, heat, or cold.
- If your primary focus is reducing fatigue while maintaining a low-profile boot: Alloy toes provide a lightweight metal alternative that is often less bulky than composite options.
- If your primary focus is passing through metal detectors frequently: Composite toes are essential, as they will not trigger security scanners.
Choosing the right toe material is the first step in ensuring your safety and comfort on the job.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Steel | Maximum strength, low cost, conducts temperature/electricity | Heavy-duty industrial sites, maximum protection |
| Composite | Lightweight, non-conductive, non-metallic | Electricians, extreme temperatures, secure facilities |
| Alloy | Lightweight metal, strong, low-profile design | Reducing fatigue, maintaining metal strength |
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of safety boots and shoes with steel, composite, and alloy toe boxes. Let us help you select or manufacture the perfect safety footwear for your needs and market. Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Premium Grain Leather Safety Boots for Bulk Supply
- Heavy Duty Nubuck Safety Boots Safety Shoes for Global Distribution
- Premium Sport Style Safety Boots for Bulk Orders
- Premium Suede Sport Safety Shoes for Wholesale & Bulk Orders
- Advanced KPU Athletic Safety Shoe with Steel Toe Cap Anti-Slip Rotary Lacing System
People Also Ask
- What is EVA and what are its advantages in safety shoes? Lightweight Cushioning for All-Day Comfort
- How is human joint motion monitoring technology applied to the research and development of safety shoes? Design Insights
- How does the selection of specific occupational protective footwear contribute to the prevention of FD? Expert Guide
- What are safety shoes also known as? A Guide to Protective Footwear Terms
- What is the OSHA standard for safety-toe boots? Ensuring Compliance and Worker Protection
- What does OSHA standard 29 CFR 1910.136(a) state about the use of protective footwear? Ensure Full Compliance
- What is the purpose of the heel cap in safety footwear? Essential for Stability and Injury Prevention
- How does the heel cushioning system in protective footwear regulate walking loads? Enhance Joint Health with Tech



















