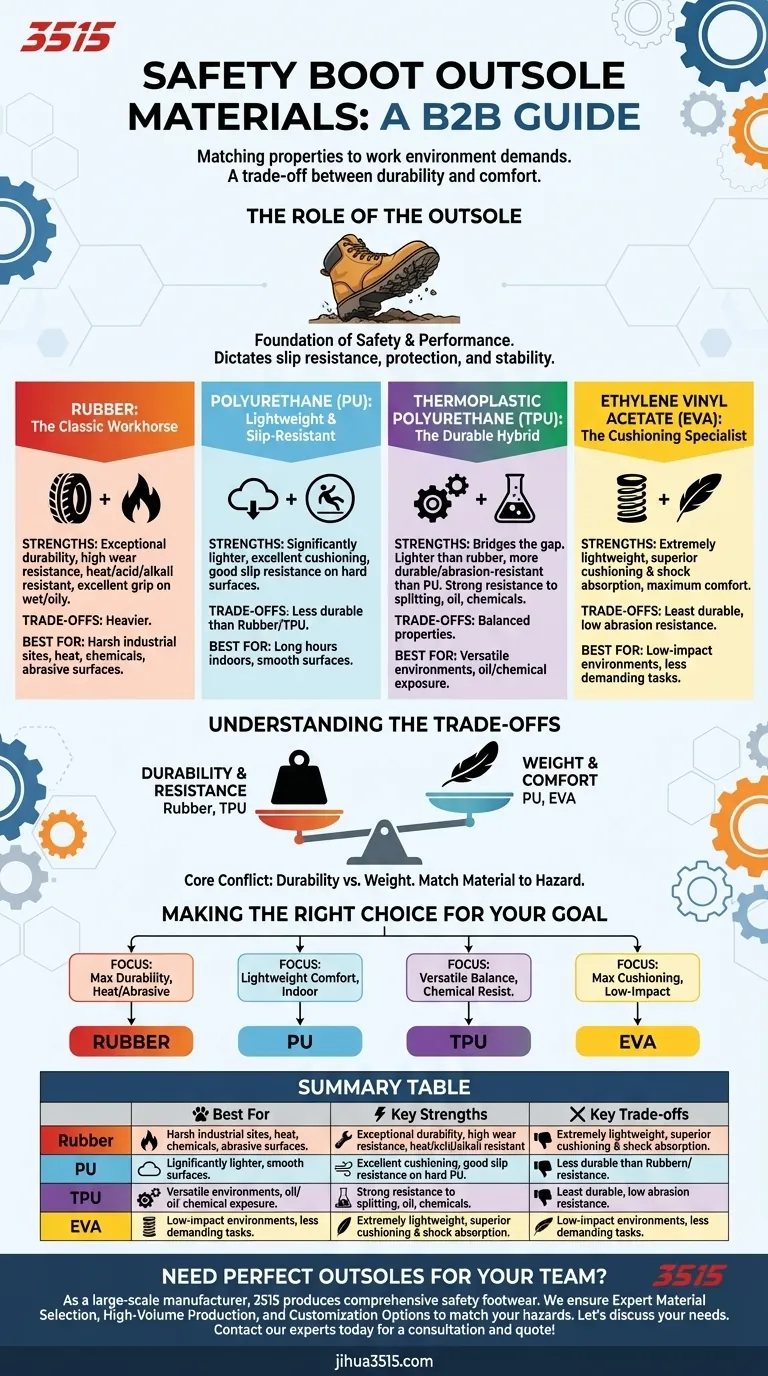
To put it simply, the most common materials used for safety boot outsoles are Rubber, Polyurethane (PU), Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU), and Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA). Each material is chosen for a specific balance of durability, grip, weight, and resistance to environmental factors like heat or chemicals.
The choice of an outsole material is not about finding the single "best" option, but about matching the material's specific properties to the demands of your work environment. This decision always involves a trade-off, most often between heavy-duty durability and lightweight comfort.

The Role of the Outsole
The Foundation of Safety and Performance
The outsole is the part of the boot that makes direct contact with the ground. Its material composition is critical for performance.
It dictates key safety features like slip resistance, protection from abrasion, and stability on uneven surfaces.
More Than Just a Single Material
While we often talk about a single material, many modern outsoles are composites. They are engineered to combine the best properties of different materials to optimize performance for specific tasks.
Breaking Down the Common Materials
Rubber: The Classic Workhorse
Rubber is the traditional choice for heavy-duty work boots, prized for its exceptional durability and wear resistance.
Its high-friction properties provide excellent grip and traction, especially on wet or oily surfaces. It is also highly resistant to heat, acids, and alkalis, making it a staple in harsh industrial environments.
Polyurethane (PU): Lightweight and Slip-Resistant
Polyurethane is significantly lighter than rubber, making it a popular choice for boots designed for long hours on your feet.
It offers excellent cushioning and slip resistance, providing both comfort and safety on smoother, hard surfaces.
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU): The Durable Hybrid
TPU is a modern material that bridges the gap between rubber and polyurethane. It is lighter than rubber but more durable and abrasion-resistant than PU.
It offers strong resistance to splitting, oil, and chemicals, making it a versatile and high-performance option for a wide range of conditions.
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA): The Cushioning Specialist
EVA is an extremely lightweight, foam-like material primarily known for its superior cushioning and shock absorption.
While it provides excellent comfort, it is the least durable of the common materials and is less resistant to abrasion and wear. It is often used in midsoles or on boots intended for less demanding environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Core Conflict: Durability vs. Weight
The fundamental choice in outsole materials comes down to a trade-off between durability and weight.
Materials like rubber and TPU offer maximum resistance to wear, cuts, and abrasion, but they are heavier. This makes them ideal for rough terrain and harsh industrial sites.
Conversely, materials like PU and EVA are much lighter, reducing foot fatigue over a long day. However, this comes at the cost of durability, making them better suited for indoor work or smoother surfaces.
Matching Material to the Hazard
Beyond weight, consider the specific hazards you face. For exposure to high heat or certain chemicals, rubber is often the superior choice.
For environments with significant oil or solvent exposure, TPU provides a more reliable and long-lasting barrier.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the best outsole, you must first define your primary need.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and heat resistance on abrasive surfaces: Choose a boot with a Rubber outsole.
- If your primary focus is lightweight comfort and slip-resistance for long hours indoors: A Polyurethane (PU) outsole is your ideal choice.
- If your primary focus is a versatile balance of durability, light weight, and chemical resistance: Look for a boot featuring a TPU outsole.
- If your primary focus is maximum cushioning and minimal weight in a low-impact environment: An EVA outsole will provide the most comfort.
Choosing the right outsole material is a critical step in ensuring your safety, comfort, and performance on the job.
Summary Table:
| Material | Best For | Key Strengths | Key Trade-offs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber | Harsh industrial sites, heat, chemicals | Superior durability, excellent grip, heat/chemical resistant | Heavier than other options |
| Polyurethane (PU) | Long hours on hard, indoor surfaces | Lightweight, good slip resistance, excellent cushioning | Less durable than rubber/TPU |
| Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) | Versatile environments, oil/chemical exposure | Great balance of durability, light weight, and chemical resistance | - |
| Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) | Low-impact environments, maximum comfort | Extremely lightweight, superior cushioning and shock absorption | Least durable, low abrasion resistance |
Need Safety Boots with the Perfect Outsole for Your Team?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of safety shoes and boots, allowing us to match the ideal outsole material—be it rugged Rubber, lightweight PU, versatile TPU, or cushioned EVA—to your specific workplace hazards and comfort requirements.
We ensure:
- Expert Material Selection: Guidance to choose the best outsole for durability, grip, and comfort.
- High-Volume Production: Reliable supply to meet the demands of distributors and large clients.
- Customization Options: Tailor footwear to your brand's specifications and safety standards.
Let's discuss your needs and enhance your safety footwear line. Contact our experts today for a consultation and quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
- Premium Grain Leather Safety Boots for Bulk Supply
- Puncture-Resistant Velcro Safety Boots for Wholesale & Custom Manufacturing
- Customizable Anti-Smash Safety Boots for Wholesale & Private Label Manufacturing
People Also Ask
- How do safety shoes contribute to cost savings for companies? A Strategic Investment in Risk and Cost Management
- What type of footwear is required in meatpacking and poultry plants due to slippery conditions? Essential Safety Boots for Slippery Floors
- What are the cultural perspectives on wearing shoes in the house? A Guide to Home Etiquette & Hygiene
- What cultural and environmental considerations are tied to wearing shoes indoors? Balance Hygiene, Tradition, and Foot Health
- Can heavy duty work boots be worn daily outside of work? Discover Durable, All-Day Comfort



















