Thinsulate is a synthetic insulation material designed to trap body heat while remaining exceptionally lightweight and breathable. Commonly found in work boots, it utilizes microfibers to capture air molecules, creating a thermal barrier that provides reliable warmth in cold environments without the bulk associated with traditional insulation.
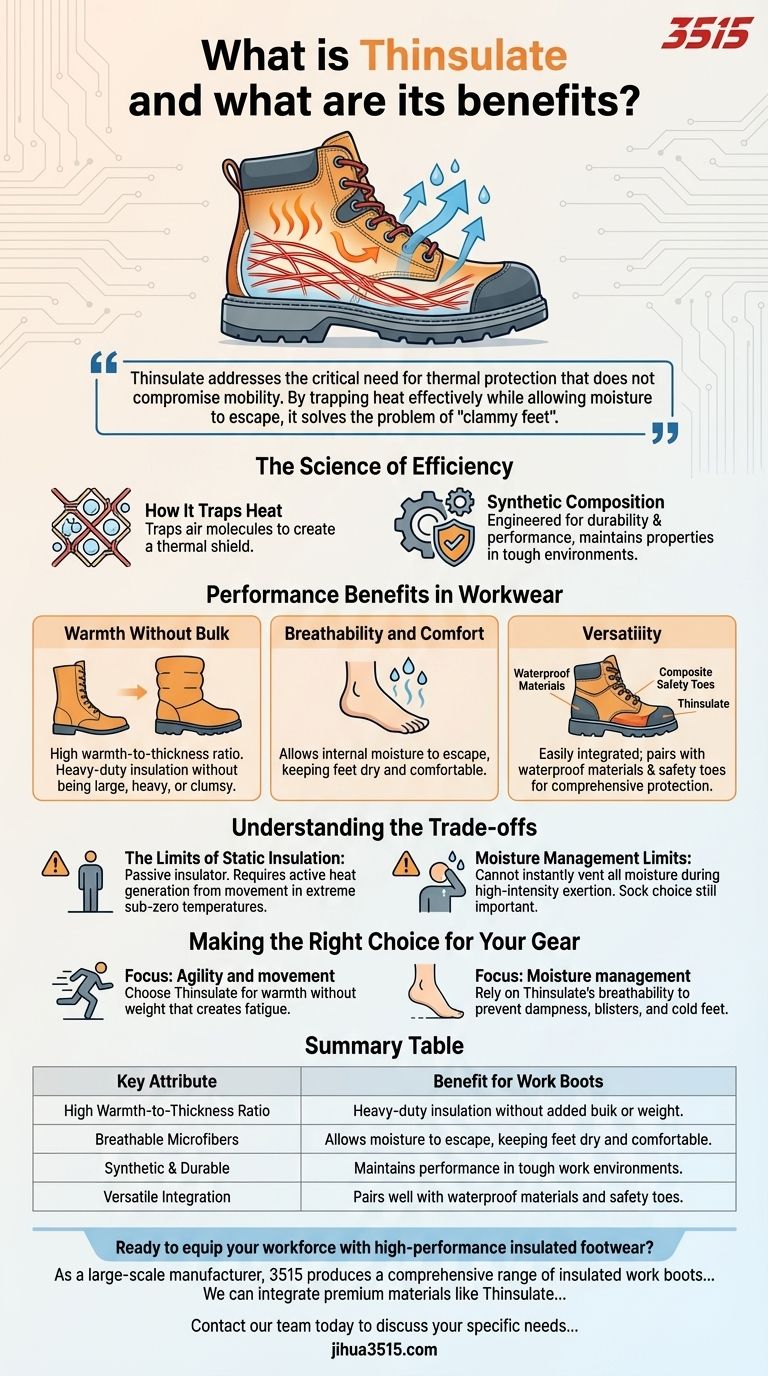
Thinsulate addresses the critical need for thermal protection that does not compromise mobility. By trapping heat effectively while allowing moisture to escape, it solves the problem of "clammy feet" often caused by heavy, non-breathable winter gear.

The Science of Efficiency
How It Traps Heat
Thinsulate functions on a microscopic level by trapping air molecules within its fiber structure. Since air is a poor conductor of heat, these trapped pockets create an effective shield against the cold.
Synthetic Composition
As a synthetic material, it is engineered specifically for durability and performance. Unlike some natural fibers, it maintains its insulating properties even in challenging work environments.
Performance Benefits in Workwear
Warmth Without Bulk
The primary advantage of Thinsulate is its high warmth-to-thickness ratio. It provides heavy-duty insulation without making boots large, heavy, or clumsy to walk in.
Breathability and Comfort
Insulation is useless if it causes you to sweat excessively. Thinsulate allows internal moisture to escape, ensuring that your feet stay dry and comfortable during extended periods of wear.
Versatility
Because it is thin and pliable, Thinsulate is easily integrated into various footwear styles. It is frequently paired with waterproof materials and composite safety toes, offering comprehensive protection without compromising fit.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Limits of Static Insulation
While Thinsulate is highly effective, it is a passive insulator. It works by retaining the heat your body generates. If you are completely stationary in extreme sub-zero temperatures, even the best insulation requires active heat generation from movement to be fully effective.
Moisture Management Limits
Although Thinsulate is breathable, no material can instantly vent all moisture during high-intensity exertion. In scenarios of extreme physical activity, users must still manage sock choice to aid the moisture-wicking process initiated by the insulation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Gear
If you are selecting footwear for professional or outdoor use, consider how Thinsulate aligns with your specific environment.
- If your primary focus is agility and movement: Choose Thinsulate for its ability to provide warmth without the weight that creates fatigue over a long shift.
- If your primary focus is moisture management: Rely on Thinsulate’s breathable nature to prevent the dampness that leads to blisters and cold feet.
Thinsulate remains the definitive choice for professionals who demand high-performance thermal regulation without the penalty of added weight.
Summary Table:
| Key Attribute | Benefit for Work Boots |
|---|---|
| High Warmth-to-Thickness Ratio | Provides heavy-duty insulation without added bulk or weight. |
| Breathable Microfibers | Allows moisture to escape, keeping feet dry and comfortable. |
| Synthetic & Durable | Maintains performance in tough work environments. |
| Versatile Integration | Pairs well with waterproof materials and safety toes for comprehensive protection. |
Ready to equip your workforce with high-performance insulated footwear?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of insulated work boots for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of safety footwear, and we can integrate premium materials like Thinsulate to create boots that offer superior warmth, comfort, and durability for your customers.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific needs and discover how we can build the perfect insulated footwear solution for your market.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Premium Wholesale Waterproof Safety Boots High Performance Protection for Industrial Markets
- Custom Wholesale Leather Safety Boots Direct Factory Manufacturing
- Premium Wholesale Wheat Nubuck Safety Boot with Rapid Lacing System
- Premium Grain Leather Safety Boots for Bulk Supply
People Also Ask
- What are the protective functions of industrial safety boots in sugar factory clarification stations? Thermal & Slip Experts
- What should be considered when choosing winter work boots? Key Factors for Safety & Warmth
- What are the basic considerations for finding the best work shoes? A Guide to Safety, Fit, and Durability
- What is the primary purpose of a harness boot? Built for Protection and Durability
- What type of footwear is required in meatpacking and poultry plants due to slippery conditions? Essential Safety Boots for Slippery Floors
- How do professional-grade protective boots manage thermal protection? Master Heat Resistance for Safer Riding
- What does electric shock resistance in ASTM standards entail? A Guide to EH-Rated Footwear Safety
- What materials are used in composite toe work boots? Lighter, Non-Conductive Safety Explained



















