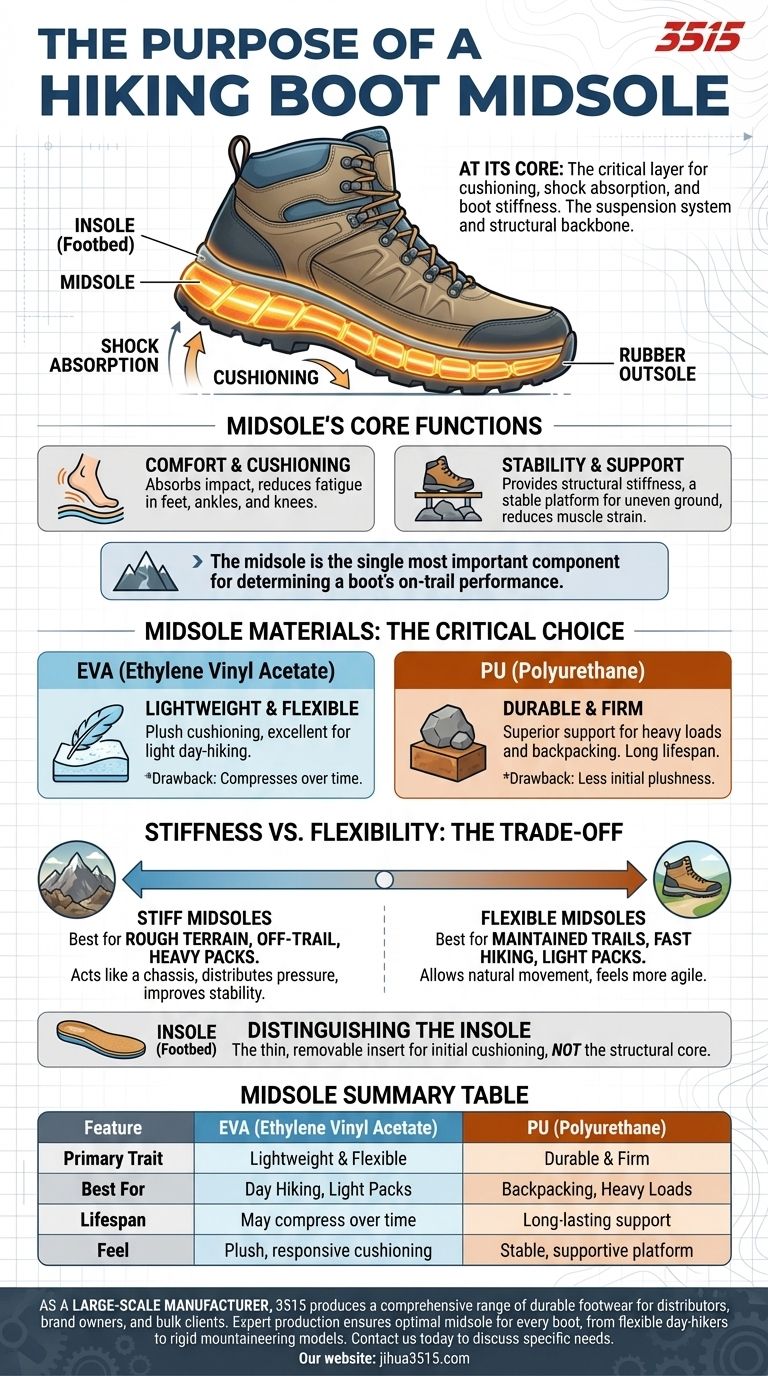
At its core, a hiking boot's midsole is the critical layer responsible for cushioning your foot, absorbing shock from the trail, and determining the boot's overall stiffness. Sandwiched between the insole your foot rests on and the rubber outsole that grips the ground, it acts as the boot's suspension system and structural backbone.
The midsole is the single most important component for determining a boot's on-trail performance. Its material and stiffness dictate your comfort, stability, and foot fatigue more than any other feature.

Deconstructing the Boot: The Midsole's Core Functions
To truly understand a hiking boot, you must look beyond the fit and the tread. The unseen midsole layer is where the engineering truly happens.
The Hidden Engine of Comfort
The midsole's primary job is to provide cushioning. As you walk, it compresses slightly to absorb the impact of each step, preventing the jarring force from traveling up your joints.
This shock absorption is crucial for reducing fatigue in your feet, ankles, knees, and back over the course of a long hike.
A Platform for Stability
The midsole also provides the boot's structural integrity, or stiffness. This is often misunderstood as a negative trait, but for hiking on uneven ground, it is essential.
A stiffer midsole creates a stable platform under your foot. It prevents your foot from wrapping around every rock and root, which significantly reduces muscle strain and improves your balance.
Midsole Materials: The Critical Choice
The material used in the midsole defines its characteristics. The two most common options create a clear trade-off between soft cushioning and firm durability.
EVA (Ethylene Vinyl Acetate)
EVA is a foam-like material that is light, flexible, and provides excellent cushioning. It is less expensive to produce, making it common in everything from trail running shoes to light day-hiking boots.
The primary drawback of EVA is that it can compress and lose its cushioning ability over time, especially under the weight of a heavy pack.
Polyurethane (PU)
Polyurethane is a denser, firmer, and significantly more durable material than EVA. It provides less initial "plush" cushioning but offers superior support and a much longer lifespan.
Because of its firmness and durability, PU is the standard for serious backpacking and mountaineering boots designed to carry heavy loads over rugged terrain.
Understanding the Key Trade-off: Stiffness vs. Flexibility
The choice between a stiff or flexible midsole is a functional one. There is no single "best" option; the right choice depends entirely on the terrain you plan to tackle.
Why Stiff Midsoles Excel on Rough Terrain
On rocky, uneven, or off-trail routes, a stiff midsole is your best friend. It acts like a chassis, distributing the pressure from sharp points across your entire foot instead of allowing them to poke you.
This platform provides the stability needed for carrying a heavy pack and reduces the small, fatiguing movements your foot would otherwise have to make to conform to the ground.
When Flexibility Provides an Advantage
For well-maintained trails, fast hiking, or shorter trips with a light pack, a more flexible midsole (typically made of EVA) is often preferred.
This flexibility allows your foot to move more naturally and can make the boot feel more agile and responsive. It requires less energy to walk, but it comes at the cost of support on technical ground.
Distinguishing the Midsole from the Insole
It's crucial not to confuse the midsole with the insole, also known as the footbed. The insole is the thin, often removable insert that your foot rests on directly.
While the insole provides initial cushioning and arch support, the midsole is the permanent, structural core of the boot that does the heavy lifting for shock absorption and stability.
Matching the Midsole to Your Goal
Choosing the right boot starts with identifying your primary hiking style and matching the midsole technology to that need.
- If your primary focus is day hiking on established trails: Look for a boot with a more flexible EVA midsole that prioritizes lightweight comfort.
- If your primary focus is multi-day backpacking with a heavy pack: Choose a boot with a firm and durable Polyurethane midsole for maximum support and stability.
- If your primary focus is off-trail travel or scrambling: A stiff midsole is non-negotiable, as it provides a reliable platform on unpredictable and challenging surfaces.
By understanding the midsole, you can select a boot based on its performance engine, ensuring comfort and stability on any trail you choose.
Summary Table:
| Midsole Feature | EVA (Ethylene Vinyl Acetate) | PU (Polyurethane) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Trait | Lightweight & Flexible | Durable & Firm |
| Best For | Day Hiking, Light Packs | Backpacking, Heavy Loads |
| Lifespan | May compress over time | Long-lasting support |
| Feel | Plush, responsive cushioning | Stable, supportive platform |
Need high-performance hiking boots for your customers? As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of durable footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our expert production capabilities ensure every boot, from flexible day-hikers to rigid mountaineering models, features the optimal midsole for superior comfort and support. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and elevate your product line with reliable, trail-tested footwear.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Wholesale Modern Comfort Shoes with Dial Closure for Private Label & Bulk Orders
- Durable Rubber-Soled Utility Shoes for Wholesale & Custom Brand Manufacturing
- Wholesale Durable & Breathable Training Shoes for Custom Brands
- Wholesale Training Shoes with Dial Lacing System Custom OEM Manufacturing
- Premium Wholesale Waterproof Safety Boots High Performance Protection for Industrial Markets
People Also Ask
- What is the conclusion about wearing hiking boots versus shoes? Choose the Right Footwear for Your Hike
- What are the typical price ranges for trail runners, hiking shoes, and hiking boots? A Guide to Smart Footwear Investment
- How should hiking boots be prepared before applying waterproofing treatment? Ensure Deep, Lasting Protection
- What are the two main reasons to wear waterproof hiking boots? Keep Your Feet Dry and Warm
- How can you check for proper toe room in hiking boots? Prevent Pain & Black Toenails
- How does hiking speed affect the choice of footwear? Choose the Right Shoe for Your Pace
- What are the different boot height options and their purposes? Find Your Perfect Fit for Any Trail
- Are trekking shoes worth it? Essential for Safety and Comfort on the Trail



















