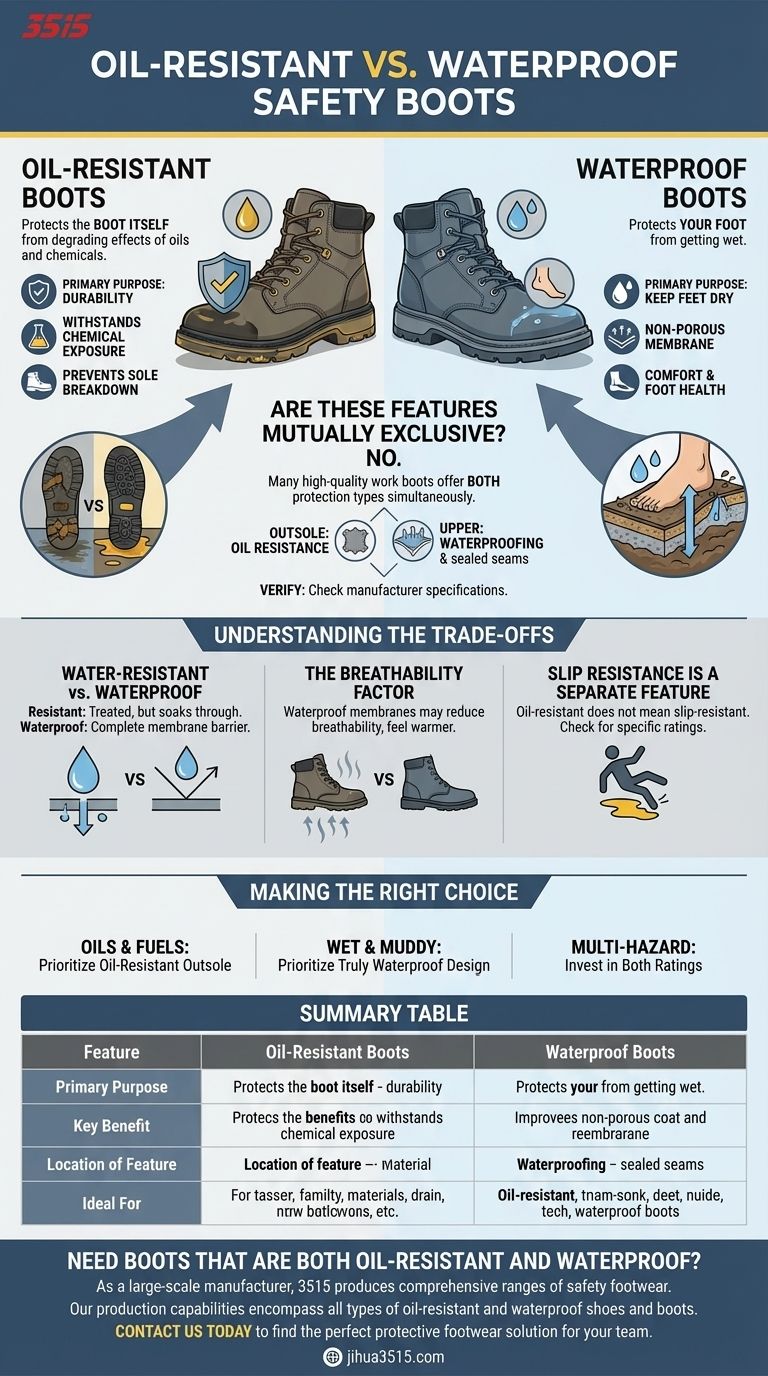
At its core, the difference is about what is being protected. Oil-resistant boots are designed to protect the boot itself from the degrading effects of oils and chemicals. Waterproof boots are designed to protect your foot from getting wet.
Choosing between oil-resistant and waterproof boots isn't about which is superior, but about accurately identifying the primary hazard in your work environment—material degradation versus moisture penetration.

Deconstructing the Core Functions
To select the right footwear, you must understand the specific problem each feature is engineered to solve. They address fundamentally different workplace risks.
Oil-Resistant Boots: Protecting the Boot Itself
The primary purpose of an oil-resistant boot is durability. Certain oils, solvents, and chemicals can attack the compounds used in a boot's outsole, causing them to soften, swell, or break down prematurely.
This degradation compromises the structural integrity of the boot, reducing its lifespan and potentially its safety features. An oil-resistant rating certifies that the sole's materials can withstand this chemical exposure without failing.
Waterproof Boots: Protecting the Wearer's Foot
The goal of a waterproof boot is to keep your feet dry. This is typically achieved with a special non-porous membrane or liner built into the boot's upper.
This barrier prevents external liquids—like water, mud, or other non-corrosive fluids—from penetrating the boot. This is critical for comfort, preventing blisters, and maintaining foot health in wet conditions or sanitary environments like food production.
Are These Features Mutually Exclusive?
No, they are not. Many high-quality work boots are engineered to offer both types of protection simultaneously.
The Role of the Outsole
Oil resistance is almost exclusively a property of the boot's outsole. Manufacturers use specific rubber or synthetic compounds designed not to react with petroleum-based substances.
The Role of the Upper and Membrane
Waterproofing is a function of the boot's upper construction. It involves sealed seams and a waterproof, breathable membrane that sits between the outer material and the liner.
How to Verify
Because these features reside in different parts of the boot, a single boot can easily have both. Always check the manufacturer's specifications for explicit mentions of "oil-resistant" and "waterproof" ratings to ensure you are covered for both hazards.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a boot involves balancing protection with comfort and other performance factors.
"Water-Resistant" vs. "Waterproof"
Be aware of the distinction. Water-resistant often refers to leather that has been treated to repel water, but it will eventually soak through under sustained exposure. Waterproof implies a sealed membrane that provides a complete barrier.
The Breathability Factor
A true waterproof membrane can sometimes reduce a boot's breathability. While modern materials are designed to let sweat vapor escape, they may feel warmer than a non-waterproof equivalent, which is a key consideration for work in hot climates.
Slip Resistance is a Separate Feature
An oil-resistant sole will not break down from oil, but that doesn't automatically mean it's slip-resistant on an oily surface. While often paired, look for a specific slip-resistant rating to ensure you have proper traction in hazardous areas.
Making the Right Choice for Your Environment
Analyze your daily tasks to determine your primary need.
- If your primary focus is working with oils, fuels, or industrial chemicals: Prioritize an oil-resistant outsole to ensure the longevity and safety of your footwear.
- If your primary focus is working in wet, muddy, or sanitary conditions: Prioritize a truly waterproof design to keep your feet dry, comfortable, and healthy.
- If your primary focus is a multi-hazard environment (e.g., an industrial site with both chemical and water exposure): Invest in a boot that is explicitly rated as both oil-resistant and waterproof.
Ultimately, the right boot is a specialized tool engineered for the specific challenges of your job.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Oil-Resistant Boots | Waterproof Boots |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Protects the boot's material from degradation | Protects the wearer's foot from moisture |
| Key Benefit | Durability and longevity of the footwear | Comfort and foot health in wet conditions |
| Location of Feature | Outsole material | Upper construction and membrane |
| Ideal For | Environments with oils, fuels, solvents | Wet, muddy, or sanitary environments |
Need boots that are both oil-resistant AND waterproof?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of oil-resistant and waterproof shoes and boots, engineered to meet the specific demands of your work environment.
Contact us today to find the perfect protective footwear solution for your team and enhance workplace safety and comfort.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
- Wholesale Customizable Safety Boots Durable & Protective Footwear Manufacturing
- Wholesale Safety Footwear Manufacturer for Bulk & Custom OEM Orders
- Heavy Duty Nubuck Safety Boots Safety Shoes for Global Distribution
People Also Ask
- Why are slip-resistant soles important in oilfield safety shoes? Essential Traction to Prevent Falls
- What are the advantages of composite toe boots over steel or alloy toe boots? Lightweight, Non-Conductive Safety
- How does the mechanism of Negativity Bias apply to safety footwear? Safeguard Your Brand Reputation and Compliance
- What is the role of image tracking software in processing impact test videos for safety shoe toe caps? Key Data Insights
- Which industries commonly use safety Wellington boots? Essential Footwear for Wet & Hazardous Work
- What do the slip resistance certifications SRA, SRB, and SRC indicate? Choose the Right Safety Footwear
- Why is safety footwear critical in power station construction? Compare Professional Protection vs. Regular Shoes
- How do safety shoes contribute to cost savings for companies? A Strategic Investment in Risk and Cost Management



















