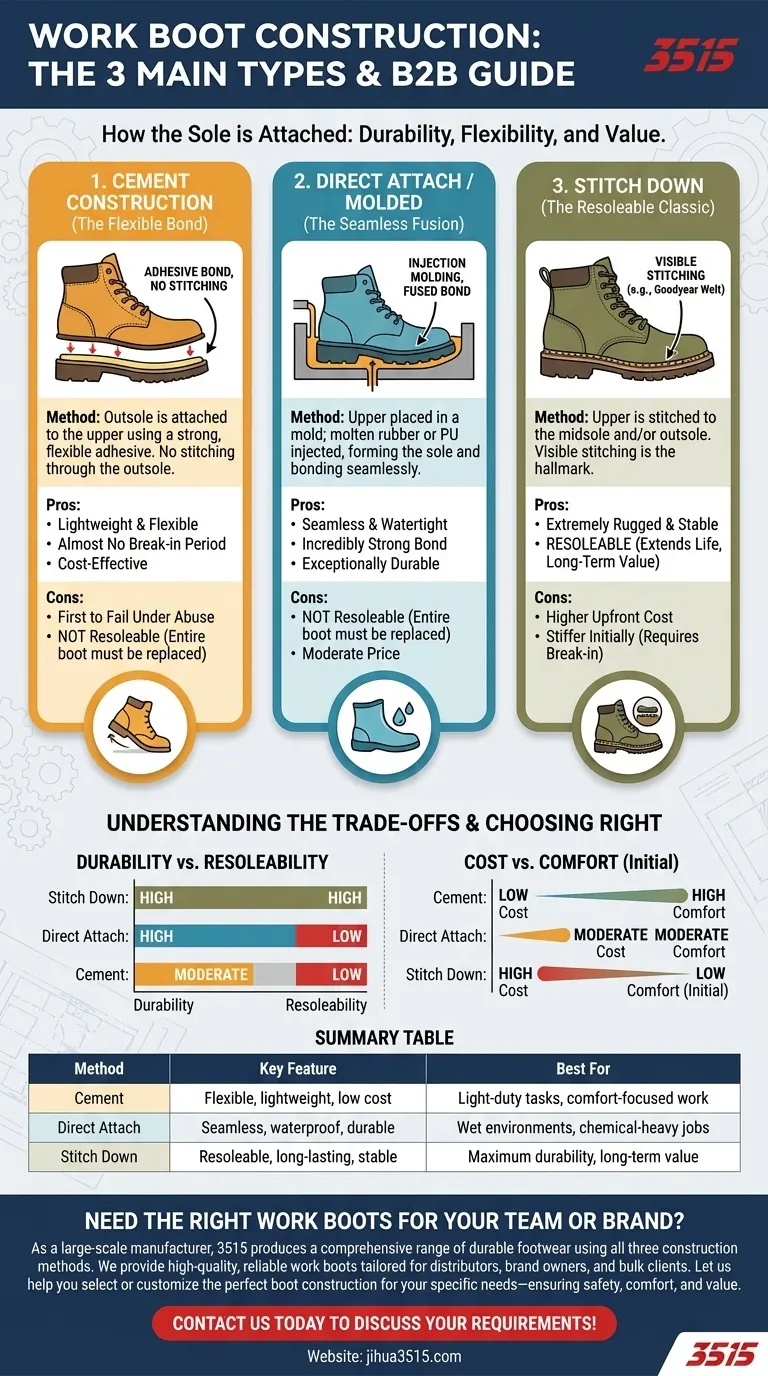
The three primary methods used to construct work boots are cement, direct attach (or molded), and stitch down construction. Each technique involves a different way of joining the boot's upper (the part that covers your foot) to the sole, which directly impacts the boot's durability, flexibility, water resistance, and long-term value.
Understanding the construction method of a work boot is more important than almost any other feature. It dictates the fundamental trade-off between flexibility, cost, and the boot's long-term durability and repairability.
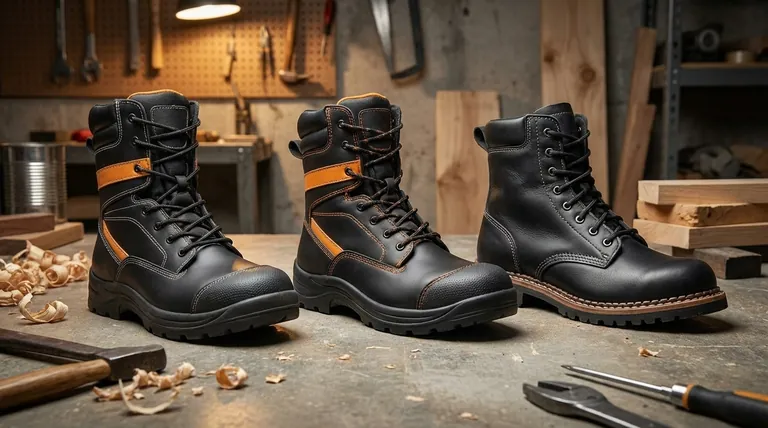

How a Boot's Sole is Attached
The "construction" of a work boot refers specifically to the method used to attach the sole to the upper. This connection point is a major stress area and is critical to the boot's overall performance and lifespan. While features like steel toes and reinforced arches are crucial for safety, the construction method is the foundation upon which that safety is built.
The Three Core Construction Methods Explained
Each method offers a distinct set of advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different types of work and environments.
Cement Construction (The Flexible Bond)
In this common and cost-effective method, the boot's outsole is attached to the upper using a strong, flexible adhesive. There is no stitching that goes through the outsole.
This creates a lightweight and highly flexible boot from day one, requiring almost no break-in period.
Direct Attach / Molded Construction (The Seamless Fusion)
This is a modern, high-tech process where the upper is placed into a mold. Molten rubber or polyurethane (PU) is then injected into the mold, forming the sole and bonding to the upper as it cools.
This method creates a seamless, watertight, and incredibly strong bond between the sole and the upper, making it exceptionally durable.
Stitch Down Construction (The Resoleable Classic)
This is a family of traditional techniques, including the well-known Goodyear Welt, where the upper is stitched to the midsole and/or outsole. This visible stitching around the edge of the boot is the hallmark of this construction.
It creates an extremely rugged and stable platform. More importantly, it is the only common method that allows a boot to be easily and repeatedly resoled by a cobbler.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cost vs. Lifespan
Choosing the right construction involves balancing your immediate needs with your long-term expectations for the boot.
The Durability Spectrum
Direct attach and stitch down methods create the strongest and most durable bonds. They are built to withstand constant twisting, flexing, and harsh conditions without the sole separating. Cement construction, while strong, can be the first to fail under extreme, daily abuse.
The Resoleability Factor
This is the single biggest difference. Stitch down construction is designed to be resoled. This means when the tread wears out, you can replace the sole for a fraction of the cost of new boots, dramatically extending their life.
Cement and direct attach boots are generally not resoleable. Once the sole is worn down, the entire boot must be replaced.
The Cost and Comfort Equation
Cement construction is typically the least expensive and most flexible out of the box. Stitch down boots are often the most expensive and stiffest initially, requiring a break-in period. Direct attach falls in the middle, offering a balance of high durability at a moderate price point.
How to Choose the Right Construction for Your Work
- If your primary focus is maximum long-term value and durability: Choose a Stitch Down boot, as its resoleable nature means your investment can last for many years.
- If your primary focus is a guaranteed waterproof seal and a tough bond for wet or chemical-heavy jobs: A Direct Attach / Molded boot provides superior resistance to sole separation and moisture.
- If your primary focus is lightweight comfort, flexibility, and a lower upfront cost for less demanding work: A Cement construction boot is often the most practical and comfortable choice.
Understanding how your boot is built is the first step to trusting it with your safety on the job.
Summary Table:
| Construction Method | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Cement | Flexible, lightweight, low cost | Light-duty tasks, comfort-focused work |
| Direct Attach / Molded | Seamless, waterproof, durable | Wet environments, chemical-heavy jobs |
| Stitch Down | Resoleable, long-lasting, stable | Maximum durability and long-term value |
Need the right work boots for your team or brand?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of durable footwear using all three construction methods. We provide high-quality, reliable work boots tailored for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients.
Let us help you select or customize the perfect boot construction for your specific needs—ensuring safety, comfort, and value.
Contact us today to discuss your requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
- Heavy Duty Nubuck Safety Boots Safety Shoes for Global Distribution
- Premium Sport Style Safety Boots for Bulk Orders
- Customizable Anti-Smash Safety Boots for Wholesale & Private Label Manufacturing
- Premium Suede Sport Safety Shoes for Wholesale & Bulk Orders
People Also Ask
- What does the 'M' in ASTM F2413-18 M/I/C EH PR MT stand for? Decoding Safety Footwear Labels
- What issues do construction workers face with traditional work shoes? Uncover the Hidden Costs of Poor Footwear
- How does the sole design of Rigmaster boots improve traction? Master Diamond-Plate Surfaces
- Why is slip resistance a critical feature for safety boots? Prevent Secondary Accidents in Aluminum Processing Centers
- How do fire boots differ from standard tactical or work boots? Essential Safety Insights for High-Risk Environments
- What are the common hazards that safety work boots protect against? Essential Protection for Your Job Site
- What is the importance of using corrosion-resistant materials in protective boots? Ensure Longevity in High-Disinfection
- What is the historical significance of cowboy boots? From Essential Workwear to Cultural Icon



















