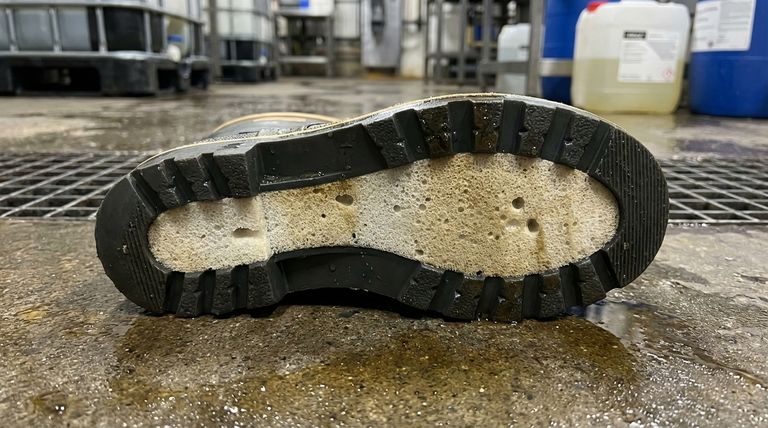
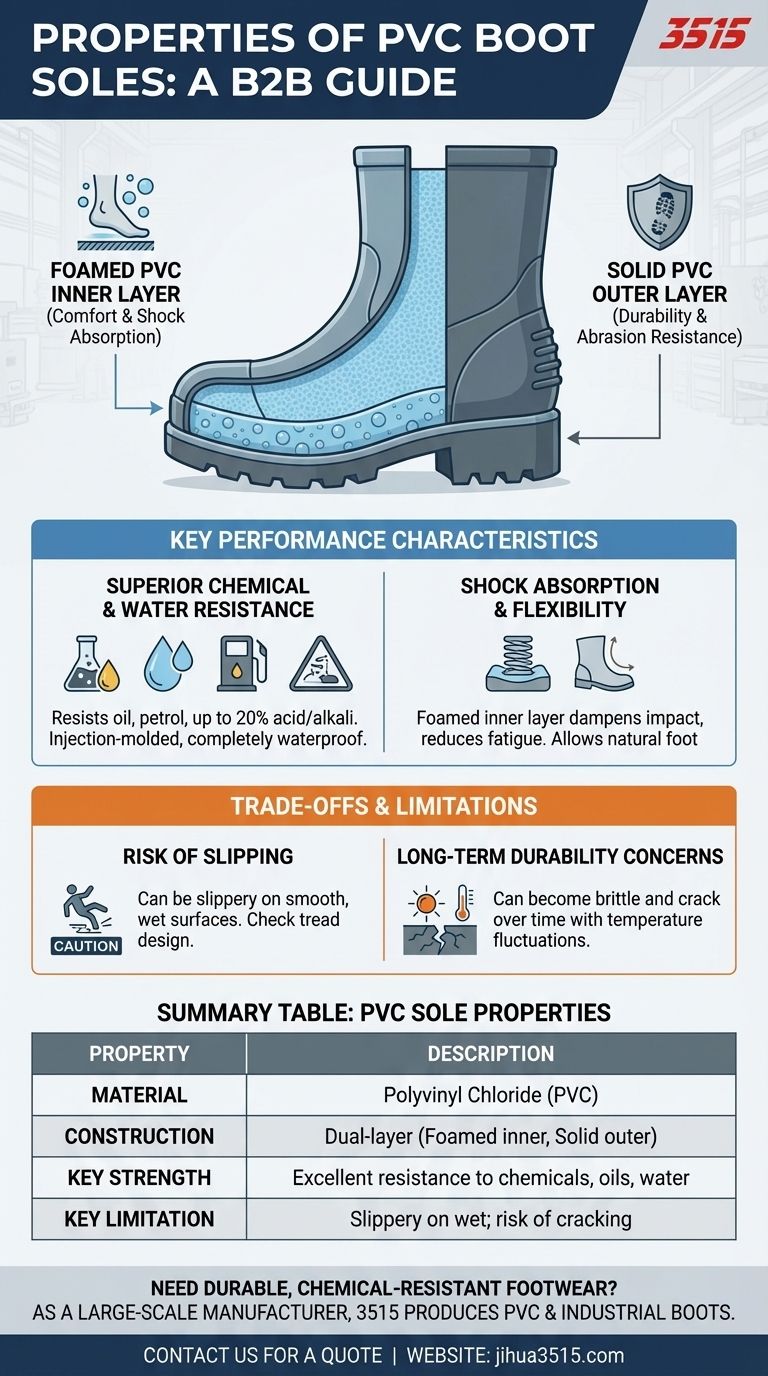
The sole of a PVC boot is engineered as a dual-layer system designed for specific industrial and wet-weather applications. It offers excellent chemical resistance and shock absorption due to its unique construction, which features a foamed polyvinyl chloride inner layer for comfort and a solid outer layer for durability.
A PVC sole's primary value lies in its exceptional resistance to chemicals, oils, and water at a low cost. However, this benefit must be weighed against its potential drawbacks, including a tendency to be slippery and the risk of cracking over time.

Deconstructing the PVC Sole: A Two-Layer System
Most PVC work boot soles are not a single, solid piece of material. They are intelligently constructed with two distinct layers, each serving a specific purpose.
The Inner Layer: Built for Comfort
The intermediate layer, which sits closest to your foot, is typically made of foamed polyvinyl chloride.
This material contains tiny air bubbles, which gives it shock-absorbing properties. Its primary job is to dampen the impact of walking on hard surfaces, reducing fatigue.
The Outer Layer: Built for Durability
The running layer, or outsole, is the part that makes contact with the ground. This is made of a more solid, dense PVC.
This layer is engineered to be resistant to deformation and abrasion, ensuring the boot holds its shape and withstands rough use without wearing down quickly.
Key Performance Characteristics
The material and structure of a PVC sole give it a distinct set of performance benefits, making it ideal for certain environments.
Superior Chemical and Water Resistance
The standout feature of PVC is its inertness. The material provides a reliable barrier against a range of harsh substances.
It is highly resistant to oil, petrol, and other oil-based products. It can also withstand exposure to acid and alkali solutions with concentrations of up to 20%.
Furthermore, the injection-molding process used to create PVC boots makes the entire boot, including the sole, a completely waterproof unit.
Shock Absorption and Flexibility
The foamed inner layer provides significant cushioning, making the boots more comfortable during long periods of standing or walking.
PVC as a material offers good flexibility, allowing for natural foot movement without the stiffness found in some other boot materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While PVC soles are highly effective in specific contexts, it is critical to understand their inherent limitations to ensure safety and performance.
The Risk of Slipping
One of the most significant drawbacks of PVC is that it can be slippery, especially on smooth, wet surfaces.
While many boots feature deep tread patterns to improve traction, the base material itself does not offer the same grip as rubber or other specialized sole compounds.
Long-Term Durability Concerns
Although the outsole is designed for abrasion resistance, PVC can become brittle over time.
This can lead to the sole developing cracks, particularly in environments with frequent temperature fluctuations, which compromises its waterproof integrity and structural support.
Is a PVC Sole Right for Your Needs?
Choosing the right boot sole depends entirely on the demands of your environment and task.
- If your primary focus is working in industrial or chemical environments: The exceptional resistance to oils, acids, and alkalis makes PVC an ideal and safe choice.
- If your primary focus is general wet-weather protection: The seamless waterproofing and low cost of PVC boots make them a highly practical option for farming, construction, or general use.
- If your primary focus is high-traction or long-term daily wear: You should carefully evaluate the tread design and be aware that other materials may offer superior grip and long-term crack resistance.
Ultimately, understanding a PVC sole's specific strengths and weaknesses empowers you to select the right tool for the job.
Summary Table:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Material | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
| Construction | Dual-layer: foamed inner for comfort, solid outer for durability |
| Key Strength | Excellent resistance to oils, chemicals (up to 20% acids/alkalis), and water |
| Key Limitation | Can be slippery on wet surfaces; may crack over time, especially with temperature changes |
Need durable, chemical-resistant footwear for your team?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of PVC and other industrial boots for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of safety footwear, ensuring you get the right balance of protection, comfort, and value.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Durable Rubber-Soled Utility Shoes for Wholesale & Custom Brand Manufacturing
- Factory-Direct Wholesale Canvas Boots with High-Traction Rubber Soles
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
- Wholesale Comfortable Business Casual Shoes Custom Manufacturing
- Wholesale Modern Comfort Shoes with Dial Closure for Private Label & Bulk Orders
People Also Ask
- What are the main drawbacks of traditional wellingtons for extended use? Find Your Perfect Fit
- Can canvas shoes be worn in rainy conditions? The Truth About Water Resistance
- Why is staying active important when wearing wellies in cold weather? The Key to Warm Feet
- Are PVC boots durable despite being lightweight? Yes, and Here's Why
- Are all Wellington boots available in a range of calf widths? Find Your Perfect, Tailored Fit
- Describe the injection molding process for PVC rain boots. High-Speed, Seamless Production
- How does the tall height of PVC boots enhance protection? Achieve Maximum Leg and Ankle Safety
- Where can consumers buy FSC-certified Wellington boots in the UK? Find Sustainable & Ethical Wellies



















