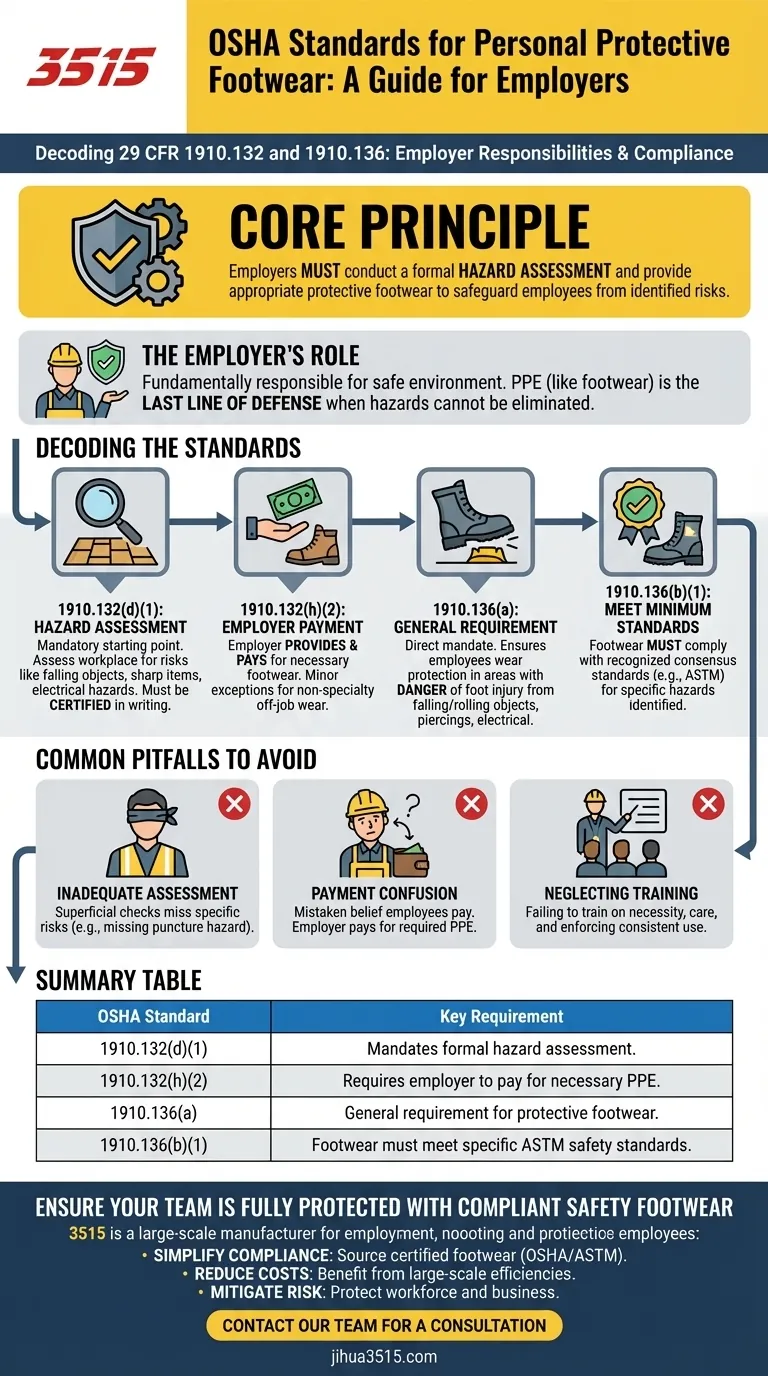
The OSHA standards referenced are 29 CFR 1910.132(d)(1), 1910.132(h)(2), 1910.136(a), and 1910.136(b)(1). These regulations are not just a list of rules; they form a complete system that places the responsibility on the employer to assess workplace hazards and provide appropriate protective footwear to safeguard employees.
The core principle of these standards is straightforward: employers are required to conduct a formal hazard assessment of the workplace, and if foot injuries are a risk, they must provide and pay for protective footwear that meets specific safety criteria.

The Employer's Role in Workplace Safety
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) establishes that employers are fundamentally responsible for providing a safe work environment. This includes identifying potential dangers and mitigating them.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), such as safety footwear, is considered a last line of defense when a hazard cannot be eliminated through engineering or administrative controls.
Decoding the Specific Footwear Standards
Each regulation cited plays a distinct role in ensuring worker safety. They build on one another to create a comprehensive requirement for employers.
1910.132(d)(1): The Foundation is Hazard Assessment
This standard is the mandatory starting point. It requires the employer to assess the workplace to determine if hazards that necessitate the use of PPE are present.
For footwear, this means looking for risks like falling or rolling objects, sharp objects that could pierce a sole, or exposure to electrical hazards. This assessment must be certified in writing.
1910.132(h)(2): The Question of Payment
This regulation clarifies that if the hazard assessment determines protective footwear is necessary, the employer must provide it at no cost to the employee.
There are minor exceptions, such as for non-specialty safety-toe footwear that an employee is permitted to wear off the job site, but the general rule is that the employer pays for required PPE.
1910.136(a): The General Requirement for Foot Protection
This is the direct mandate for foot protection. It states that employers must ensure each affected employee uses protective footwear when working in areas with a danger of foot injury.
The standard specifically lists injuries from falling or rolling objects, objects piercing the sole, and electrical hazards from static-discharge or electric-shock.
1910.136(b)(1): Ensuring Equipment Meets a Minimum Standard
This rule ensures the protective footwear is actually effective. It requires that the footwear complies with recognized consensus standards, such as those from the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM).
Simply providing a "steel-toe boot" is not enough. The equipment must be certified to protect against the specific hazards identified in the initial assessment.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Implementing a compliant foot protection program requires careful attention to detail. Misinterpretations can lead to compliance issues and, more importantly, employee injuries.
Inadequate Hazard Assessment
A common failure is conducting a superficial assessment that misses specific risks. For example, a workplace may have a risk of falling objects (requiring a safety toe) and also sharp debris on the floor (requiring a puncture-resistant sole). Both must be identified.
Confusion Over Payment Rules
Employers sometimes mistakenly believe employees are responsible for all footwear. If the footwear is required to protect against a workplace hazard, the employer must provide and pay for it.
Neglecting Training and Enforcement
Providing the equipment is only half the battle. Employers must also train employees on why the footwear is necessary and how to care for it, and they must enforce its use consistently.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Whether you are an employer implementing a policy or an employee seeking to understand your rights, your focus should be on the underlying hazard.
- If you are an employer: Your primary focus must be on conducting and documenting a thorough hazard assessment to identify every potential foot injury risk.
- If you are an employee: Your primary focus is on consistently and correctly using the specific protective footwear your employer provides for the tasks you perform.
Ultimately, a successful safety program is built on a clear understanding of the risks and a shared commitment to mitigating them.
Summary Table:
| OSHA Standard | Key Requirement |
|---|---|
| 1910.132(d)(1) | Mandates a formal workplace hazard assessment. |
| 1910.132(h)(2) | Requires employer to pay for necessary PPE. |
| 1910.136(a) | General requirement for protective footwear. |
| 1910.136(b)(1) | Footwear must meet specific ASTM safety standards. |
Ensure Your Team is Fully Protected with Compliant Safety Footwear
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of certified safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of compliant shoes and boots designed to meet the specific hazards identified in your OSHA assessment.
We help you:
- Simplify Compliance: Source certified footwear that meets OSHA and ASTM standards.
- Reduce Costs: Benefit from our large-scale manufacturing efficiencies.
- Mitigate Risk: Protect your workforce and your business from costly violations and injuries.
Let's discuss your specific needs. Contact our team today for a consultation on compliant safety footwear solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Premium KPU Injection Athletic Style Safety Shoes
- Wholesale Anti-Smash & Puncture-Proof Safety Shoes Custom Manufacturing for Brands
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
- Heavy-Duty Waterproof Nubuck Safety Boots Safety Shoes for Bulk Supply
People Also Ask
- Are employers required to provide steel-toe rubber boots at no cost to employees? Yes, under OSHA rules.
- What materials are used for safety toes? Choose Steel, Composite, or Aluminum for Your Work Boots
- Is it normal to wear shoes in the house? A Guide to Hygiene, Comfort & Culture
- What are the cultural perspectives on wearing shoes in the house? A Guide to Home Etiquette & Hygiene
- Can heavy duty work boots be worn daily outside of work? Discover Durable, All-Day Comfort



















