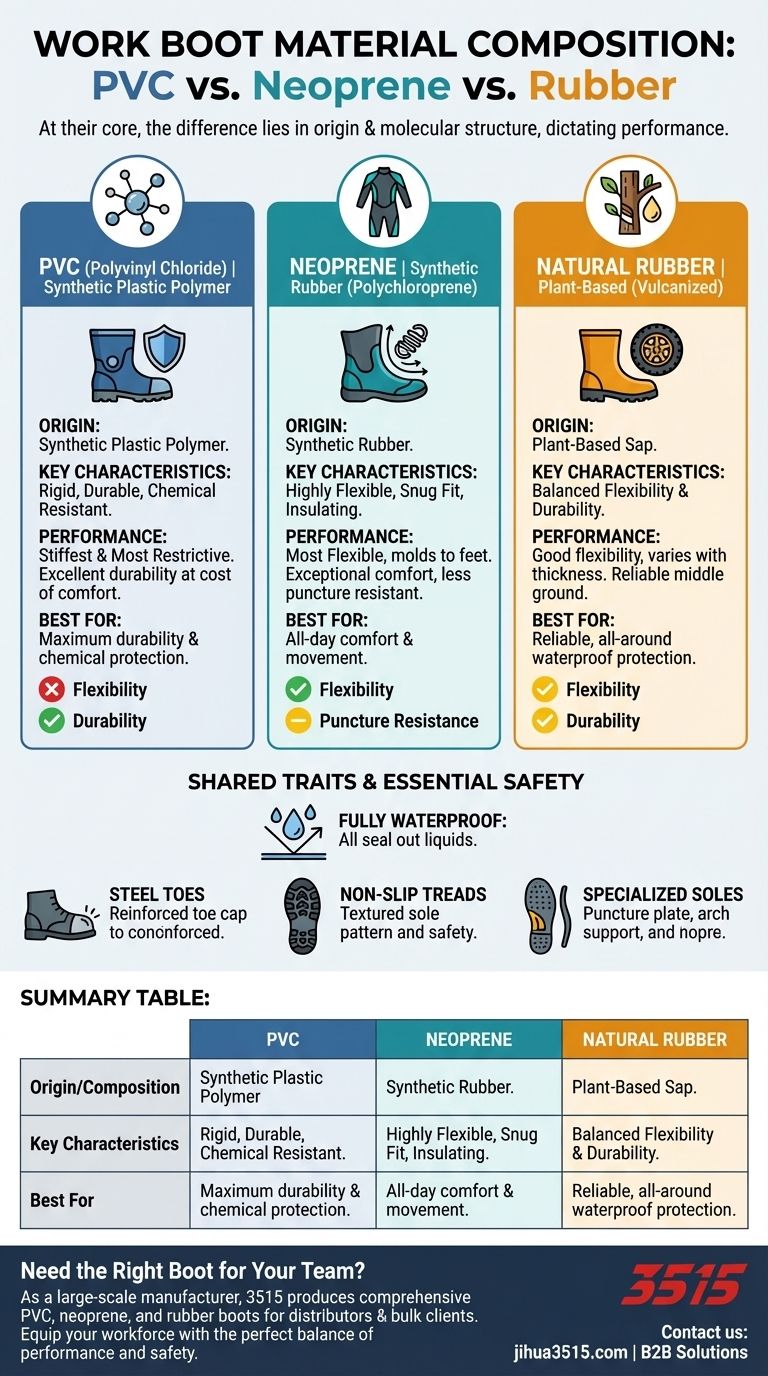
At their core, the primary difference between these work boot materials lies in their origin and molecular structure. Natural rubber is a plant-based material, while PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) is a rigid plastic polymer, and neoprene is a flexible synthetic rubber. These fundamental differences directly dictate their performance in terms of flexibility, fit, and durability.
The choice between PVC, neoprene, and rubber is not about which is universally better, but about matching the material's inherent properties—specifically its stiffness or flexibility—to the demands of your specific work environment.

Deconstructing the Core Materials
Understanding the origin of each material is the first step in selecting the right boot. Each has a distinct composition that defines its behavior and ideal use case.
Natural Rubber: The Classic Protector
Rubber is a natural material sourced from the sap of plants. To be used in footwear, it undergoes a process called vulcanization, which uses heat and additives to improve its strength, elasticity, and waterproof properties.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): The Rigid Defender
PVC is a synthetic plastic polymer. It is known for its inherent stiffness and durability, making it highly resistant to abrasions and many chemicals. Its rigid structure provides robust protection.
Neoprene: The Flexible Insulator
Neoprene is also a synthetic material, specifically a type of synthetic rubber made from polychloroprene. It was developed as a substitute for natural rubber and is prized for its exceptional flexibility and insulating properties.
How Composition Dictates Performance
While all three materials are waterproof, their underlying composition creates significant differences in how they feel and function during a workday.
Waterproofing: A Shared Trait
All three materials—PVC, neoprene, and rubber—are fully waterproof. They effectively seal out liquids, making them suitable for wading or working in extremely wet conditions.
Flexibility and Fit: The Key Differentiator
This is where the materials diverge most significantly. Neoprene is the most flexible, easily molding to the shape of your feet and calves for a snug, personalized fit that allows for maximum movement.
Natural rubber offers good flexibility, but its adaptability depends on the thickness of the material. It sits in the middle ground between neoprene and PVC.
PVC is by far the stiffest and most restrictive material. While this provides rigid protection, it significantly limits the natural motion of your foot and ankle.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing one material means prioritizing certain features over others. There is no single material that excels in every category.
PVC: Durability vs. Comfort
The primary trade-off with PVC is its rigidity. You gain excellent durability and chemical resistance at the cost of flexibility and day-long comfort. The lack of give can lead to fatigue if your job requires a lot of walking or squatting.
Neoprene: Flexibility vs. Puncture Resistance
Neoprene's exceptional flexibility and comfort are its main advantages. However, this softness can make it less resistant to punctures or slashes from sharp objects compared to the hard shell of a PVC boot.
Rubber: A Balanced, but Variable, Approach
Natural rubber offers a reliable balance of flexibility and durability. However, the quality and thickness can vary, impacting both its comfort and its lifespan. It provides a solid middle ground but may not be specialized enough for extreme conditions.
Beyond the Primary Material: Essential Safety Features
The boot's shell material is only one part of the equation. True work boots integrate crucial safety components regardless of whether they are made of PVC, rubber, or neoprene.
Structural Reinforcement
Look for features like steel toes to protect against compression and impact. Many also include reinforced sole plates to prevent punctures from below and supportive arches for stability when climbing ladders.
Specialized Soles
The outsole is critical for safety. Features like non-slip treads are essential for maintaining traction on wet or slick surfaces, while some boots offer insulation against electrical hazards.
Making the Right Choice for Your Work Environment
Your final decision should be based on the specific tasks you perform daily.
- If your primary focus is all-day comfort and movement: Choose neoprene for its superior flexibility and personalized fit.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and chemical protection: Choose PVC for its rigid, non-reactive structure.
- If your primary focus is a reliable, all-around waterproof boot: Choose natural rubber as the classic, balanced option.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental composition of each material empowers you to select a boot that functions as a true tool for your job.
Summary Table:
| Material | Origin / Composition | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVC | Synthetic Plastic Polymer | Rigid, Durable, Chemical Resistant | Maximum durability & chemical protection |
| Neoprene | Synthetic Rubber (Polychloroprene) | Highly Flexible, Snug Fit, Insulating | All-day comfort and movement |
| Natural Rubber | Plant-Based (Vulcanized) | Balanced Flexibility & Durability | Reliable, all-around waterproof protection |
Need the Right Boot for Your Team?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of PVC, neoprene, and rubber work boots for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our expertise ensures you get the perfect balance of material performance, safety features, and value.
Let us help you equip your workforce with the ideal footwear for their specific job demands.
Contact our team today for a consultation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Premium KPU Injection Athletic Style Safety Shoes
- Wholesale Safety Footwear Manufacturer for Bulk & Custom OEM Orders
- Wholesale Anti-Smash & Puncture-Proof Safety Shoes Custom Manufacturing for Brands
- Premium High-Cut Waterproof Safety Boots Manufacturing & Wholesale Solutions
- High Performance Fire-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots
People Also Ask
- What is the benefit of using a leather protecting cream on work boots? Prevent Cracking & Extend Boot Life
- What is the best material for work boots and why? Match the Material to Your Job's Hazards
- What are the disadvantages of synthetic/leather boots? The Long-Term Value Trade-Off
- How can the lifespan of PVC boots be extended? Protect Your Investment with Simple Care
- What are kiltie boots? A Guide to Rugged Style and Maximum Durability
- What is the purpose of safety toe boots? Ultimate Protection for Your Work Environment
- What type of protective agent is better for suede and nubuck leather boots? Use a Dedicated Waterproofing Spray
- What are some tips for maintaining and cleaning motorcycle boots? Extend the Life of Your Safety Gear



















