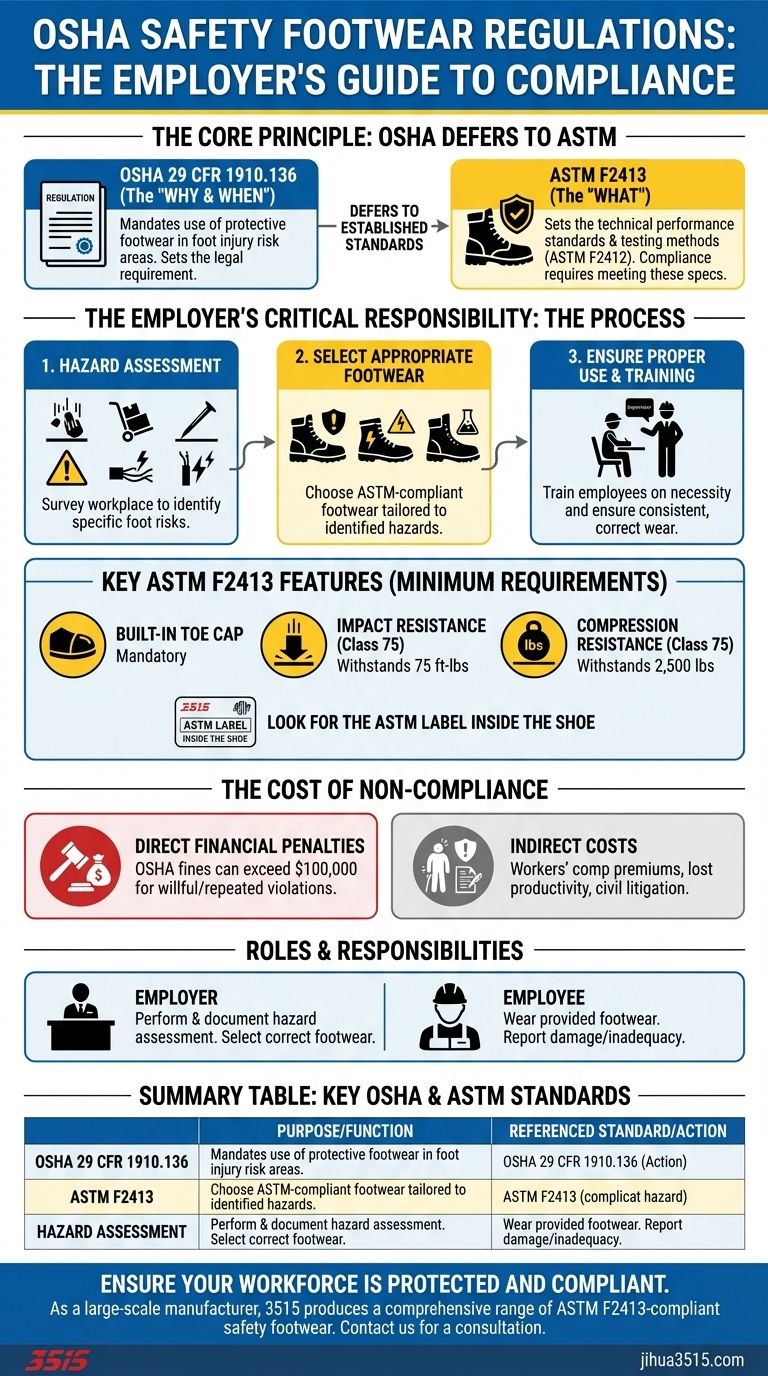
The core OSHA regulation for safety footwear is 29 CFR 1910.136, which mandates that employers must ensure employees use protective footwear in areas with foot injury risks. Critically, OSHA itself does not publish detailed footwear specifications; instead, it requires that all safety footwear complies with the technical standards set by organizations like the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), with ASTM F2413 being the current prevalent standard.
The central takeaway is that OSHA compliance is not about a specific type of boot, but about a process. Employers must first conduct a workplace hazard assessment and then select footwear that meets the appropriate ASTM standard to protect against those specific identified risks.

The Core Principle: OSHA Defers to ASTM Standards
OSHA's approach to personal protective equipment (PPE) is to establish the legal requirement for its use and then defer to established industry consensus standards for the technical performance specifications.
What is 29 CFR 1910.136?
This is OSHA's specific standard for foot protection. It legally obligates employers to ensure employees use protective footwear when they are exposed to dangers from falling objects, rolling objects, items that could pierce the sole, or electrical hazards.
This regulation is the "why" and "when" of safety footwear. It sets the requirement based on workplace risk.
What is ASTM F2413?
This is the standard that provides the "what." The ASTM F2413 standard, titled Standard Specification for Performance Requirements for Protective (Safety) Toe Cap Footwear, outlines the minimum design, performance, testing, and classification requirements.
To be compliant with OSHA's rule, the footwear must meet or exceed the specifications laid out in this ASTM document.
Key Requirements of an ASTM-Compliant Boot
Footwear that meets the ASTM F2413 standard is tested according to methods in ASTM F2412. The label inside the shoe will indicate which standards it meets.
Key performance criteria include:
- Built-in Toe Cap: This is a mandatory, non-negotiable component of any footwear certified under this standard.
- Impact Resistance: Protection against falling objects.
- Compression Resistance: Protection against rolling objects.
The highest rating for both is Class 75, meaning the toe cap can withstand 75 foot-pounds of impact and 2,500 pounds of compression.
The Employer's Critical Responsibility: The Hazard Assessment
The entire compliance process begins with the employer's legal duty to analyze the workplace and identify specific dangers to employees' feet.
Identifying the Need for Protection
An employer must survey the work environment and identify potential hazards. This includes risks from heavy materials, rolling carts, sharp objects like nails, chemical spills, or live electrical circuits.
This hazard assessment is the foundational step. Without it, you cannot select the appropriate level of protection.
Selecting the Appropriate Footwear
Once hazards are known, the employer must select footwear designed to counter them. A worksite with falling lumber requires impact-rated boots, while an area with exposed wiring demands electrical hazard (EH) rated footwear.
Features like non-skid soles or oil resistance are not universal mandates but are chosen based on the specific needs revealed in the hazard assessment, such as wet floors or oily surfaces.
Ensuring Proper Use
Providing the footwear is only part of the responsibility. Employers must also train employees on why the footwear is necessary and ensure they wear it consistently and correctly whenever they are exposed to the identified hazards.
Understanding the Stakes: The Cost of Non-Compliance
Failing to adhere to OSHA's footwear standards is not just a safety risk; it's a significant financial and operational liability.
Direct Financial Penalties
OSHA can issue citations and fines for non-compliance. These can range from warnings for minor infractions to severe penalties for serious issues.
For willful or repeated violations, fines can exceed $100,000, creating a substantial financial burden on the business.
Indirect Costs of Failure
Beyond OSHA fines, a workplace foot injury can lead to immense indirect costs. These include increased workers' compensation premiums, lost productivity during an employee's absence, and the potential for civil litigation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Role
The responsibility for foot safety is shared, but the primary obligations are defined by your role in the workplace.
- If you are an employer: Your first and most critical duty is to perform and document a thorough hazard assessment to determine the specific footwear needed for each job task.
- If you are an employee: Your responsibility is to wear the provided protective footwear as required and to immediately inform your supervisor if you believe it is damaged or inadequate for the task.
Properly understood, safety footwear regulations are the framework for a collaborative effort that protects both workers and the business itself.
Summary Table:
| Key OSHA Regulation | Purpose | Referenced Standard |
|---|---|---|
| 29 CFR 1910.136 | Mandates use of protective footwear where foot injury risks exist. | ASTM F2413 (Performance Requirements) |
| Hazard Assessment | Employer's legal duty to identify workplace-specific foot hazards. | Informs selection of appropriate ASTM-rated footwear (e.g., Impact, Compression, EH). |
Ensure your workforce is fully protected and your business is OSHA-compliant.
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of ASTM F2413-compliant safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of safety shoes and boots, from impact and compression-resistant models to electrical hazard-rated options.
We help you meet your legal obligations and protect your employees by providing high-quality, certified footwear tailored to the specific risks identified in your hazard assessment.
Contact 3515 today for a consultation on your safety footwear needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Wholesale Durable Safety Boots | Custom Steel Toe & Puncture-Resistant Manufacturing
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
- Advanced KPU Athletic Safety Shoe with Steel Toe Cap Anti-Slip Rotary Lacing System
- Custom Wholesale Leather Safety Boots Direct Factory Manufacturing
People Also Ask
- What is the current safety footwear standard in Europe? Your Guide to EN ISO 20345
- What are chemical-resistant shoes and what industries require them? Essential PPE for Hazardous Workplaces
- What does electrical hazard protection (EH) in safety footwear entail? Essential Safety for High-Risk Environments
- How do steel, aluminium, and composite toe caps compare? Choose the Right Safety Toe for Your Job
- How do high-traction, slip-resistant outsoles on safety boots contribute to worker safety in mines? | Prevent Mining Falls
- Can firefighter boots be resoled? A Guide to Safe & Cost-Effective Repair
- What are the basic ratings of security guard safety boots? A Guide to EN ISO 20345 Standards
- Why are metatarsal boots important in high-impact workplaces? Essential Protection for Heavy Industry



















