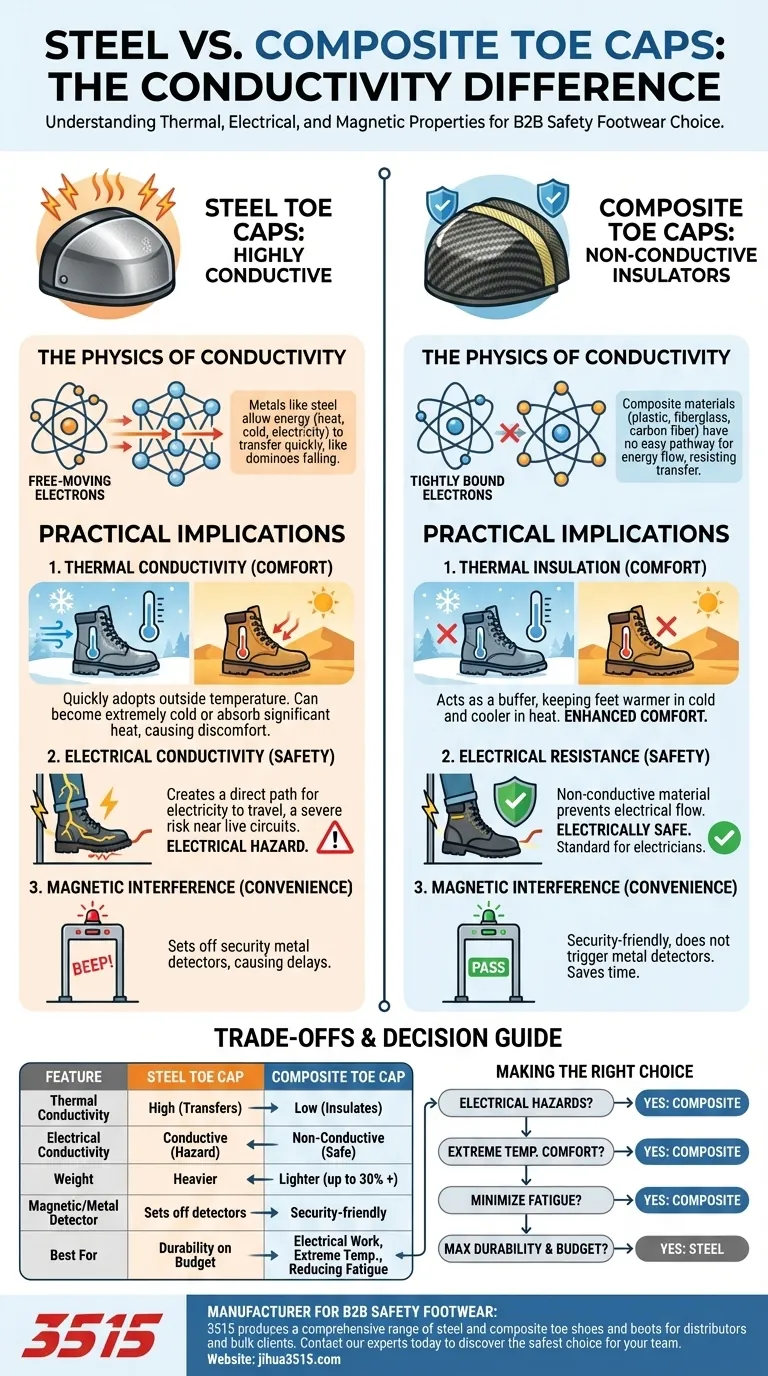
The fundamental difference in conductivity is that steel toe caps are highly conductive, while composite toe caps are non-conductive. Steel readily transfers heat, cold, and electricity, creating potential comfort and safety issues. Composite materials, such as plastic, carbon fiber, or Kevlar, act as insulators against these elements.
Choosing the right safety toe is not just about impact resistance; it's about matching the material's properties to your specific work environment. The critical distinction is that steel conducts energy while composite insulates against it, a factor that directly impacts both your safety and your daily comfort.

The Physics of Conductivity in Safety Toes
To understand the practical differences, we first need to look at why these materials behave so differently. The core distinction lies in their atomic structure and how easily energy can pass through them.
How Steel Toes Transfer Energy
Steel is a metal alloy. Metals have a crystalline structure with free-moving electrons that are not tightly bound to any single atom.
This "sea" of electrons allows energy—whether thermal (heat/cold) or electrical—to transfer through the material quickly and efficiently. Think of it like a line of dominoes; one push at the start travels rapidly to the end.
Why Composite Toes Act as Insulators
Composite materials are non-metallic and are often made from plastics, fiberglass, or carbon fiber. The electrons in these materials are tightly bound to their atoms.
Because there are no free-moving electrons, there is no easy pathway for energy to flow. This structure effectively resists the transfer of heat, cold, and electricity, making the material an excellent insulator.
Practical Implications for Your Workday
This difference in conductivity has direct, tangible effects on safety, comfort, and even convenience on the job.
Thermal Conductivity: Comfort in Extreme Temperatures
Steel's high thermal conductivity means it quickly adopts the temperature of its surroundings. In cold weather, the steel cap becomes very cold, pulling heat away from your feet. In hot environments, it can absorb and hold heat, creating significant discomfort.
Composite toes, being insulators, provide a buffer against outside temperatures. They help keep your feet warmer in the cold and cooler in the heat, maintaining a much more stable and comfortable internal environment.
Electrical Conductivity: The Critical Safety Factor
For anyone working with or near live electrical circuits, this is the most important distinction. Steel's conductivity creates a direct path for electricity to travel through the boot to your body if you make contact with a live source.
Composite toe caps are non-conductive and do not present this risk. This makes them the standard and often required choice for electricians, utility workers, and maintenance professionals in high-risk electrical environments.
Magnetic Interference: The Metal Detector Problem
A secondary consequence of steel's metallic properties is its interaction with security systems. Steel toe boots will consistently set off metal detectors.
Composite toes are "security friendly" and will not trigger these detectors, saving time and hassle for workers who must frequently pass through security checkpoints.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Conductivity is a critical factor, but it isn't the only one. A truly informed decision requires weighing all the pros and cons.
Protection and Durability
Both steel and composite toe caps must meet the same ANSI/ASTM safety standards for impact and compression resistance.
However, steel is generally more durable against everyday wear and can withstand a higher maximum impact load before fracturing. After a significant impact, a composite toe may crack and must be replaced, whereas a steel toe might only dent.
Weight and Fatigue
Composite toe caps are significantly lighter than their steel counterparts—often by 30% or more.
This weight reduction can lead to a noticeable decrease in foot fatigue over the course of a long shift or work week, contributing to overall comfort and endurance.
Cost and Availability
Steel has been the industry standard for decades. This has made steel toe footwear more affordable and available in a much wider variety of styles and brands.
Composite technology is newer and more expensive to produce, which is reflected in the higher retail price of the boots.
Making the Right Choice for Your Environment
Your specific job site and daily tasks should be the ultimate guide in your decision.
- If your primary focus is working with or near electrical hazards: Composite is the only acceptable choice due to its essential non-conductive safety feature.
- If your primary focus is comfort in extreme hot or cold climates: Composite's thermal insulation will provide a significant advantage in keeping your feet comfortable.
- If your primary focus is minimizing daily fatigue from walking or standing: The lighter weight of a composite toe will make a noticeable difference.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability on a strict budget: Steel remains a reliable, cost-effective, and widely available option for general-purpose protection.
Ultimately, understanding the role of conductivity empowers you to choose safety footwear that protects you from more than just impact.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Steel Toe Cap | Composite Toe Cap |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | High (Transfers heat/cold) | Low (Insulates against temperature) |
| Electrical Conductivity | Conductive (Electrical hazard) | Non-Conductive (Electrically safe) |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter (up to 30%+) |
| Magnetic/Metal Detector | Sets off detectors | Security-friendly |
| Best For | Maximum durability on a budget | Electrical work, extreme temperatures, reducing fatigue |
Need Safety Toe Boots That Match Your Specific Job Hazards?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of steel and composite toe shoes and boots, ensuring you get the precise combination of protection, comfort, and compliance your workforce needs.
Let us help you make the safest choice. Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and discover how our durable, comfortable, and job-specific safety boots can benefit your team.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Premium High-Cut Waterproof Safety Boots Manufacturing & Wholesale Solutions
- Wholesale Safety Boots Manufacturer for Custom & Private Label Orders
- Premium KPU Injection Athletic Style Safety Shoes
- Premium Grain Leather Safety Boots for Bulk Supply
- Premium Wholesale Wheat Nubuck Safety Boot with Rapid Lacing System
People Also Ask
- How can one prevent blisters when wearing steel toe boots? A Complete Guide to Pain-Free Workdays
- Are steel toe boots only for construction workers? Discover the Right Safety Footwear for Your Industry
- What type of safety toe is recommended for hunting boots? Choose the Right Toe for Your Hunt
- How do steel toe shoes protect workers in areas with large, movable machinery? Essential Safety Guide
- What is the difference between safety toe and steel toe footwear? Choose the Right Protection for Your Job
- What are some common myths about steel toe work boots? Debunked for Modern Workers
- What industries are safety toe work boots best suited for? Protect Your Feet in High-Risk Environments
- Are steel or composite toe boots OSHA approved? Decoding the Standards for Workplace Safety



















