At its core, OSHA requires employers to ensure their employees wear protective footwear when working in areas where there is a danger of foot injuries. This includes protection from falling or rolling objects, punctures, and electrical hazards. While OSHA sets this mandate, it relies on consensus standards from organizations like ASTM International to define the specific performance criteria that compliant footwear must meet.
The central requirement isn't about a specific brand or style of shoe. It's about a mandatory process: the employer must first assess workplace foot hazards and then provide footwear that meets the specific ASTM F2413 standard for protection against those identified hazards.

The OSHA and ASTM Connection: Who Sets the Rules?
Understanding safety footwear compliance means understanding the relationship between two key organizations: OSHA and ASTM. They play distinct but complementary roles.
OSHA's Role: The "Why" and "When"
OSHA, through its regulations (specifically 29 CFR 1910.136), legally requires the use of protective footwear.
Their mandate is broad: if a workplace hazard assessment reveals a risk to an employee's feet, the employer is legally obligated to ensure the employee has and uses appropriate protective footwear.
OSHA inspectors verify that this process is being followed, but they don't certify the footwear itself.
ASTM's Role: The "What" and "How"
ASTM International sets the technical specifications. The current standard, ASTM F2413, details the minimum requirements for performance.
This standard outlines exactly how a shoe must be designed, tested, and labeled to be considered "safety footwear." When OSHA requires protective footwear, they are referring to footwear that meets this ASTM standard.
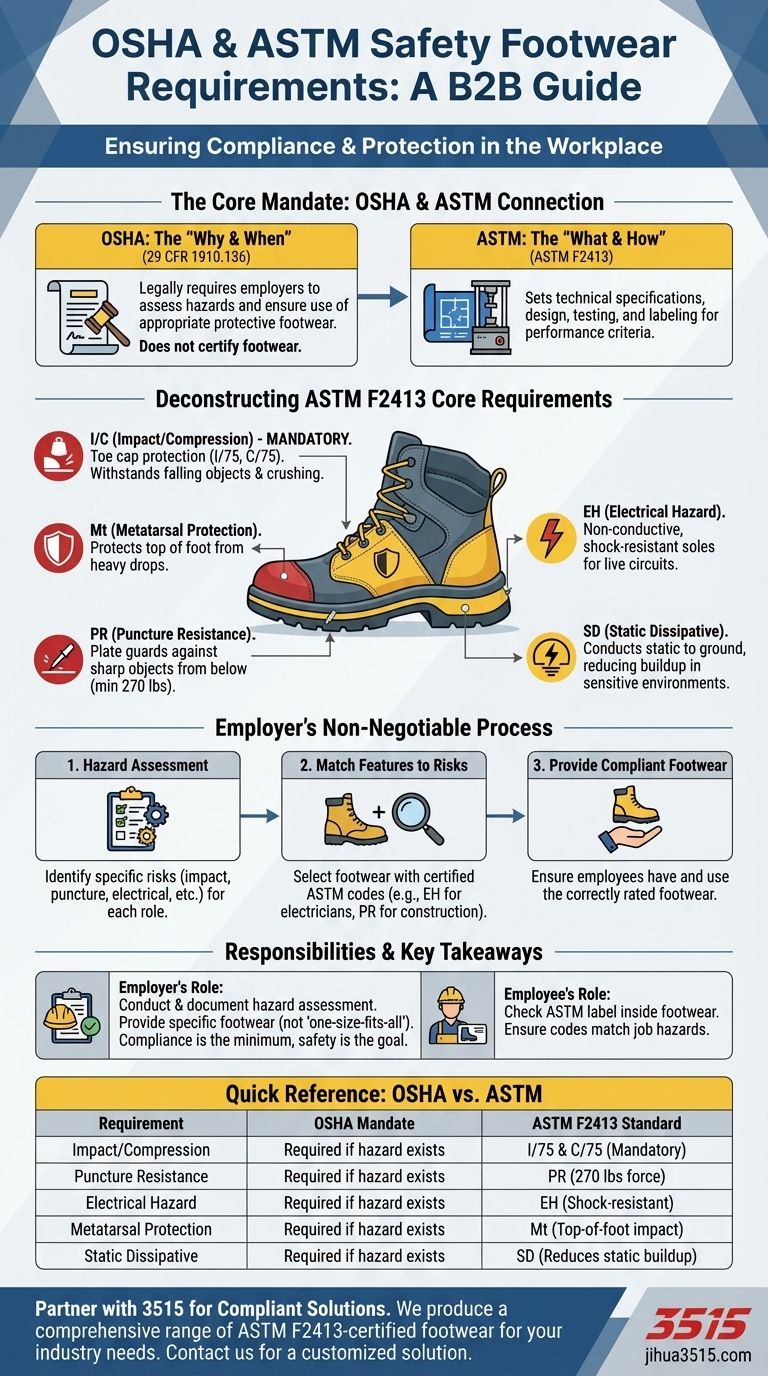
Deconstructing the Core ASTM F2413 Requirements
To be compliant, safety footwear must be certified by an independent lab to meet specific criteria. The most critical requirements are identified by codes on a label inside the shoe.
Impact (I) and Compression (C) Resistance
This is the most fundamental requirement and is mandatory for any ASTM-compliant safety shoe. It ensures the shoe protects the toes from falling objects and crushing forces.
The highest rating is I/75 and C/75, which means the toe cap can withstand 75 foot-pounds of impact and 2,500 pounds of compression.
Metatarsal Protection (Mt)
This provides protection for the top of the foot (the metatarsal bones) from impact. It is a crucial feature in environments with a high risk of heavy objects dropping directly onto the foot.
Puncture Resistance (PR)
Footwear with a PR rating includes a puncture-resistant plate built into the sole to protect the foot from sharp objects like nails, glass, or metal shards from below.
The plate must withstand a minimum of 270 pounds of force.
Electrical Hazard Protection (EH)
EH-rated footwear is designed with non-conductive, shock-resistant soles and heels.
It is a secondary source of protection intended to reduce the potential for electric shock when the soles are exposed to live electrical circuits.
Static Dissipative (SD)
SD-rated footwear is designed to reduce the buildup of static electricity by conducting it safely to the ground.
This is critical in environments where static discharge could damage sensitive electronics or ignite flammable materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Responsibilities
Simply buying a "safety shoe" is not enough to ensure compliance or true safety. The context of the work environment is paramount.
The Hazard Assessment is Non-Negotiable
The employer's primary responsibility is to perform a thorough hazard assessment for each job role.
This assessment dictates the specific features required. An electrician needs EH-rated boots, while a roofer needs PR-rated boots. Using the wrong one provides a false sense of security.
Compliance is the Minimum, Not the Goal
Meeting the OSHA and ASTM standards is the legal baseline. The true goal is to prevent injury.
Employers are encouraged to select footwear that exceeds minimum requirements when a hazard assessment indicates a higher level of risk.
One Type of Shoe Rarely Fits All
A common mistake is selecting a single type of safety shoe for an entire facility.
A warehouse worker, a welder, and a maintenance technician face vastly different foot hazards and require footwear with different protective features.
How to Ensure Compliance and Safety
Making the right choice comes down to matching the footwear's certified features to the specific hazards of the job.
- If you are an employer: Your first step is to conduct and document a hazard assessment to identify the specific risks (impact, puncture, electrical, etc.) for each job role.
- If you are an employee: Look for the ASTM F2413 label inside the footwear and ensure the specific protection codes (like EH, PR, Mt) match the known hazards of your job.
- For general construction or warehouse work: Prioritize footwear with I/75 and C/75 ratings for impact and compression, and strongly consider PR for puncture resistance.
- For electricians or maintenance near live circuits: You must select footwear specifically rated for Electrical Hazard (EH) protection.
Ultimately, workplace safety is a shared responsibility built on a clear understanding of the risks and the proper selection of equipment designed to mitigate them.
Summary Table:
| Requirement | OSHA Mandate | ASTM F2413 Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Impact/Compression | Required if hazard exists | I/75 & C/75 (Mandatory) |
| Puncture Resistance | Required if hazard exists | PR (270 lbs force) |
| Electrical Hazard | Required if hazard exists | EH (Shock-resistant) |
| Metatarsal Protection | Required if hazard exists | Mt (Top-of-foot impact) |
| Static Dissipative | Required if hazard exists | SD (Reduces static buildup) |
Ensure your workforce is fully protected with compliant safety footwear from 3515.
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of ASTM F2413-certified footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of safety shoes and boots, designed to meet the specific hazards of your industry—from impact and compression to electrical and puncture risks.
Let us help you meet OSHA requirements and enhance workplace safety. Contact us today for a customized solution tailored to your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
- Advanced KPU Athletic Safety Shoe with Steel Toe Cap Anti-Slip Rotary Lacing System
- Wholesale Premium Waterproof Nubuck Safety Shoes Boots
- Premium Suede Metatarsal Guard Safety Boots Work Shoes
People Also Ask
- Why do my feet hurt in safety shoes? How to Fix the Safety vs. Comfort Conflict
- What is the significance of studying foot kinematics on coronal wedged surfaces for safety and orthopedic footwear?
- How does a universal pressing machine ensure the bonding quality of safety shoes? Achieve Superior Structural Fusion
- Why is compliance with safety standards important for oilfield safety shoes? Ensure Uncompromising Foot Protection
- What are the primary protective functions of industrial safety boots in granite quarry environments? Essential Guide
- What is the scenario described in the letter regarding safety toe protective footwear? Understanding Employer Payment Obligations
- What are the advantages of using Polyurethane (PU) for safety shoe outsoles? Lightweight & Ergonomic Solutions
- What are the disadvantages of using fabrics in safety shoe uppers? Balancing Comfort with Durability



















