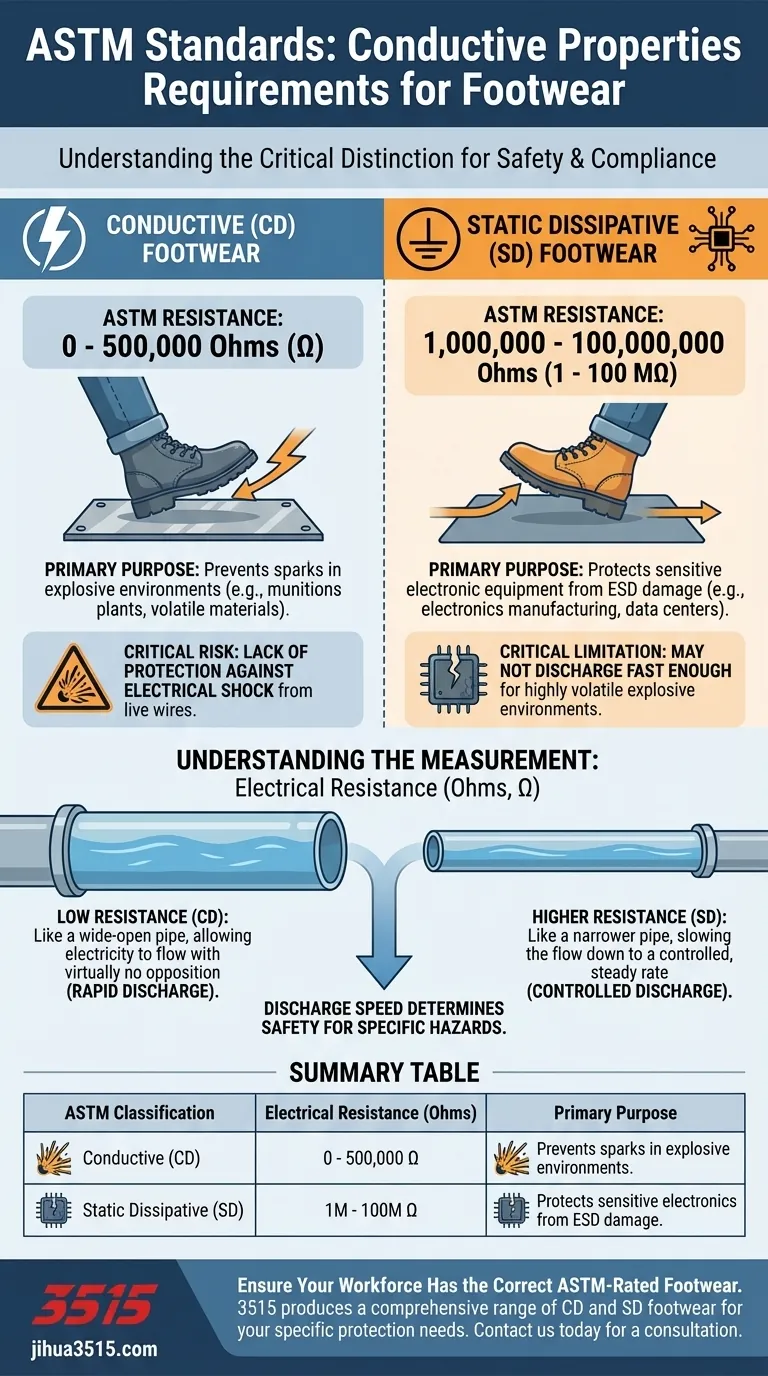
Under ASTM standards, there are two primary classifications for footwear designed to manage static electricity: Conductive (CD) and Static Dissipative (SD). For footwear to be rated as Conductive (CD), it must have an electrical resistance between 0 and 500,000 Ohms. For Static Dissipative (SD) footwear, the resistance must be between 1,000,000 and 100,000,000 Ohms.
The core principle is about the speed of electrical discharge. Conductive (CD) footwear discharges static buildup almost instantly, while Static Dissipative (SD) footwear does so in a slower, more controlled manner. Choosing the correct type is critical for matching the specific hazard of your environment.

Conductive vs. Static Dissipative: A Critical Distinction
While both types of footwear manage static electricity, their applications and protective mechanisms are fundamentally different. Confusing them can lead to significant safety risks.
Conductive (CD) Footwear
Conductive footwear is designed for the most rapid possible discharge of static electricity from the body to the ground. This minimizes the chance of a static spark.
The ASTM requirement for this classification is an electrical resistance between 0 and 500,000 Ohms.
This type of protection is essential in highly hazardous environments, such as munitions plants or facilities handling sensitive and volatile explosive materials, where even a tiny spark could be catastrophic.
Static Dissipative (SD) Footwear
Static Dissipative footwear is engineered to reduce static buildup at a more controlled rate. This protects sensitive electronic equipment from damage caused by electrostatic discharge (ESD).
The ASTM standard includes several levels of protection, typically rated as SD 10, SD 35, or SD 100. These ratings indicate the maximum allowable resistance in megohms (millions of Ohms).
For example, an SD 100 rated boot must maintain a resistance below 100 megohms (100,000,000 Ohms). The higher the number, the higher the allowable resistance.
Understanding the Measurement: Electrical Resistance
The unit used to measure these properties is the Ohm (Ω), which quantifies electrical resistance.
What is Resistance?
Think of electrical resistance like friction in a water pipe. A very low resistance (like in Conductive footwear) is like a wide-open pipe, allowing electricity to flow with virtually no opposition.
A higher resistance (like in Static Dissipative footwear) is like a narrower pipe, slowing the flow down to a controlled, steady rate.
Why the Rate of Discharge Matters
A rapid, high-energy discharge is necessary to prevent sparks around volatile explosives. However, this same rapid discharge can destroy sensitive microelectronics.
For electronics manufacturing or data centers, a slower, controlled discharge is ideal to bleed off static charge without creating a damaging surge.
Key Trade-offs and Safety Risks
Selecting the wrong type of footwear is not just inefficient—it can be extremely dangerous. Understanding the limitations of each is non-negotiable.
The Risk of Conductive Footwear
The primary risk of Conductive (CD) footwear is its lack of protection against electrical shock from equipment, circuits, or live wires.
Because it provides a direct path to ground, wearing CD footwear while accidentally contacting a live electrical source can lead to severe injury or electrocution. It should never be worn where this is a risk.
The Limits of Static Dissipative Footwear
While excellent for protecting electronics, Static Dissipative (SD) footwear may not discharge static fast enough in highly volatile or explosive environments.
Its higher resistance means it cannot guarantee the instantaneous discharge needed to prevent ignition of certain sensitive materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific work environment and the hazards within it are the only factors that should determine your choice.
- If your primary focus is preventing explosions around volatile materials: You must use Conductive (CD) rated footwear with a resistance of 0 to 500,000 Ohms.
- If your primary focus is protecting sensitive electronic components from static damage: Static Dissipative (SD) footwear with a resistance between 1 and 100 megohms is the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is protecting workers from live electrical circuits: Neither CD nor SD footwear is appropriate; you need footwear specifically rated for Electrical Hazard (EH).
Ultimately, matching the specific ASTM rating to the specific hazard is the only way to ensure true safety and compliance.
Summary Table:
| ASTM Classification | Electrical Resistance (Ohms) | Primary Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Conductive (CD) | 0 - 500,000 Ω | Prevents sparks in explosive environments (e.g., munitions plants). |
| Static Dissipative (SD) | 1,000,000 - 100,000,000 Ω | Protects sensitive electronics from ESD damage (e.g., manufacturing). |
Ensure your workforce has the correct ASTM-rated footwear for maximum safety and compliance. As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of conductive (CD) and static dissipative (SD) footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of safety shoes and boots, ensuring you get the precise protection your specific environment demands. Contact us today for a consultation and get the right footwear solution for your safety goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Wholesale Customizable Safety Boots Durable & Protective Footwear Manufacturing
- Premium Suede Sport Safety Shoes for Wholesale & Bulk Orders
- Wholesale Safety Footwear Manufacturer for Bulk & Custom OEM Orders
- Heavy Duty Nubuck Safety Boots Safety Shoes for Global Distribution
People Also Ask
- What features are often included in welted work boots for comfort? A Guide to All-Day Support
- What are the main disadvantages of cowboy boots? From Saddle to Sidewalk Limitations
- What are some characteristics of top-performing oil field boot brands? Built for Safety, Durability & Comfort
- What features are essential in cowboy boots for construction work? Prioritize Certified Safety & Durability
- In what work environments are cowboy boots versatile? A Guide to Durable & Safe Work Footwear
- What are the key features of EMS boots? Essential Protection for Emergency Responders
- What is the ASTM standard for electrical hazard protection in boots? Ensure Secondary Safety from Live Circuits
- Why is leather considered one of the best materials for work boot uppers? Discover Unmatched Durability & Comfort



















