Composite toe boots offer several distinct advantages over their steel or alloy counterparts, primarily centered on reduced weight, non-conductivity of electricity and heat, and being metal-free. These characteristics make them a preferred choice in specific work environments where comfort, safety from electrical hazards, or the need to pass through metal detectors are paramount.
Composite toe boots provide a lighter, more comfortable, and non-conductive alternative to steel or alloy toes, meeting essential safety standards while catering to environments sensitive to metal, extreme temperatures, or electrical hazards.

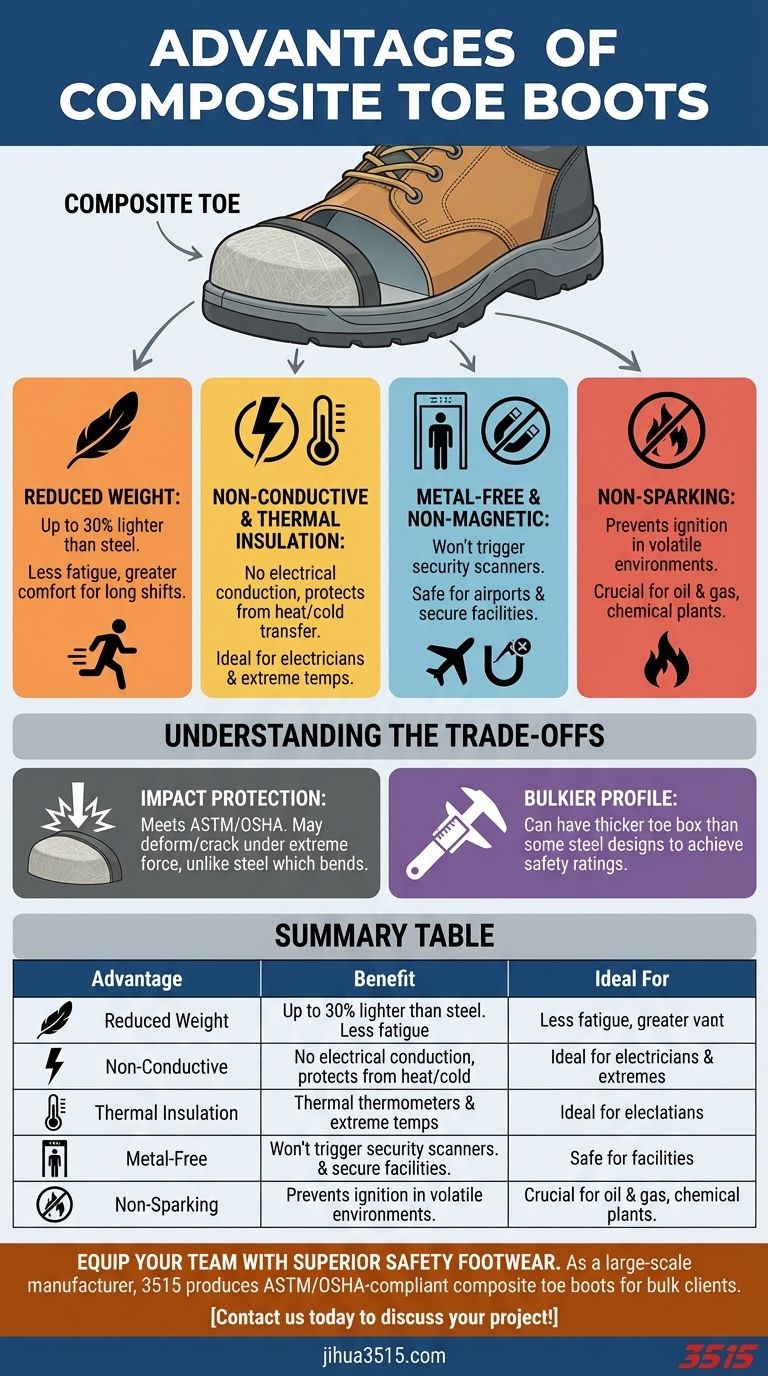
Key Advantages of Composite Toe Boots
Composite toe boots are engineered from non-metallic materials, providing safety without the typical drawbacks of metal components.
Reduced Weight and Enhanced Comfort
Composite toe boots are significantly lighter than steel toe boots, often by about 30 percent. This lighter weight reduces fatigue during long shifts. It also contributes to greater overall comfort, especially for those who spend extended periods on their feet or moving quickly.
Non-Conductivity of Electricity
Materials like carbon fiber, fiberglass, Kevlar, or plastic do not conduct electricity. This makes composite toe boots ideal for electricians and engineers working with live circuits or in environments with electrical hazards. They help prevent accidental electrical conduction through the footwear.
Superior Thermal Insulation
Composite toes are less sensitive to ambient temperatures. They do not conduct heat or cold into the boot, maintaining a more stable internal temperature for the foot. This provides better resistance to extreme weather conditions, enhancing comfort in both very hot and very cold environments.
Metal-Free and Non-Magnetic Properties
Composite toes do not contain metal, meaning they will not trigger metal detectors. This is a significant advantage for workers in environments with security checkpoints, such as airports, courthouses, or certain manufacturing facilities. Being non-magnetic also prevents interference with sensitive electronic equipment or magnetic fields.
Prevention of Sparking
The non-metallic nature of composite toes means they will not create sparks. This is crucial in volatile environments where a spark could ignite flammable materials or gases.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While offering numerous benefits, it's important to consider where composite toe boots might differ from steel or alloy options.
Impact Protection Considerations
Composite toes meet the same ASTM/OSHA safety requirements for impact and compression as steel toes. However, some experts suggest that steel toes, due to their inherent material strength, might offer a slightly greater margin of protection in extreme, crushing impact scenarios. When a composite toe experiences a severe impact, it may deform and crack, whereas a steel toe typically bends but maintains its structure.
Bulkier Profile
To achieve the required safety rating with non-metallic materials, composite toe caps can sometimes be thicker than steel caps. This can result in a slightly bulkier toe box profile compared to some steel toe designs.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Choosing between composite, steel, or alloy toes depends directly on the specific demands of your work environment and personal priorities.
- If your primary focus is electrical hazard protection or working around metal detectors: Opt for composite toe boots due to their non-conductive and metal-free properties.
- If your primary focus is comfort during long hours or in extreme temperatures: Composite toe boots offer significant advantages in lighter weight and thermal insulation.
- If your primary focus is maximum impact protection in high-risk crushing environments: While composite toes meet safety standards, steel toes are often perceived to offer a higher ultimate resistance to extreme crushing forces.
- If your primary focus is working in explosive or spark-sensitive environments: Composite toe boots are the safer choice as they prevent sparking.
The choice of safety footwear is a critical decision that impacts daily comfort and long-term safety.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced Weight | Up to 30% lighter than steel, reducing fatigue | Long shifts, fast-paced work |
| Non-Conductive | Does not conduct electricity, enhancing safety | Electricians, engineers, utility workers |
| Thermal Insulation | Resists heat and cold transfer for comfort | Extreme temperature environments |
| Metal-Free | Will not trigger metal detectors | Airports, courthouses, secure facilities |
| Non-Sparking | Eliminates ignition risk in volatile areas | Oil & gas, chemical plants, firefighters |
Ready to equip your team with superior safety footwear?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of composite toe boots for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities ensure you get high-quality, ASTM/OSHA-compliant footwear tailored to your specific industry needs—whether for electrical safety, comfort during long shifts, or metal-free requirements.
Contact us today to discuss your project and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Wholesale Safety Boots Manufacturer for Custom & Private Label Orders
- High Performance Fire-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots
- Wholesale Durable Safety Boots Manufacturer Customizable Steel Toe Work Boots
- Premium High-Cut Waterproof Safety Boots Manufacturing & Wholesale Solutions
- Premium Wholesale Waterproof Safety Boots High Performance Protection for Industrial Markets
People Also Ask
- How do I choose the best safety shoes? Match Certified Features to Your Hazards
- Why is the provision of individual-specific industrial safety shoes mandatory? Block Pathogens & Secure Your Logistics
- What are the application advantages of using Conductive Adhesives in smart safety shoes? Enhance Durability & Flexibility
- How do shoe lasts made from recyclable materials contribute to the sustainability of safety shoe manufacturing?
- How does the structured support design in safety shoes protect high-risk individuals? Optimize Foot Health & Safety
- Why is quality control important in safety footwear? Ensuring Life-Saving Protection on the Job
- What are the essential comfort and durability features of security guard safety boots? Ensure All-Day Protection & Performance
- Why are industrial-grade safety shoes essential for metal stamping? Prevent Injuries with Advanced Protection



















