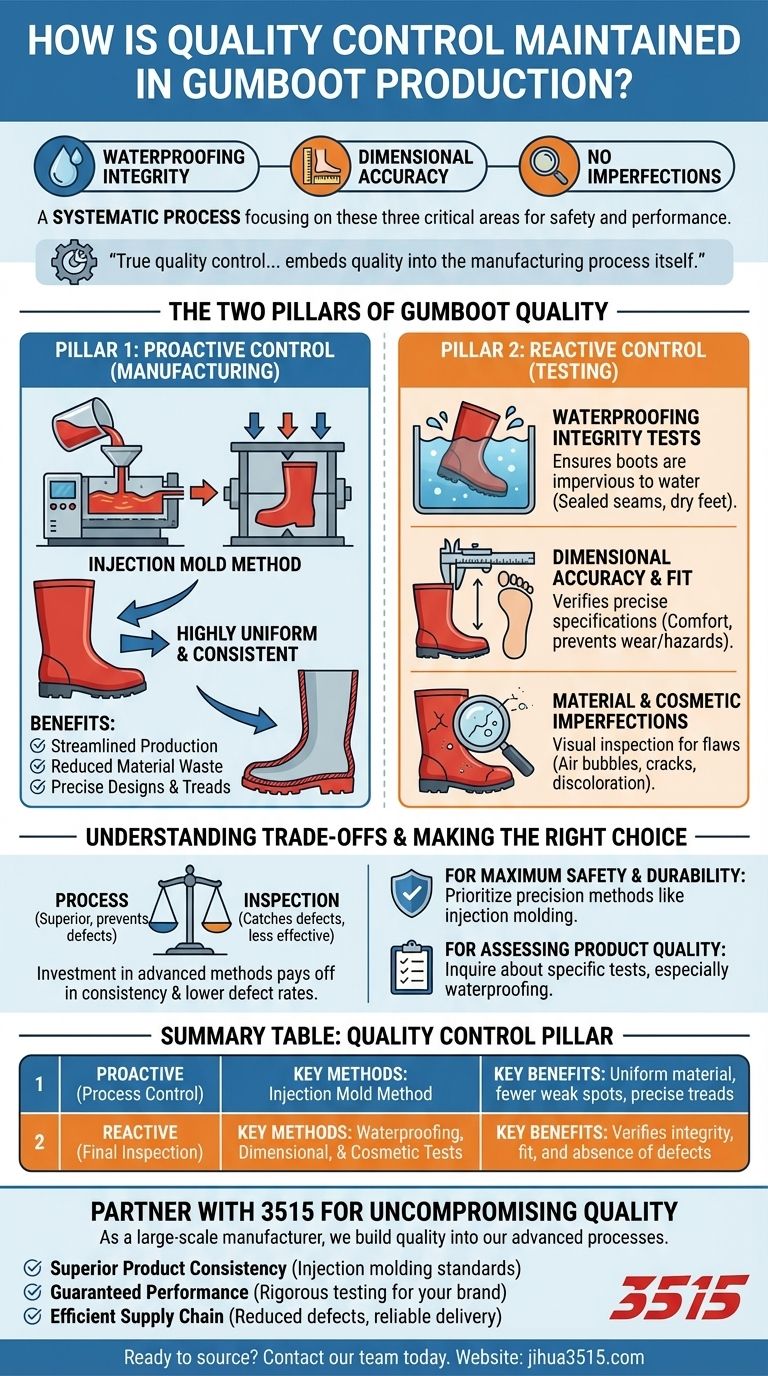
At its core, quality control in gumboot production is a systematic process maintained through rigorous inspection checks. These checks focus on three critical areas: waterproofing integrity, dimensional accuracy for proper fit, and the absence of cosmetic or structural imperfections. This ensures every boot meets exacting safety and performance standards before reaching the market.
True quality control in this industry isn't just about catching defects at the end of the line. It's a comprehensive strategy that embeds quality into the manufacturing process itself, using advanced techniques to prevent flaws before they happen.

The Two Pillars of Gumboot Quality
Effective quality control is not a single action but a dual approach. It combines proactive process control with reactive, detailed inspections.
Pillar 1: Proactive Control in Manufacturing
The most effective way to ensure quality is to build it directly into the product from the start.
The Injection Mold Method
A cutting-edge technique like the injection mold method is a form of proactive quality control. Molten rubber is injected into a boot mold under high pressure.
This process ensures a highly uniform and consistent result from one boot to the next, significantly reducing the chance of weak spots or material inconsistencies.
Benefits of Advanced Manufacturing
By using methods like injection molding, manufacturers streamline production and reduce material wastage. More importantly, it allows for the creation of intricate designs and tread patterns with absolute precision, which is critical for safety and function.
Pillar 2: Reactive Control Through Rigorous Testing
After production, boots undergo a series of tests to verify their integrity and performance.
Waterproofing Integrity Tests
This is the most crucial test. Boots are checked to ensure they are completely impervious to water, guaranteeing the user's feet stay dry and safe. This confirms the material and seams are perfectly sealed.
Dimensional Accuracy and Fit
Inspectors verify that each boot meets precise specifications for size, height, and sole thickness. Inaccurate dimensions can lead to poor comfort, premature wear, and even safety hazards.
Material and Cosmetic Imperfections
Finally, each boot is visually inspected for any flaws. This includes looking for air bubbles in the rubber, cracks, discoloration, or any other imperfection that could compromise the boot's durability or safety.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No quality control system is without its context, which often involves a balance between technology, labor, and cost.
Process vs. Inspection
Relying solely on end-of-line manual inspection is less effective than using a superior manufacturing process from the outset. A process like injection molding prevents defects, while manual inspection only catches them.
Investment in Consistency
Advanced manufacturing methods may require a higher initial investment, but they pay off through lower defect rates and reduced material waste. This leads to a more consistently high-quality product and ultimately, greater customer satisfaction and brand trust.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this process allows you to evaluate footwear more effectively.
- If your primary focus is maximum safety and durability: Prioritize boots made with precision methods like injection molding, as this process inherently produces a more uniform and reliable product.
- If your primary focus is assessing product quality: Inquire about the specific tests performed, especially for waterproofing, as this is the most critical function of a gumboot.
By understanding the relationship between the manufacturing process and final inspection, you can more accurately judge the true quality and reliability of the footwear.
Summary Table:
| Quality Control Pillar | Key Methods | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Proactive (Process Control) | Injection Mold Method | Uniform material, fewer weak spots, precise treads |
| Reactive (Final Inspection) | Waterproofing, Dimensional, & Cosmetic Tests | Verifies integrity, fit, and absence of defects |
Partner with 3515 for Uncompromising Quality
As a large-scale manufacturer, we produce a comprehensive range of footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our quality control isn't just a final step—it's built into our advanced manufacturing processes from the start.
We deliver:
- Superior Product Consistency: Advanced techniques like injection molding ensure every boot meets exacting standards.
- Guaranteed Performance: Rigorous testing for waterproofing, fit, and durability protects your brand reputation.
- Efficient Supply Chain: Reduced defect rates and material waste mean reliable delivery and better value.
Ready to source gumboots with proven reliability? Contact our team today to discuss your specific needs and see how our production capabilities can work for you.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Durable Rubber-Soled Utility Shoes for Wholesale & Custom Brand Manufacturing
- Factory Direct Wholesale Rain Boots Durable Waterproof & Fully Customizable
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Factory-Direct Wholesale Canvas Boots with High-Traction Rubber Soles
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
People Also Ask
- What makes natural rubber rain boots a good choice? Unbeatable Durability & Cold-Weather Performance
- What was the significance of rubber Wellington boots during WWI? A Life-Saving Innovation for Soldiers
- What are the best practices for storing rubber boots? Protect Your Investment for Years
- What materials are commonly used to make gumboots? Rubber vs. PVC for Durability & Comfort
- What are the key features to look for in wellington boots for gardening? Expert Guide to Superior Protection & Comfort
- How did Wellington boots become a fashion trend? From War Hero to Wardrobe Staple
- How can the lifespan of natural rubber boots be prolonged? A Guide to Proper Cleaning and Conditioning
- Why is outdoor play in wellington boots beneficial for children's health? Unlock Essential Development



















