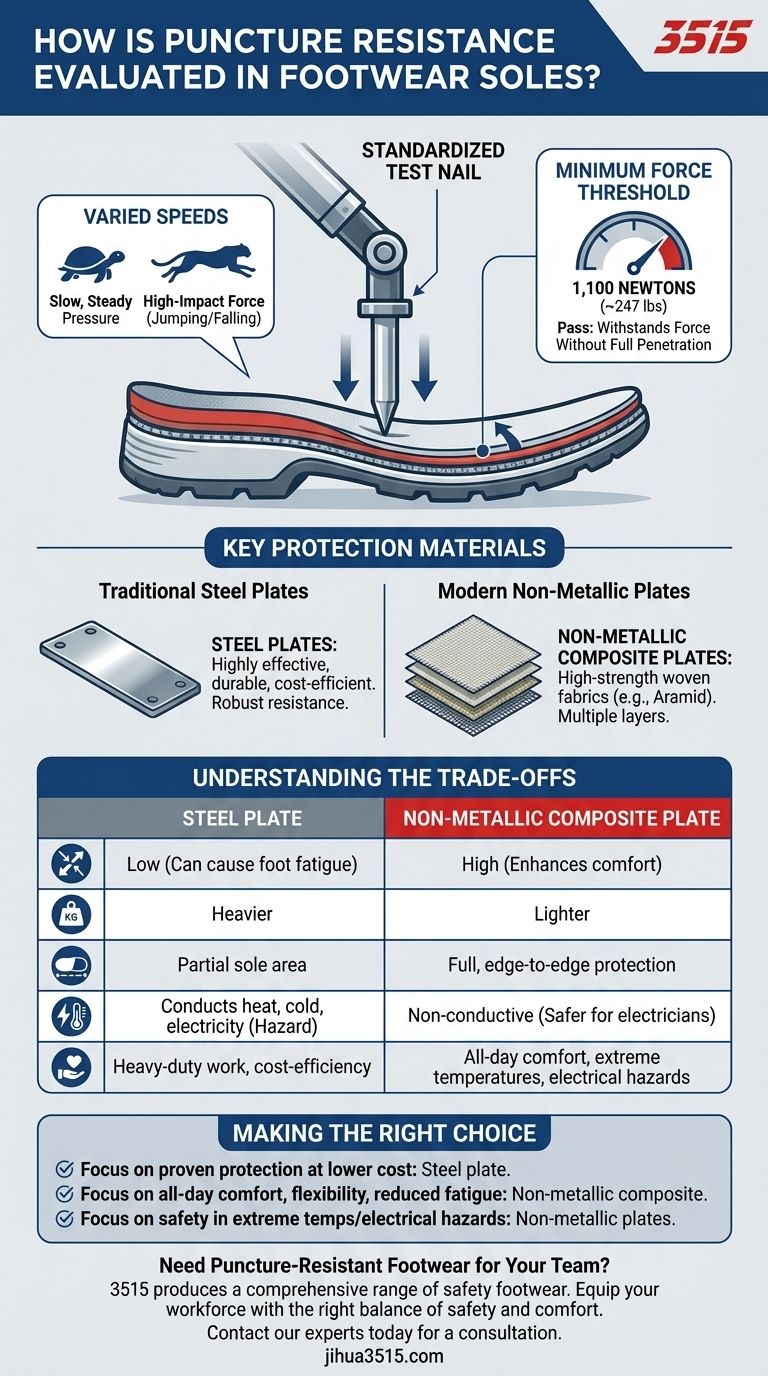
To evaluate puncture resistance in footwear, a standardized mechanical test is performed where a specific test pin, similar to a nail, is driven through the sole. This test is conducted at varying speeds to simulate different real-world scenarios, from a slow, steady pressure to the high-impact force of a person jumping onto a sharp object. The sole's ability to resist penetration under a required minimum force determines its performance.
The core principle of puncture resistance testing is not just to see if a sole can stop a nail, but to measure its resilience against both static and dynamic forces, ensuring reliable protection under a wide range of hazardous conditions.
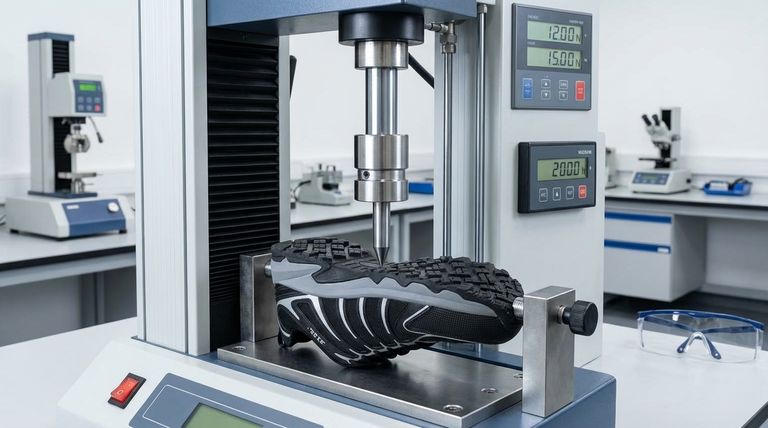

The Mechanics of the Puncture Resistance Test
To ensure safety footwear provides reliable protection, the evaluation method must be consistent, repeatable, and relevant to real-world hazards. The process is defined by specific international standards.
The Standardized Test Nail
The object used for penetration is not an arbitrary pin. It's a standardized test nail with a precisely defined diameter, length, and tip geometry. Using a consistent object ensures that results from different tests and different labs can be accurately compared.
Applying Force at Varied Speeds
The test measures the force required to puncture the sole. Crucially, this is done at different speeds. A slow press simulates the pressure of stepping on a nail, while a high-velocity impact, as mentioned in the references, simulates jumping or falling onto a sharp object. This dynamic testing is vital, as some materials behave differently under sudden impact.
Defining Success: The Minimum Force Threshold
A sole "passes" the test if it can withstand a specific minimum force without being fully penetrated by the test nail. For safety footwear under standards like EN ISO 20345 or ASTM F2413, this force is typically 1,100 Newtons (approximately 247 pounds of force).
Key Materials That Provide Protection
The test evaluates the performance of the protective insert layered within the sole. The choice of material for this insert is the primary factor in a sole's puncture resistance.
Traditional Steel Plates
For decades, thin steel plates have been the standard for puncture protection. They are highly effective, durable, and cost-efficient. They offer robust and reliable resistance against sharp, narrow objects.
Modern Non-Metallic Plates
More recently, non-metallic, anti-penetration inserts have become common. These are typically made from multiple layers of high-strength woven fabrics, such as aramid (Kevlar) or other ballistic fibers. These composite plates offer a different set of advantages over steel.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a puncture-resistant material is not just about stopping a nail; it's about balancing protection with the overall performance and comfort of the footwear.
Protection vs. Flexibility
A rigid steel plate offers excellent protection but significantly reduces the flexibility of the shoe, which can lead to foot fatigue. Non-metallic composite plates are far more flexible, moving with the foot for greater comfort, especially for workers who spend a lot of time crouching or climbing.
Coverage Area and Weight
Steel plates must be cut to a specific shape, meaning they don't protect the entire sole area. In contrast, fabric-based inserts can be cut to match the full footprint of the shoe, offering edge-to-edge protection. They are also significantly lighter than steel, reducing wearer fatigue.
Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
A major drawback of steel is that it conducts heat, cold, and electricity. This can be a serious comfort issue in extreme temperatures and a safety hazard for electricians. Non-metallic plates are non-conductive, making them the superior choice for these environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The right type of puncture resistance depends entirely on the intended application and priorities of the wearer.
- If your primary focus is proven protection at a lower cost for heavy-duty work: A traditional steel plate remains a reliable and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is all-day comfort, flexibility, and reduced fatigue: Non-metallic composite plates offer a clear ergonomic advantage.
- If your primary focus is safety in extreme temperatures or around electrical hazards: Non-metallic plates are essential for their non-conductive properties.
Ultimately, understanding how puncture resistance is tested empowers you to look beyond a simple safety rating and choose footwear that offers the right balance of protection, comfort, and function for the task at hand.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Steel Plate | Non-Metallic Composite Plate |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Protection | Excellent against sharp, narrow objects | Excellent against sharp objects |
| Flexibility | Low (can cause foot fatigue) | High (enhances comfort) |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Coverage | Partial sole area | Full, edge-to-edge protection |
| Conductivity | Conducts heat, cold, electricity | Non-conductive (safer for electricians) |
| Ideal For | Heavy-duty work, cost-efficiency | All-day comfort, extreme temperatures, electrical hazards |
Need Puncture-Resistant Footwear for Your Team?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Whether your priority is maximum protection with steel inserts or all-day comfort with modern composite plates, we have the production capabilities and expertise to meet your exact requirements.
Let us help you equip your workforce with the right balance of safety and comfort.
Contact our experts today for a consultation to discuss your specific needs and explore our full product catalog.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Premium KPU Athletic Safety Shoes for Wholesale
- Premium Lightweight Safety Shoes for Wholesale & Bulk Orders
- Custom Safety Shoe Manufacturer for Wholesale & OEM Brands
- Wholesale Durable Breathable Safety Boots Custom OEM Manufacturer
- Wholesale Leather Safety Boots with Customizable Protective Toe
People Also Ask
- Is it safe to ride without motorcycle boots? The Critical Footwear Safety Gap Every Rider Must Know
- What are the implications of the regulatory classification and management of new sensitizers like acetophenone azine?
- Why are elastic materials such as Lycra or Spandex selected for elderly footwear? Achieve Pain-Free Adaptive Comfort
- What is the significance of applying a high-pass filter to the z-axis for heel-strike detection? Optimize IMU Gait Data
- Why is a centralized production background critical? Ensure Peak Safety and Quality for Safety Shoes and Tactical Boots
- What are the key features of long riding boots? Essential Support & Safety for Equestrians
- What long-term health issues can the right footwear prevent? Safeguard Your Joints and Mobility
- How are force plates utilized to evaluate the effectiveness of vibratory insoles on postural stability? Proven Results



















