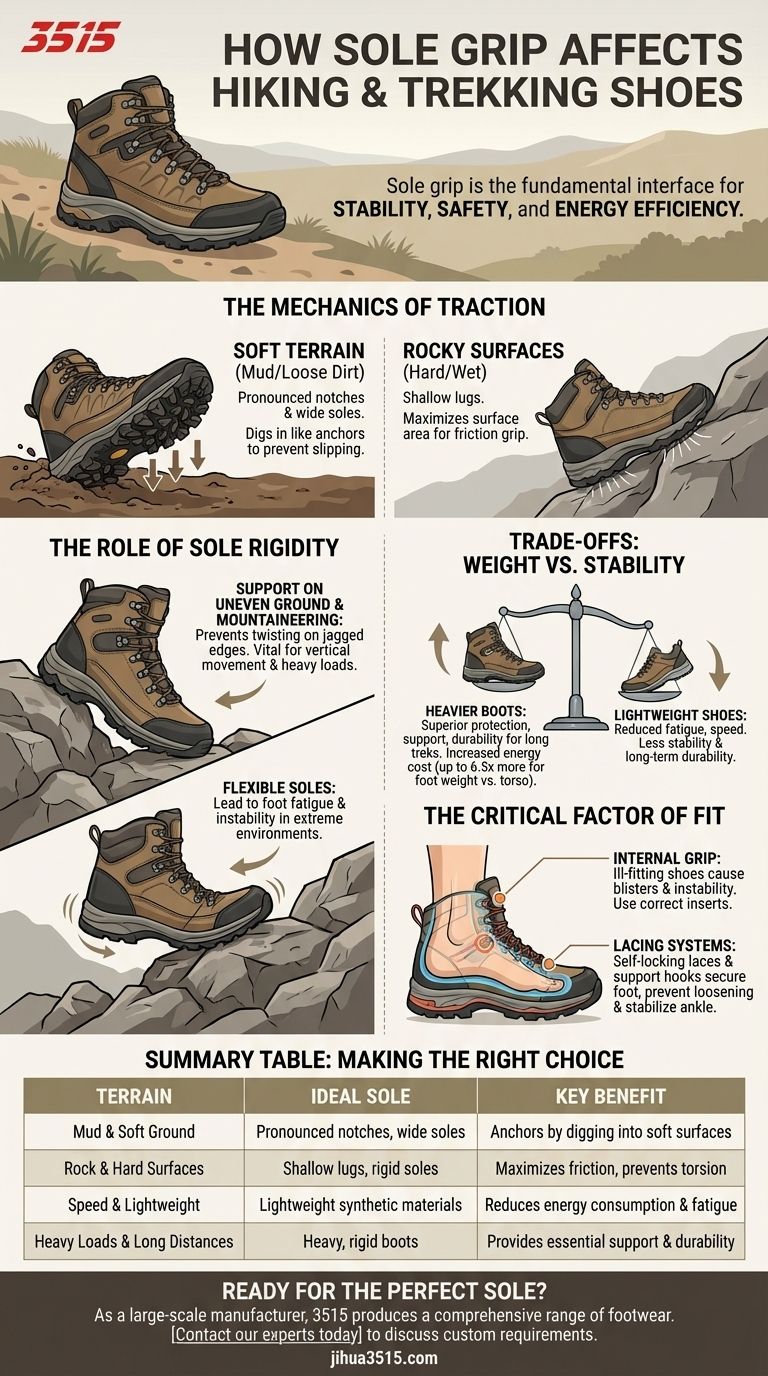
Sole grip is the fundamental interface between you and the trail, directly dictating your stability, safety, and energy efficiency. At a surface level, the grip configuration determines traction on specific surfaces: pronounced notches and wide soles are engineered to dig into soft mud, while shallow lugs provide superior contact area for friction on hard, rocky terrain.
Core Takeaway The effectiveness of a hiking shoe is not universal; it relies on matching the sole’s architecture—specifically lug depth and rigidity—to your intended terrain. Misalignment here leads to compromised traction, increased fatigue, and reduced stability.

The Mechanics of Traction
Navigating Soft Terrain
In conditions involving mud or loose dirt, surface area contact is less effective than penetration. Shoes designed for these environments feature pronounced notches and wider soles.
These deep indentations act like anchors. They dig into the soft surface to prevent slipping, allowing the hiker to push off securely.
Conquering Rocky Surfaces
Conversely, hard terrain requires a different approach. On wet or dry rocks, deep lugs can actually reduce the amount of rubber touching the ground.
For these environments, shallow lugs are superior. They maximize the surface area in contact with the rock, relying on friction rather than penetration to maintain grip.
The Role of Sole Rigidity
Support on Uneven Ground
Grip is not just about the tread pattern; it is also about the stiffness of the platform. Rigid soles are critical for navigating uneven or technical terrain.
A stiff sole prevents the shoe from bending excessively under load. This prevents the foot from twisting and slipping when you step on jagged edges or unstable surfaces.
Mountaineering Requirements
This rigidity is particularly vital for high-altitude hikes and mountaineering.
In these extreme environments, a flexible shoe would lead to rapid foot fatigue and instability. A rigid foundation provides the durability and strong grip necessary for vertical movement and heavy load-bearing.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Weight vs. Stability
The Energy Cost of Stability
There is an inherent compromise between a shoe's support capabilities and the energy required to wear it. Heavier footwear, such as rigid hiking boots, significantly increases oxygen consumption.
The references note a common adage: "A pound on your feet equals five pounds on your back." Moving heavy boots requires up to 6.5 times more energy than carrying weight on your torso.
The Durability Factor
However, shedding weight often means sacrificing performance in other areas. Lightweight shoes, often made of synthetic materials with less cushioning, reduce fatigue but offer less stability and durability.
Heavier boots, while taxing to lift, provide superior protection and support. For long treks or heavy packs, the added weight may be a necessary investment to ensure the shoe survives the journey and supports your ankles.
The Critical Factor of Fit
Internal Grip
External grip is useless if your foot slides inside the shoe. Ill-fitting shoes can lead to blisters and instability, regardless of how advanced the sole is.
Hikers must account for biomechanics like pronation or supination. Using correct inserts ensures the foot remains planted, translating the sole's grip effectively to the ground.
Lacing Systems
The connection between foot and sole is secured by the lacing system. Self-locking laces and support hooks prevent loosening during a hike.
These mechanisms stabilize the ankle and ensure that the shoe reacts instantly to your movements, rather than shifting around your foot.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct footwear, you must prioritize the terrain you encounter most often and the duration of your activity.
- If your primary focus is muddy or soft terrain: Prioritize shoes with pronounced notches and wide soles to ensure deep penetration and anchoring.
- If your primary focus is rocky or technical climbing: Choose footwear with shallow lugs and rigid soles to maximize friction and prevent shoe torsion on uneven edges.
- If your primary focus is speed and energy conservation: Opt for lightweight synthetic shoes, accepting that you will trade some long-term durability and ankle stability for reduced fatigue.
- If your primary focus is carrying heavy loads over long distances: Select heavier, rigid boots, as the increased energy cost is justified by the essential structural support and longevity.
True performance is achieved when your footwear's mechanical design perfectly mirrors the demands of your environment.
Summary Table:
| Terrain Type | Ideal Sole Characteristics | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Mud & Soft Ground | Pronounced notches, wide soles | Anchors by digging into soft surfaces |
| Rock & Hard Surfaces | Shallow lugs, rigid soles | Maximizes friction and prevents torsion |
| Speed & Lightweight | Lightweight synthetic materials | Reduces energy consumption and fatigue |
| Heavy Loads & Long Distances | Heavy, rigid boots | Provides essential support and durability |
Ready to find the perfect sole for your next adventure?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of shoes and boots, ensuring you get the precise combination of grip, rigidity, and weight for your target market's needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss your custom hiking or trekking shoe requirements and leverage our manufacturing expertise for superior traction solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Premium KPU Athletic Safety Shoes for Wholesale
- Durable Rubber-Soled Utility Shoes for Wholesale & Custom Brand Manufacturing
- Wholesale Durable Camouflage Canvas Shoes with High-Traction Cleated Rubber Sole
- Wholesale Training Shoes with Dial Lacing System Custom OEM Manufacturing
- Premium Lightweight Safety Shoes for Wholesale & Bulk Orders
People Also Ask
- What are the differences between mountaineering boots and trekking shoes? A Guide to Choosing the Right Footwear
- How does leather treatment benefit hiking boots? Extend Life, Boost Waterproofing & Comfort
- What factors are important when choosing hiking footwear? Match Your Boots to Your Trail for Optimal Performance
- What are trail runners best suited for? Ideal Footwear for Trail Running & Light Hikes
- What are heavy hiking boots designed for? Essential Gear for Heavy Loads & Rugged Terrain
- What is the difference between hiking shoes and trail shoes? Choose the Right Footwear for Your Adventure
- What are the main benefits of investing in specialized hiking footwear? Enhance Safety, Comfort & Performance
- What are eyelets in hiking shoes, and what are some specialty types? Choose the Right Lacing System for Your Hike



















