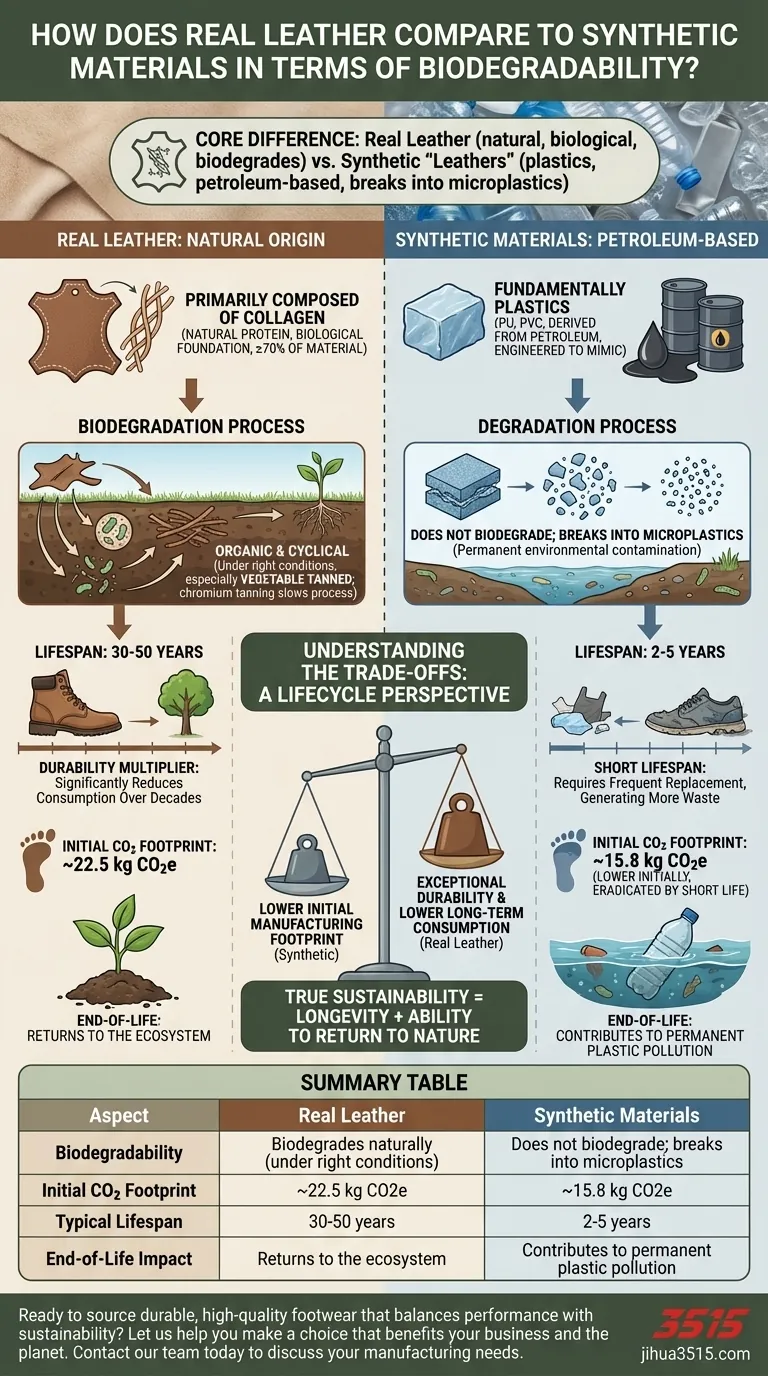
In terms of biodegradability, real leather holds a distinct advantage over synthetic materials. Because it is a natural product derived from animal hide, genuine leather can break down and return to the soil under the right conditions, a process that plastic-based synthetics are incapable of performing.
The core difference is simple: real leather is a biological material that can biodegrade, while synthetic "leathers" are plastics that break down into microplastics, persisting in the environment indefinitely. However, the true measure of sustainability requires looking beyond biodegradability to the entire product lifecycle.

The Fundamental Difference in Composition
To understand the end-of-life impact of these materials, we must first look at what they are made of. Their origin dictates their ultimate fate.
Real Leather: A Natural Origin
Real leather is produced from tanned animal skins, which are primarily composed of collagen, a natural protein. This biological foundation, comprising at least 70% of the material, is what gives leather its potential to biodegrade.
Synthetic "Leathers": A Petroleum-Based Product
Most synthetic alternatives, such as polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC) leather, are fundamentally plastics derived from petroleum. They are engineered to mimic the look of leather but share no biological similarities.
How Each Material Actually Breaks Down
The terms "biodegrade" and "break down" are not interchangeable. One process returns a material to the ecosystem, while the other simply creates smaller pollutants.
The Biodegradation of Leather
Under the right environmental conditions, microorganisms in the soil can consume the collagen fibers in leather, breaking the material down into its natural elements. This process is organic and cyclical.
The Critical Role of the Tanning Process
However, not all leather is created equal. The tanning method used to preserve the hide significantly impacts its ability to biodegrade. Leathers treated with heavy metals like chromium may decompose much more slowly and can leach chemicals, while those using natural vegetable tanning methods break down more easily and safely.
The Fate of Synthetics
Synthetic materials do not biodegrade. Instead, they undergo a process of degradation, breaking into progressively smaller pieces of plastic known as microplastics. These particles contaminate soil and water systems permanently.
Understanding the Trade-offs: A Lifecycle Perspective
A material's end-of-life is only one part of its environmental story. To make a truly informed decision, you must consider its entire lifecycle, from production to disposal.
Initial Carbon Footprint
At first glance, synthetics can appear to be a better choice. The production of a synthetic product emits approximately 15.8 kg of CO2e, compared to 22.5 kg of CO2e for a leather product.
The Durability Multiplier
This initial advantage is completely erased by the vast difference in lifespan. A well-made leather product can last 30 to 50 years. In contrast, a synthetic equivalent typically lasts only 2 to 5 years.
This means you might purchase ten or more synthetic items—each with its own manufacturing footprint—in the time you would own a single leather one. When viewed over decades, leather's durability makes it a far more sustainable option by promoting reduced consumption.
End-of-Life Realities
The final stage of the lifecycle confirms leather's advantage. One product has the potential to return to the earth, while the other contributes to long-term plastic pollution.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your final decision depends on which aspect of sustainability you prioritize most heavily.
- If your primary focus is end-of-life impact: Real leather is the superior choice, as it is the only material of the two that can truly biodegrade and exit the ecosystem.
- If your primary focus is reducing long-term consumption: The exceptional durability of leather makes it the clear winner, drastically lowering the need for replacement and its associated environmental costs over time.
- If your primary focus is a lower initial manufacturing footprint: A synthetic product has a lower carbon cost for a single production cycle, but this benefit is lost due to its short lifespan.
Ultimately, true sustainability is measured not just in a material's creation, but in its longevity and its ability to return to nature.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Real Leather | Synthetic Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Biodegradability | Biodegrades naturally under right conditions | Does not biodegrade; breaks into microplastics |
| Initial CO2 Footprint | ~22.5 kg CO2e | ~15.8 kg CO2e |
| Typical Lifespan | 30-50 years | 2-5 years |
| End-of-Life Impact | Returns to the ecosystem | Contributes to permanent plastic pollution |
Ready to source durable, high-quality footwear that balances performance with sustainability?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of shoes and boots, including those made with genuine leather for superior longevity and a lower long-term environmental footprint.
Let us help you make a choice that benefits your business and the planet. Contact our team today to discuss your manufacturing needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Wholesale Comfort Leather Business Shoes with Dial Lacing System
- Wholesale Leather Derby Shoes Manufacturer | Customizable Business & Dress Footwear
- Dial Closure Leather Business Casual Shoes for Wholesale & Private Label
- Wholesale Modern Perforated Leather Derby Shoes with Chunky Sole for Custom Branding
- Classic Leather Derby Dress Shoes Wholesale & Custom Manufacturing
People Also Ask
- How does pull-up leather behave in shoes? It develops a unique, evolving patina.
- What are the environmental benefits of choosing real leather shoes? Durability and Waste Reduction
- What are the benefits of seamless leather in office work shoes? Eliminate Friction for All-Day Comfort
- What are the key features of high-quality leather in shoes? Invest in Durability and a Perfect Fit
- How can crocodile-inspired leather dress shoes make a statement at formal events? Command Attention with Bold Style





