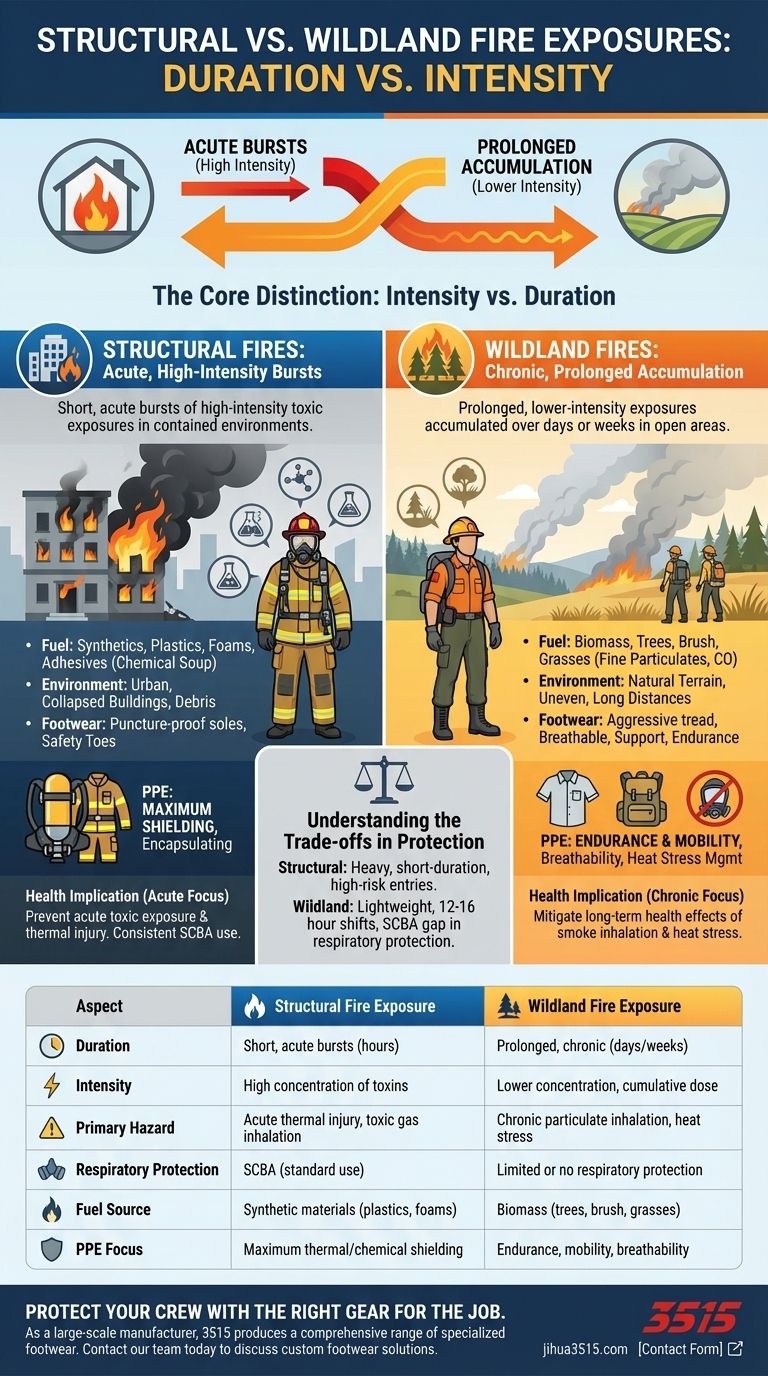
The fundamental difference between wildland and structural fire exposures lies in their signature: duration versus intensity. Structural firefighting involves short, acute bursts of high-intensity toxic exposures in a contained environment. In contrast, wildland firefighting is characterized by prolonged, lower-intensity exposures accumulated over days or weeks in open areas.
While a single structural fire may present a higher immediate concentration of toxins, the cumulative exposure a wildland firefighter endures over an entire season—often without respiratory protection—creates a distinct and significant long-term health risk.

The Core Distinction: Intensity vs. Duration
Structural Fires: Acute, High-Intensity Bursts
A structural fire is an intense, short-duration event. Firefighters face highly concentrated levels of heat and a complex mix of chemical byproducts within an enclosed space.
The standard use of a Self-Contained Breathing Apparatus (SCBA) is a direct response to this immediately life-threatening toxic atmosphere.
Wildland Fires: Chronic, Prolonged Accumulation
Wildland fire exposures are defined by their length. A single incident can mean working in smoky conditions for many days or even weeks.
While the smoke concentration may be lower at any given moment, the total toxic dose accumulates over a long operational period. Crucially, respiratory protection is not consistently used, leading to direct and sustained inhalation of harmful particulates.
The Nature of the Hazard
The Fuel Source: Synthetics vs. Biomass
Structural fires consume man-made materials like plastics, foams, adhesives, and treated woods. This combustion releases a uniquely hazardous chemical soup containing carcinogens and asphyxiants not typically found in nature.
Wildland fires primarily burn biomass—trees, brush, and grasses. This produces vast quantities of fine particulate matter, carbon monoxide, and other harmful organic compounds like benzene.
The Physical Environment: Urban vs. Natural Terrain
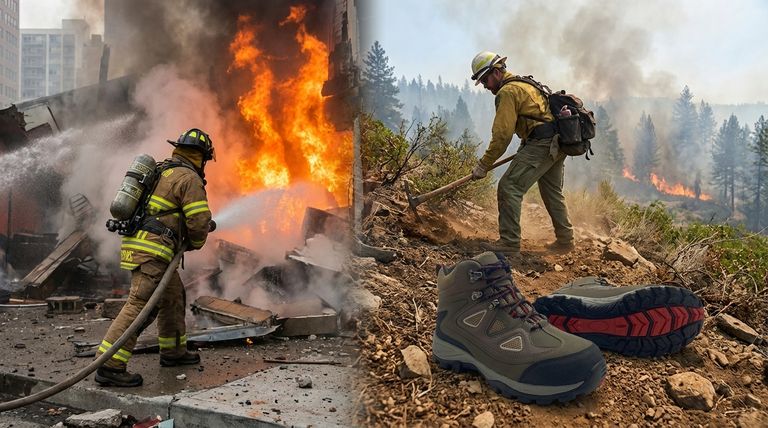
The work environment dictates the physical risks and the required equipment. This is clearly illustrated by the differences in footwear.
Structural boots are built for urban hazards, with puncture-proof soles and safety toes for protection against nails and debris in a collapsed, compromised building.
Wildland boots are built for endurance over miles of uneven, natural terrain. They feature aggressive tread for traction and prioritize breathability and support to prevent injury and exhaustion during long shifts.
Understanding the Trade-offs in Protection
Structural PPE: Maximum Shielding
Gear for structural fires, including heavy turnout coats and SCBAs, is designed for maximum thermal and respiratory protection against overwhelming, immediate hazards.
This equipment is heavy and encapsulating, making it suitable only for the short-duration, high-risk entries typical of a building fire.
Wildland PPE: Endurance and Mobility
Wildland gear prioritizes breathability, lightweight design, and comfort for extended wear. The goal is to manage heat stress and exhaustion over 12- to 16-hour shifts.
This design philosophy highlights a critical trade-off. Standard SCBAs are too heavy and have too limited an air supply to be practical on a fire line, creating a significant and well-known gap in respiratory protection for wildland crews.
Key Implications for Health and Safety
A clear understanding of these exposure differences is critical for implementing the correct safety protocols and protecting firefighter health.
- If your primary focus is structural fire safety: The critical imperative is preventing acute toxic exposure and thermal injury through consistent SCBA use and advanced decontamination procedures.
- If your primary focus is wildland fire safety: The critical imperative is mitigating the long-term health effects of chronic smoke inhalation and managing physical stressors like heat and exhaustion over entire seasons.
Recognizing that each discipline faces a unique hazard profile is the first step toward ensuring firefighter health and longevity.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Structural Fire Exposure | Wildland Fire Exposure |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | Short, acute bursts (hours) | Prolonged, chronic (days/weeks) |
| Intensity | High concentration of toxins | Lower concentration, cumulative dose |
| Primary Hazard | Acute thermal injury, toxic gas inhalation | Chronic particulate inhalation, heat stress |
| Respiratory Protection | SCBA (standard use) | Limited or no respiratory protection |
| Fuel Source | Synthetic materials (plastics, foams) | Biomass (trees, brush, grasses) |
| PPE Focus | Maximum thermal/chemical shielding | Endurance, mobility, breathability |
Protect Your Crew with the Right Gear for the Job
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of specialized footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Whether your team needs durable structural boots with puncture-proof soles for urban hazards or rugged wildland boots built for endurance and traction on challenging terrain, we have the production capabilities to meet your exact needs.
Contact our team today to discuss custom footwear solutions that enhance firefighter safety and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
- Premium Grain Leather Safety Boots for Bulk Supply
- Premium Wholesale Waterproof Safety Boots High Performance Protection for Industrial Markets
- Customizable Anti-Smash Safety Boots for Wholesale & Private Label Manufacturing
People Also Ask
- What makes Cordura fabric a preferred choice for bags? Unmatched Durability for Demanding Use
- What are the most common types of horse boots? A Guide to Choosing the Right Leg Protection
- What is the function of 3D force plates in testing footwear soles? Science-Backed Cushioning Analysis
- Why does the quality of leather matter in Goodyear welted shoes? Ensure Durability & Resoling Success
- How do high-density pressure sensor grids improve gait measurement? Enhance Accuracy with Precision Biomechanics
- What is the primary function of the multi-layer composite structure in medical sensor insoles? Optimize Footwear Tech
- What type of shoes are best for plantar fasciitis? Find Supportive Footwear for Pain Relief
- What are the advantages of arch support structures in orthopedic insoles? Prevent Diabetic Foot Collapse and Rotation



















