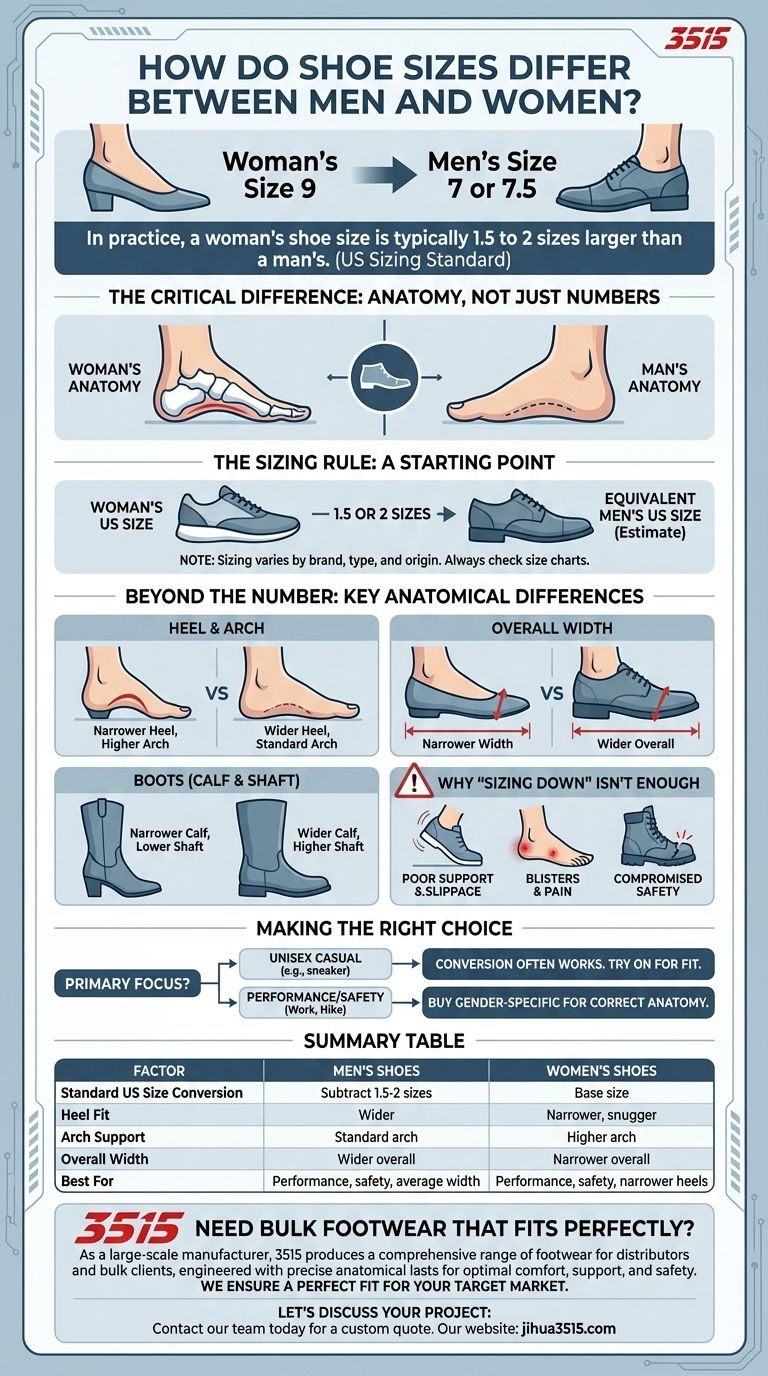
In practice, a woman's shoe size is typically 1.5 to 2 sizes larger than a man's. For example, a woman who wears a size 9 would likely fit into a men's size 7 or 7.5. This conversion is the most common industry standard for US sizing and serves as a reliable starting point.
The critical difference between men's and women's footwear is not the size number, but the anatomy. Men's shoes are built on a fundamentally different last (the foot-shaped model used for construction), impacting width, arch, and heel fit.

The Sizing Rule: A Starting Point, Not a Guarantee
Relying solely on the size number conversion can lead to a poor fit. It’s essential to understand what the numbers represent and why they are only part of the story.
The Standard Conversion Rule
The most widely accepted conversion is to subtract 1.5 or 2 sizes from a woman's US size to get the equivalent men's US size. For instance, a women's 8.5 is roughly a men's 7.
This rule exists because the numbering systems are scaled differently based on historical manufacturing standards for different average foot shapes.
Why It's Only an Estimate
This conversion is a general guideline, not a universal law. Sizing can vary between brands, shoe types (e.g., athletic vs. dress shoe), and country of origin. Always refer to a specific brand's size chart if possible.
Beyond the Number: Key Anatomical Differences
The true distinction lies in the shape and dimensions of the shoe, which are designed to accommodate the structural differences between the average man's and woman's foot.
Heel and Arch Shape
Women's feet typically have a narrower heel in proportion to the front of the foot. Women's shoes are designed to accommodate this, providing a snugger fit to prevent heel slippage.
Furthermore, women's footwear often incorporates a higher arch in the insole to provide better support and comfort.
Overall Foot Width
Men's shoes are generally wider overall. They are built with less variation in width from the heel to the toe area. A woman wearing a "sized-down" men's shoe may find it too roomy, especially in the heel and midfoot.
Calf and Shaft Fit (For Boots)
The difference is especially pronounced in boots. Women's boots, such as wellies or work boots, are designed with a narrower calf and a lower shaft to better match the average female leg shape.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why "Sizing Down" Isn't Enough
Choosing a shoe from the other gender's category can work for some, but it comes with potential downsides, especially in performance or safety footwear.
The Risk of Poor Support
Simply wearing a smaller men's shoe can lead to significant fit issues. The wider heel can cause slippage and instability, while the mismatched arch can lead to arch pain and fatigue over time.
The Problem with Blisters and Pain
An improper fit is the primary cause of blisters. If a shoe is too wide, the foot can slide internally, creating friction. This constant rubbing, especially in the heel or toe area, is a recipe for discomfort.
Compromised Safety in Technical Footwear
For work boots or hiking boots, a precise fit is a matter of safety. A loose boot offers insufficient protection and can increase the risk of an ankle roll. Safety features like steel toes may not align correctly if the shoe's proportions are wrong for your foot.
Making the Right Choice for Your Foot
Your goal determines how strictly you should adhere to gender-specific sizing. Use this framework to guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is a unisex casual style (like a sneaker): Using the 1.5-size conversion is often successful, but prioritize trying the shoe on to check for excessive width or heel slippage.
- If your primary focus is performance or safety (work, hiking, athletics): You should almost always buy footwear designed for your gender to ensure correct anatomical support and protection.
- If you have wider or narrower feet than average: You may find a better fit by exploring options across categories, but focus on the shoe's actual fit, not the size number on the box.
Ultimately, the best shoe is the one that fits your unique foot anatomy, providing comfort and support where you need it most.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Men's Shoes | Women's Shoes |
|---|---|---|
| Standard US Size Conversion | Subtract 1.5-2 sizes from women's | Base size |
| Heel Fit | Wider | Narrower, snugger fit |
| Arch Support | Standard arch | Higher arch |
| Overall Width | Wider overall | Narrower overall |
| Best For | Performance, safety, average width | Performance, safety, narrower heels |
Need Bulk Footwear That Fits Perfectly?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our production capabilities encompass all types of shoes and boots, engineered with precise anatomical lasts for optimal comfort, support, and safety.
We ensure a perfect fit for your target market. Whether you need men's, women's, or unisex styles, our expertise in foot anatomy and manufacturing guarantees superior quality and customer satisfaction.
Let's discuss your project: Contact our team today for a custom quote and discover how we can be your trusted manufacturing partner.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Wholesale Women's Leather Derby Shoes Custom Factory Production
- Wholesale Comfortable Business Casual Shoes Custom Manufacturing
- Wholesale Patent Oxford Dress Shoes | Custom & Bulk Manufacturing
- Durable Waterproof Rain Boots | Custom Manufacturer for Wholesale & Brands
- Durable Rubber Sole Outdoor Shoes Wholesale & Custom Manufacturing
People Also Ask
- What are the characteristics of textiles used in footwear? A Guide to Performance & Durability
- What are western boots and what are their features? Unpacking the Iconic Riding Footwear
- What is the purpose of using 3D-printed load concentrators in smart insoles? Enhance Sensor Accuracy & Data Fidelity
- What role do load cells play in the standardization of footwear lean-and-release experimental protocols? Precise Force Data
- What is the purpose of adhering artificial turf and rubber test blocks to rigid wooden bases? Ensure Data Reliability
- What is the technical rationale for barefoot testing as a stability baseline? Understanding Footwear Biomechanics
- Which kinetic indicators do force plates provide for footwear research? Key Metrics for Gait Database Construction
- What is the primary function of a shoe last? Mastering the 3D Mold for Perfect Fit and Structural Integrity



















