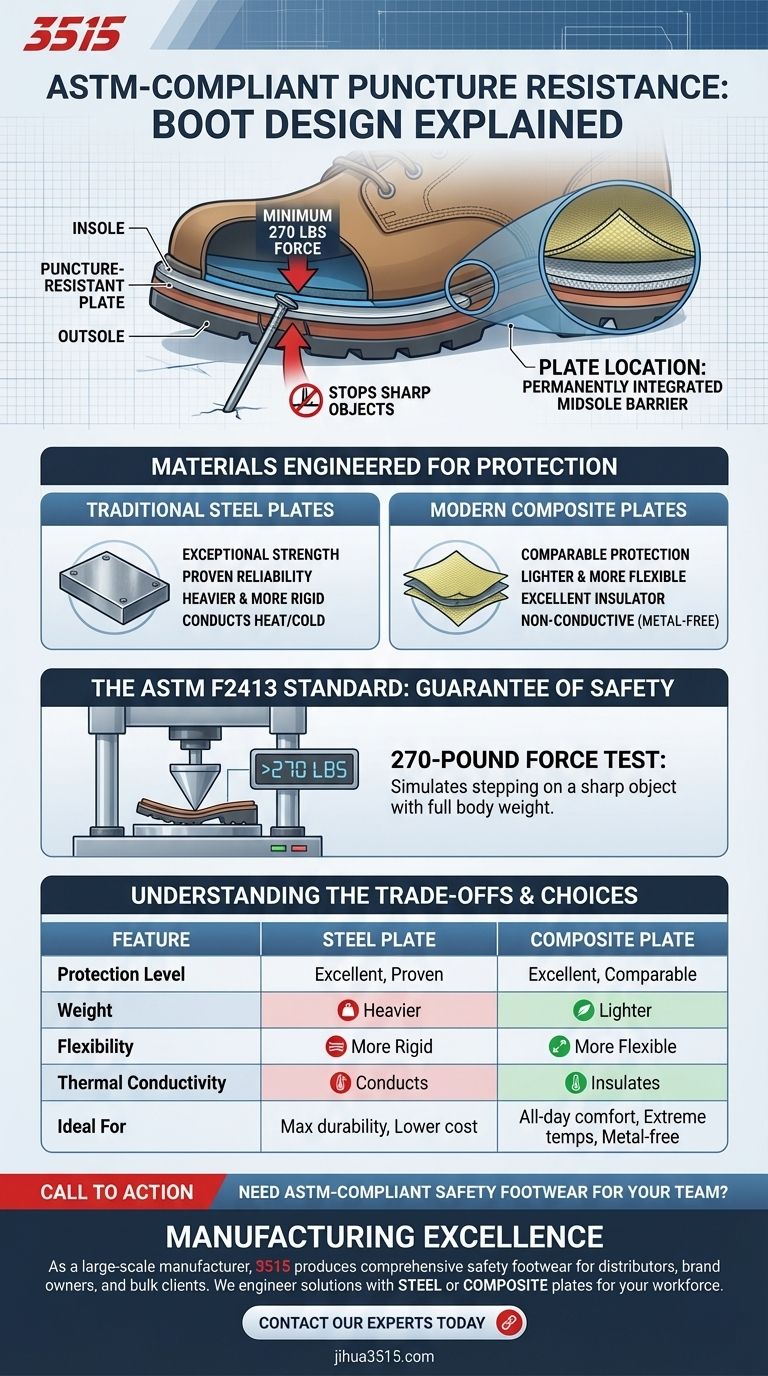
To meet the ASTM standard for puncture resistance, boots are engineered with a protective plate permanently integrated into the midsole, positioned between the insole your foot rests on and the outsole that contacts the ground. This plate is specifically designed to withstand a minimum of 270 pounds of force, preventing sharp objects like nails from penetrating the sole and injuring the foot.
The core principle is not about making the outer sole thicker, but about embedding a dedicated, force-rated barrier inside the boot that serves as a shield for the bottom of your foot.

The Anatomy of a Puncture-Resistant Boot
The Protective Plate's Location
The puncture-resistant plate is a critical internal component, not an external feature. It is built directly into the boot's construction.
This placement ensures it cannot shift or be removed, providing consistent and reliable protection across the sole and heel area every time the boot is worn.
The Plate's Function
Its sole purpose is to intercept and stop sharp objects that pierce the outsole. By blocking nails, glass shards, or other debris, it prevents them from reaching and injuring the wearer's foot.
The design is a direct response to common hazards found in construction, demolition, and industrial environments.
Materials Engineered for Protection
The choice of material for the protective plate is central to the boot's performance, balancing safety with wearer comfort.
Traditional Steel Plates
Steel is the classic material used for puncture-resistant plates. It offers exceptional strength and has a long, proven track record of providing reliable protection.
Modern Composite Plates
Newer designs often use non-metallic, composite materials, such as ballistic fabrics like Kevlar. These advanced materials offer protection comparable to steel but with several key advantages.
Composite plates are lighter, more flexible, and do not conduct heat, cold, or electricity, making them ideal for a wider range of work environments.
The ASTM F2413 Standard: A Guarantee of Safety
The ASTM standard provides a clear, objective benchmark for safety, ensuring the footwear performs as expected under pressure.
The 270-Pound Force Test
To earn the ASTM "PR" (Puncture Resistant) rating, a boot must pass a specific laboratory test. This involves ensuring the plate can withstand a penetration force of at least 270 pounds.
This test simulates the real-world scenario of a worker stepping directly onto a sharp object with their full body weight.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While essential for safety, the inclusion of a protective plate involves certain design compromises that are important to understand.
Flexibility vs. Rigidity
Adding a puncture-resistant plate, whether steel or composite, inherently reduces the overall flexibility of the boot's sole.
Steel plates tend to be more rigid, while composite plates offer significantly more flex, which can translate to greater comfort over a long workday.
Weight and Thermal Conductivity
Steel plates add noticeable weight and can conduct heat from hot surfaces or cold from icy ground directly to the foot.
Composite plates are much lighter and are excellent insulators, which is a major benefit in extreme temperature conditions or for workers who need to minimize fatigue.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and proven protection at a lower cost: A boot with a traditional steel plate is a reliable and time-tested choice.
- If your primary focus is all-day comfort, flexibility, and reduced weight: A boot with a modern composite plate is the superior option.
- If you work around metal detectors or in extreme temperatures: A non-metallic composite plate is essential for avoiding detection and providing thermal insulation.
Ultimately, choosing the right puncture-resistant boot means matching the material technology to the specific demands of your work environment.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Steel Plate | Composite Plate |
|---|---|---|
| Protection Level | Excellent, Proven | Excellent, Comparable to Steel |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Flexibility | More Rigid | More Flexible |
| Thermal Conductivity | Conducts Heat/Cold | Insulates (Non-Conductive) |
| Ideal For | Maximum durability, lower cost | All-day comfort, extreme temperatures, metal-free environments |
Need ASTM-Compliant Puncture-Resistant Boots for Your Team?
As a large-scale manufacturer, 3515 produces a comprehensive range of safety footwear for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. We can engineer the right solution for your needs, whether it's the proven reliability of steel plates or the advanced comfort of modern composites.
Let us help you protect your workforce.
Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Performance Fire-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots
- Premium Wholesale Waterproof Safety Boots High Performance Protection for Industrial Markets
- Heavy-Duty Waterproof Nubuck Safety Boots Safety Shoes for Bulk Supply
- Premium High-Cut Waterproof Safety Boots Manufacturing & Wholesale Solutions
- Premium Wholesale Wheat Nubuck Safety Boot with Rapid Lacing System
People Also Ask
- What is dielectric protective footwear used for? Essential Safety for Electrical Workers
- Are there any limitations to oil resistant safety boots? Key Risks and How to Mitigate Them
- What are the technical advantages of using puncture-resistant composite midsoles in safety footwear? | Lightweight Power
- How do high-quality safety shoes contribute to resource conservation? Maximize Longevity & Sustainable Efficiency
- What are the core functions of the GPS positioning module in smart shoes? Enhancing Safety for the Visually Impaired
- Why wear standardized industrial safety shoes in ergonomic kinetic testing? Essential Variable Control
- Why are industrial sewing machines with precise pressure control required for safety shoes? Ensuring Seam Integrity
- What role do professional safety shoes play in addressing balance and gait issues? Enhance Workplace Stability and Confidence



















