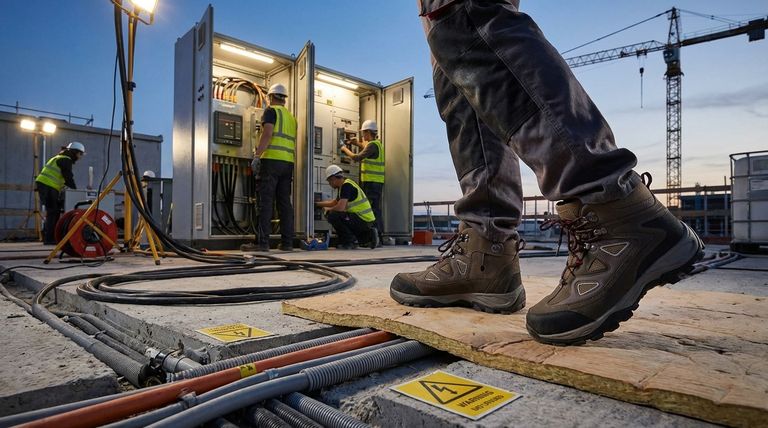
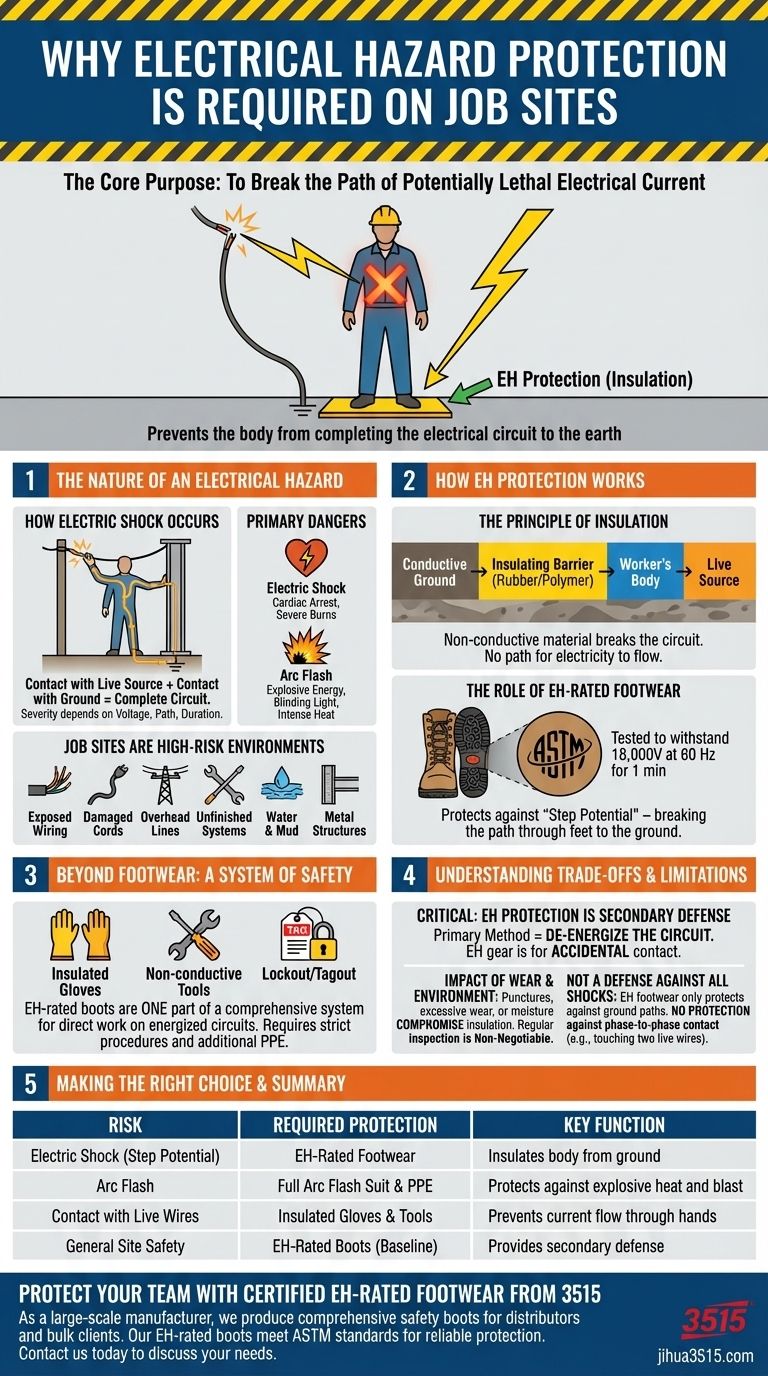
Electrical hazard protection is required on job sites to prevent severe injury or death from electric shock. This protection is mandated in environments with exposed or damaged electrical conductors, where a worker could accidentally become part of an electrical circuit, allowing dangerous current to pass through their body.
The core purpose of electrical hazard protection is to break the path of a potentially lethal electrical current. By using gear that insulates your body from the ground, you prevent yourself from becoming the path of least resistance for electricity to flow to the earth.

The Nature of an Electrical Hazard
To understand the requirement, you first need to understand the risk. An electrical hazard isn't just about a spark; it's about your body completing a circuit that was never meant to exist.
How Electric Shock Occurs
For a person to receive an electric shock, two conditions must be met. First, they must make contact with a live electrical source. Second, they must be in contact with the ground or another conductive path.
When this happens, the person's body completes the circuit, and electrical current flows through them. The severity of the shock depends on the voltage, the path the current takes through the body, and how long the contact lasts.
The Two Primary Dangers
The main risks are electric shock and arc flash. Electric shock is the flow of current through the body, which can cause cardiac arrest, muscle contractions, and severe burns.
An arc flash is an explosive release of energy when electricity jumps through the air from one conductor to another or to the ground. This creates a blinding flash of light, intense heat, and a concussive blast that can be fatal even from a distance.
Why Job Sites Are High-Risk Environments
Job sites present a unique combination of electrical risks. Exposed wiring, damaged power cords, overhead power lines, and unfinished electrical systems are common.
Furthermore, the presence of water, mud, metal scaffolding, and ladders creates numerous conductive paths to the ground, dramatically increasing the likelihood that a worker can complete a circuit and suffer a serious shock.
How Electrical Hazard (EH) Protection Works
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) designed for electrical hazards is built on the principle of insulation. It creates a non-conductive barrier between you and the ground.
The Principle of Insulation
Insulators are materials that do not conduct electricity well. Rubber and certain polymer compounds are excellent insulators.
By placing a layer of this material between your body and a potential ground source, you effectively break the circuit. Electricity cannot flow through you because there is no complete path for it to travel.
The Role of EH-Rated Footwear
The most common form of protection is EH-rated footwear. The soles and heels of these boots are made from a non-conductive material tested by ASTM International to withstand the application of 18,000 volts at 60 Hz for one minute with no current flow.
This footwear is designed to protect you from "step potential"—when you step on a live wire and your body would otherwise complete a circuit to the ground through your feet.
Beyond Footwear: A System of Safety
EH-rated boots are just one part of a comprehensive safety system. For direct work on energized circuits, workers must also use insulated gloves, non-conductive tools, and follow strict procedures like Lockout/Tagout, which ensures equipment is de-energized before service.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
It is critical to recognize that EH protection is not infallible. Understanding its limits is as important as wearing it in the first place.
EH Protection is a Secondary Defense
The primary method for preventing electrical injury is always to de-energize the circuit. EH-rated gear is a secondary line of defense for accidental or unexpected contact with a live source. It should never be used as the primary means to work on energized equipment.
The Impact of Wear and Environment
The insulating properties of EH footwear can be compromised. A puncture from a nail, excessive wear on the sole, or exposure to moisture can create a conductive path, rendering the protection useless. Regular inspection of your gear is non-negotiable.
Not a Defense Against All Shocks
EH-rated footwear only protects against currents trying to pass through your feet to the ground. It offers no protection against phase-to-phase contact—for instance, touching two separate live wires with each hand. In that scenario, the current passes through your body from arm to arm, bypassing your boots entirely.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The level of protection must match the level of risk you face.
- If your primary focus is general site safety: Wear certified EH-rated footwear as a baseline precaution if you work anywhere near potential electrical sources, even if you are not an electrician.
- If your primary focus is direct electrical work: You require a complete system, including high-voltage insulated gloves, rated tools, and arc flash suits, in addition to EH boots, under the supervision of a qualified safety professional.
- If your primary focus is working in wet or hazardous conditions: Be extremely vigilant about inspecting your boots for damage and ensuring they are dry, as moisture negates their insulating properties.
Ultimately, electrical hazard protection is required because it provides a critical final barrier in an unpredictable environment, but it must be supported by constant awareness and safe work practices.
Summary Table:
| Electrical Hazard Risk | Required Protection | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Shock (Step Potential) | EH-Rated Footwear | Insulates body from ground, breaking the circuit. |
| Arc Flash | Full Arc Flash Suit & PPE | Protects against explosive heat and blast. |
| Contact with Live Wires | Insulated Gloves & Tools | Prevents current flow through hands during accidental contact. |
| General Site Safety | EH-Rated Boots (Baseline) | Provides secondary defense in unpredictable environments. |
Protect your team with certified EH-rated footwear from 3515. As a large-scale manufacturer, we produce a comprehensive range of safety boots for distributors, brand owners, and bulk clients. Our EH-rated boots are designed to meet ASTM standards, providing a critical barrier against electrical hazards. Ensure your workforce is equipped with reliable, durable protection. Contact us today to discuss your safety footwear needs and request a catalog.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Safety Footwear Wholesale Manufacturer for Custom OEM/ODM Production
- Premium KPU Injection Athletic Style Safety Shoes
- Wholesale Anti-Smash & Puncture-Proof Safety Shoes Custom Manufacturing for Brands
- Premium Flame-Retardant Waterproof Safety Boots and Shoes
- Wholesale Safety Footwear Manufacturer for Bulk & Custom OEM Orders
People Also Ask
- How does the heel counter contribute to boot fit? The Key to Blister-Free Comfort and Stability
- What makes composite toe boots suitable for electrical work? Key Safety Features Explained
- What types of heel designs are found in western work boots? Choose the Right Heel for Your Job
- What are the advantages of leather work boots for farm work? Unmatched Durability & Protection
- What does metatarsal protection (MT) in boots safeguard against? Shielding Your Foot's Top Bones
- What are structural fire boots designed for? Essential Protection for Interior Firefighting
- What are the primary dangers of not wearing wildfire boots? The Critical Failure Points That Risk Lives
- What are five style inspirations for wearing moc toe boots? Elevate Your Style with Timeless Versatility



















